The Public Examinations Act, of 2024, was introduced to address widespread concerns about cheating, the use of unfair means, and corruption in the conduct of public examinations, which play a crucial role in the educational and professional landscape of the country. Read here to learn more.
The Public Examinations Act punishes organised cheating in government exams.
The legislation is being hailed as the solution to the demands of making public examinations fair.
However, the new law does not impose penalties directly on test takers; their punishments will be determined by the rules set forth by their respective testing authorities.
Public Examinations Act, 2024
The Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Act, 2024, is a legislative measure aimed at curbing malpractice and ensuring the integrity of public examinations in India.
Key Provisions of the Act:
- Definition of Unfair Means: The act defines “unfair means” to include any form of cheating, impersonation, bribery, possession of unauthorized materials, and use of electronic devices to gain an unfair advantage during public examinations.
- Scope of the Act:
- Applies to all public examinations conducted by various government bodies, educational institutions, and examination boards across India.
- Includes school-level exams, university exams, competitive exams for public service jobs, and professional certification exams.
Public Examinations Act-Offenses and Penalties
- Leakage of paper or answer key: The Public Examinations Act mentions punishments for “leakage of question paper or answer key”, “directly or indirectly assisting the candidate in any manner unauthorisedly in the public examination” and “tampering with the computer network or a computer resource or a computer system” as offences done by a person, group of persons or institutions.
- Cheating: Any candidate found cheating can face penalties ranging from fines to imprisonment, depending on the severity of the offence.
- Impersonation: Severe penalties, including imprisonment, for those who impersonate or assist in impersonation during exams.
- Fake websites/admit cards: The creation of fake websites to cheat or for monetary gain, the conduct of fake examinations, issuance of fake admit cards or offer letters to cheat or for monetary gain” are punishable.
- Manipulation: Manipulation in seating arrangements, and allocation of dates and shifts for the candidates to facilitate adopting unfair means in examinations are also punishable under the law.
- Bribery and Corruption: Strict action against officials and candidates involved in bribery or corrupt practices, including dismissal from service and legal penalties.
- Unauthorized Materials: Possession or use of unauthorized materials or electronic devices during examinations can lead to disqualification, fines, and imprisonment.
- Electronic Devices: Specific provisions for dealing with the use of electronic devices like mobile phones, smartwatches, and other gadgets to cheat during exams.
- Any person or persons resorting to unfair means and offences under the Public Examinations Act shall be punished with imprisonment for a term not less than three years but which may extend to five years and with a fine up to ₹10 lakh.
Public Examinations Act-Preventive Measures
- Service provider: A service provider, engaged by the public examination authority for the conduct of examinations, shall also be liable to be punished with the imposition of a fine up to ₹1 crore and proportionate cost of the examination shall also be recovered from it, according to the Public Examinations Act.
- Such service providers shall also be barred from being assigned with any responsibility for the conduct of any public examination for four years.
- The Act defines a service provider as any agency, organisation, body, association of persons, business entity, company, partnership or single proprietorship firm, including its associates, sub-contractors and provider of support of any computer resource or any material, by whatever name it may be called, “which is engaged by the public examination authority for the conduct of public examination”.
- Stringent Security: Enhanced security measures at examination centres, including surveillance cameras, frisking, and use of metal detectors.
- Sealed Question Papers: Ensuring the integrity of question papers through secure printing, transportation, and storage processes.
- Digital Monitoring: Use of digital technologies and software to monitor and detect suspicious activities during online examinations.
- Investigative Authority:
- Establishment of a dedicated authority or committee to investigate and address complaints related to unfair means in public examinations.
- Powers to summon individuals, conduct inquiries, and recommend actions based on findings.
- Appeal and Redressal Mechanism:
- Provision for candidates and officials to appeal against penalties or disciplinary actions within a specified time frame.
- Establishment of a fair and transparent grievance redressal mechanism to address complaints and disputes related to examination malpractices.
- Awareness and Training:
- Initiatives to create awareness among students, parents, and educators about the importance of fair practices in examinations.
- Training programs for examination officials and invigilators to identify and prevent the use of unfair means.
- Confidentiality and Privacy:
- Ensuring confidentiality and privacy of candidates’ personal information during the examination process.
- Safeguarding the integrity of examination data and results.
