 Well, Indian History continues 🙂 In this article on Medieval India, we plan to cover the Delhi Sultanate. The reference material for this post is NCERT History text for Class 7 (Our past -1). Only the main points from the chapters are compiled below. These points might come quite handy during preparation of Prelims and Mains, to get a quick grasp of the subject.
Well, Indian History continues 🙂 In this article on Medieval India, we plan to cover the Delhi Sultanate. The reference material for this post is NCERT History text for Class 7 (Our past -1). Only the main points from the chapters are compiled below. These points might come quite handy during preparation of Prelims and Mains, to get a quick grasp of the subject.
Delhi: The centre of attraction
When did Delhi become strategically important as a centre of political importance? Who were the major rulers of Delhi during the medieval period? Hopefully, you will get answers to these questions in this post.
- Delhi became an important city only in the 12th century.
- Delhi first became the capital of a kingdom under the Tomara Rajputs, who were defeated in the middle of the twelfth century by the Chauhans.
Rajput Dynasty
- Tomaras [early twelfth century – 1165]
- Ananga Pala [1130 -1145]
- Chauhans [1165 -1192]
- Prithviraj Chauhan [1175 -1192]
Delhi Sultans
- By the 13th century, Sultanates transformed Delhi into a capital that controlled vast areas of the subcontinent.
- “Histories”, tarikh (singular) / tawarikh (plural), written in Persian, the language of administration under the Delhi Sultans by learned men: secretaries, administrators, poets and courtiers who lived in cities (mainly Delhi) and hardly ever in villages.
- Objectives of these writings : (a) They often wrote their histories for Sultans in the hope of rich rewards (b) they advised rulers on the need to preserve an “ideal” social order based on birthright and gender distinctions (c) their ideas were not shared by everybody.
- In 1236 Sultan Iltutmish’s daughter, Raziyya, became Sultan. Nobles were not happy at her attempts to rule independently. She was removed from the throne in 1240.
Early Turkish [1206-1290]
- Qutbuddin Aybak [1206 -1210]
- Shamsuddin Iltutmish [1210 -1236]
- Raziyya [1236 -1240]
- Ghiyasuddin Balban [1266 -1287]
The expansion of the Delhi Sultanate
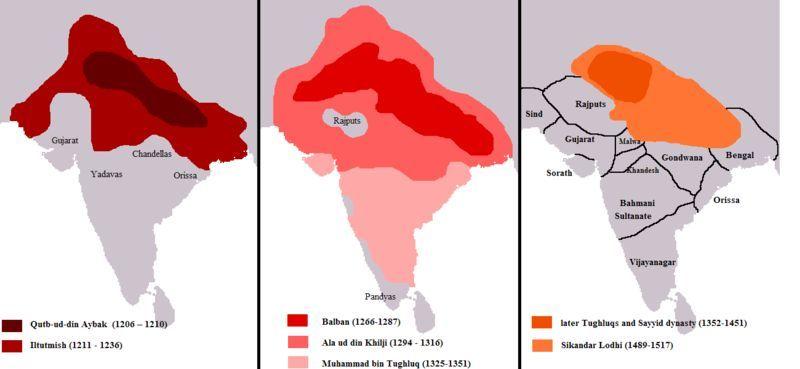
- In the early 13th century the control of the Delhi Sultans rarely went beyond heavily fortified towns occupied by garrisons.
- The Sultans seldom controlled the hinterland, the lands adjacent to a city or port that supplied it with goods and services, of the cities and were therefore dependent upon trade, tribute or plunder for supplies.
- Controlling garrison towns in distant Bengal and Sind from Delhi was extremely difficult.
- The state was also challenged by Mongol invasions from Afghanistan and by governors who rebelled.
- The expansion occurred during the reigns of Ghiyasuddin Balban, Alauddin Khalji and Muhammad Tughluq.
Khalji Dynasty [1290 – 1320]
- Jalaluddin Khalji [1290 – 1296]
- Alauddin Khalji [1296 -1316]
Tughluq Dynasty [1320 – 1414]
- Ghiyasuddin Tughluq [1320-1324]
- Muhammad Tughluq [1324 -1351]
- Firuz Shah Tughluq [1351 -1388]
- So, the first thing Sultans did was consolidate these hinterlands of the garrison towns. During these campaigns forests were cleared in the Ganga-Yamuna doab and hunter-gatherers and pastoralists were expelled from their habitat.
- These lands were given to peasants and agriculture was encouraged. New fortresses and towns were established to protect trade routes and to promote regional trade.
