
These are texts which help to build the fundamentals. In this article, we will be dealing with the important points filtered out from NCERT school text for Standard 6 History. We plan to cover main points from NCERT texts for different classes and subjects in our future posts.
NCERT History Text: Standard 6
The reference material for this post is NCERT History text for Class 6 (Our past -1). Only main points from each chapter is compiled below. Our advice is to first go through the respective NCERT text and use this compilation then for quick revision. We believe that this listing will come handy during exam time.
In the earliest cities
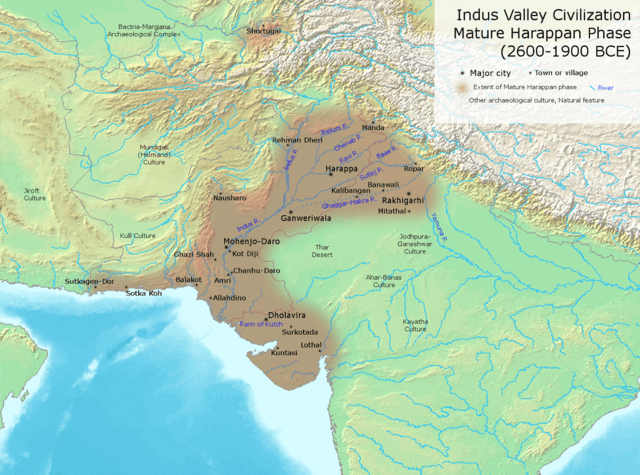
Harappa
- These cities developed about 4700 years ago.
- Many of these cities were divided into two or more parts.
- The part to the west was smaller but higher: citadels
- The part to the east was larger but lower: lower town
- The bricks were laid in an interlocking pattern and that made the walls strong.
- Special buildings were constructed on the citadel. For example, in Mohenjodaro, a tank: Great Bath.
- Kalibangan and Lothal had fire altars, where sacrifices may have been performed.
- Mohenjodaro, Harappa and Lothal had elaborate store houses.
- Houses were either one or two storeys high, with rooms built around a courtyard.
- Most houses had a separate bathing area, and some had wells to supply water.
- Many of these cities had covered drains.
- All three — houses, drains and streets — were probably planned and built at the same time.
- Most of the things are made of stone, shell and metal, including copper, bronze, gold and silver.
- Copper and bronze were used to make tools, weapons, ornaments and vessels.
- Gold and silver were used to make ornaments and vessels.
- Harappans also made seals out of stone which are rectangular and had an animal carved on them.
- Made pots with beautiful black designs.
- Cotton was probably grown at Mehrgarh from about 7000 years ago.
- Perhaps some women and men may have been specialists to perform crafts.
- The Harappans probably got copper from present-day Rajasthan, and even from Oman.
- Tin may have bought from present-day Afghanistan and Iran.
- Gold could have come all the way from present-day Karnataka.
- A new tool, the plough, was used to dig the earth for turning the soil and planting seeds but wooden plough not found while excavation.
- As this region does not receive heavy rainfall, some form of irrigation may have been used.
- Dholavira was located on Khadir Beyt in the Rann of Kutch, where there was fresh water and fertile soil.
- Dholavira was divided into three parts but other Harappan cities 2 parts.
- Large letters of the Harappan script that were carved out of white stone and perhaps inlaid in wood. Normally seals found on small objects so the above discovery was an unique one.
- Lothal stood beside a tributary of the Sabarmati.
- Here raw materials such as semi-precious stones were easily available.
- A dockyard at Lothal, where boats and ships came in from the sea and through the river channel.
Early Republic
Janapadas
- The rajas who perform big ritual sacrifices.
- The word janapada literally means the land where the jana[people] set its foot, and settled down.
- Excavations of janapadas, settlements, were found at Purana Qila in Delhi, Hastinapur near Meerut, and Atranjikhera, near Etah (the last two are in Uttar Pradesh).
- The people lived in huts, and kept cattle as well as other animals.
- They also grew a variety of crops — rice, wheat, barley, pulses, sugarcane, sesame and mustard.
- Special type of pottery found at these sites is known as Painted Grey Ware of simple lines and geometric patterns.
Mahajanapadas
- 2500 years ago, some janapadas became more important than others: mahajanapadas.
- Most had a capital city, many of these were fortified
- The new rajas now began maintaining armies.
- Soldiers were paid regular salaries.
- Changes in agriculture around this time were seen.
- One was growing use of iron ploughshares. Here more grain could be produced than with wooden plough.
- Second, people began transplanting paddy. This meant that instead of scattering seed on the ground, saplings were grown and then planted in the fields.
Magadha
- Rivers such as Ganga, Son made the transport easier. Water supplies for both drinking and agriculture.
- There were iron ore mines in the region which was able to make strong tools and weapon.
- Bimbisara and Ajatasatru, the two powerful rulers who used all means to conquer other janapadas.
- Mahapadma Nanda, extended his control up to the north-west part of subcontinent.
- Magadha’s capital was shifted from Rajagriha (present Rajgir) to Pataliputra (present Patna)
- Alexander of Macedonia reached upto the banks of river Beas in light of conquering Magadha, but his soldiers refused due to fear of Magadha’s elephant and chariot armies.
Vajji
- It was having distinct govt from Mahajanapadas.
- Govt was known as gana or sangha.
- Vaishali(Bihar) was its capital.
- This institution had many rulers (1000s)not one.
- They were called Raja. These rajas performed rituals together. They also met in assemblies for future course of action if needed.
- Women, dasas and kammakaras [landless agri labourers] could not participate in these assemblies.
- Both the Buddha and Mahavira belonged to ganas.
- These institution lasted for 1500 years, powerful Rajas tried to conquer sanghas.
- But the Gupta era started when last Sangha ruler was defeated.
Compiled by Vibin Lakshmanan






Pdf folder is not getting downloaded easily..
Plz help
ClearIAS study materials are available for download as PDF for FREE on the ClearIAS Telegram Channel (https://t.me/clearias). Join us now!
Relevant knowledge but need some deep explanation regarding terms used for different nobles or workers at the time then