Implementation and Impact
- Regulatory Oversight:
- The Public Examinations Act mandates regular audits and inspections by regulatory bodies to ensure compliance with the provisions.
- Penalties for institutions that fail to implement adequate measures to prevent unfair means in examinations.
- Deterrence and Compliance:
- By imposing strict penalties and enhancing preventive measures, the act aims to deter individuals and institutions from engaging in malpractices.
- Promotes a culture of fairness and meritocracy in the education and examination system.
- Public Trust:
- Restoring public confidence in the examination system by ensuring transparent and fair conduct of public exams.
- Ensuring that qualifications and certifications are awarded based on merit and genuine performance.
Public Examinations Act–Challenges and Considerations
- Addressing logistical and financial challenges in implementing advanced security and monitoring measures.
- Balancing strict enforcement with the need to ensure a supportive and stress-free examination environment for candidates.
- Critics argue that severe punishment alone won’t effectively address the issue, noting instances of cheating and impersonation already punishable under India’s criminal laws.
- The new law could prove to be ineffective because coaching centres collude with students to help them pass entrance examinations.
- Laws targeting cheating have proven ineffective, partly due to “organised criminals” with influential connections disrupting examinations, say experts.
Why in the news?
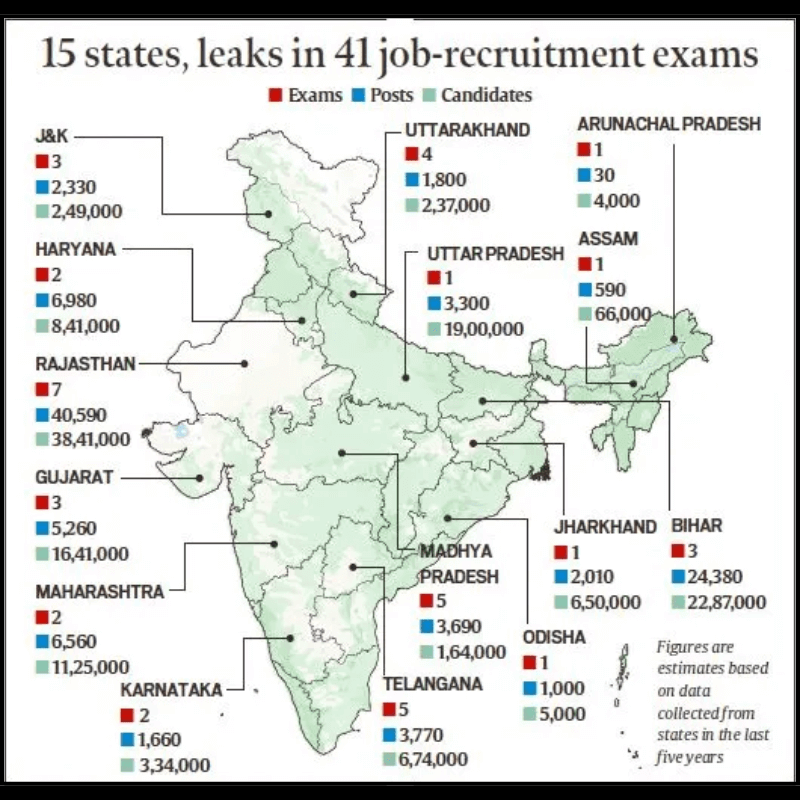
The Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Act, 2024 comes into effect in the wake of recent public examinations being cancelled for unfair practices.
- The University Grants Commission-National Eligibility Test 2024 (UGC-NET) examination that was cancelled on June 19, 2024, on grounds of being compromised and being investigated by the Central Bureau of Investigation will however not be covered by the newly enacted law.
- The Ministry of Education abruptly cancelled the June 2024 edition of the UGC-NET exam.
- Additionally, there were allegations regarding the fairness of the NEET-UG exam, citing a potential compromise of its integrity and fairness.
Conclusion
The Public Examinations Act, of 2024, represents a significant step towards enhancing the credibility and integrity of public examinations in India.
By addressing various forms of malpractice and instituting strict penalties, the act aims to uphold the principles of fairness and meritocracy, ensuring that public examinations remain a true reflection of a candidate’s abilities and knowledge.
Read: Examination system in India
-Article by Swathi Satish





Leave a Reply