- Secondly, expansion occurred along the “external frontier” of the Sultanate. Military expeditions into southern India started during the reign of Alauddin Khalji and culminated with Muhammad Tughluq.
Administration & Consolidation
- Rather than appointing aristocrats as governors, the early Delhi Sultans, especially Iltutmish, favoured their special slaves purchased for military service, called bandagan .
- The Khaljis and Tughluqs continued to use bandagan and also raised people of humble birth, who were often their clients, to high political positions.
- Slaves and clients were loyal to their masters and patrons, but not to their heirs.
- Authors of Persian tawarikh criticised the Delhi Sultans for appointing the “low and base-born” to high offices.
- Military commanders were appointed as governors of territories. This land is called iqta and their holder is called iqtadar or muqti . The duty of muqti was to lead military campaigns and maintain law and order in their iqtas.
- But still large parts of the subcontinent remained outside the control of the Delhi Sultans.
- The Mongols under Genghis Khan invaded Transoxiana in north-east Iran in 1219 and the Delhi Sultanate during the reign of Alauddin Khalji and Muhammad Tughluq.
A.Khalji’s defensive policy against Genghis
- As a defensive measure, Alauddin Khalji raised a large standing army.
- Constructed a new garrison town named Siri for his soldiers.
- In order to feed soldiers, produce was collected as tax from lands, and paddy had got fixed tax of 50% of the yield.
- Alauddin chose to pay his soldiers’ salaries in cash rather than iqtas. He made sure merchants sold supplies to these soldiers according to prescribed prices.
- So here A.Khalji’s administrative measures were highly praised due to effective intervention in markets to have prices under control.
- He successfully withstood the threat of Mongol invasions.
M.Tughluq’s offensive policy against Genghis
- The Mongol army was defeated earlier. M.Tughluq still raised a large standing army.
- Rather than constructing a new garrison town, he emptied the residents of a Delhi city named Delhi-i Kuhna and the soldiers garrisoned there.
- Produce from the same area was collected as tax and additional taxes to feed the large army. This coincided with famine in the area. .
- Muhammad Tughluq also paid his soldiers cash salaries. But instead of controlling prices, he used a “token” currency. This cheap currency could be counterfeited easily because it was made of “bronze”.
- His campaign in Kashmir was a disaster. He then gave up his plans to invade Transoxiana and disbanded his large army.
- His administrative measures created complications. The shifting of people to Daulatabad was resented. The raising of taxes and famine in the Ganga-Yamuna belt led to widespread rebellion. And finally, the “token” currency had to be recalled.
15th & 16th Century Sultanates: Sayyid, Lodi and Suri
Sayyid Dynasty [1414 – 1451]
- Khizr Khan 1414 -1421
Lodi Dynasty [1451 – 1526]
- Bahlul Lodi 1451 -1489
Suri Dynasty [1540-1555]
- Sher Shah Suri [1540-1545] captured Delhi.
- For the first time during the Islamic conquest the relationship between the people and the ruler was systematized, with little oppression or corruption.
- He challenged and defeated the Mughal emperor Humayun (1539 : Battle of Chausa, 1540 : Battle of Kannauj)
- Sher Shah introduced an administration that borrowed elements from Alauddin Khalji and made them more efficient.
- Sher Shah’s administration became the model followed by the great emperor Akbar (1556-1605) when he consolidated the Mughal Empire.
- His tomb is at Sasaram [Bihar]
Compiled by: Vibin Lakshmanan






Thanks You so much for this. I am waiting for your next article 🙂
Thanks a lot for the great work..really helpful..waiting for the next article..
thanks a lot… its very useful for preparation in upsc. im waiting for next artical
Thanks alotvwe r wating for ur next article,..
Sorry if it is offensive, but I think the heading belonging to A.Khalji and M.Tughlaq should read “Mongol” rather than “Genghis” since Genghis Khan died in 1227 way before rule of A.Khalji (1296) and M.Tughlaq (1325) . I think Iltutmis (1210) fought Genghis Khan . If I am wrong can you please explain the reason of writing “Ghenghis” ?
Ya I have a doubt
That who was ghanji khan and who was minaj I siraj
Read the first chapter of ‘our pasts 2’ … he was a chronicler. ??
N thanks.. I’ll try my best for my exams
majestic note on delhi sultanate KIU
sir i have a question please
whether it is gengheiz khan or changeiz Q’n
Can we start preparing notes from your website?