
The word bioinformatics is quite new to many of us. We often wonder what really it is.
Is it just the combination of biology and information technology?
Or is it a new branch of science?
What is Bioinformatics?
Bioinformatics is an emerging branch of biological science that emerged from the combination of both biology and information technology.
Similar to how “biotechnology” is short for “biological technology,” the term “bioinformatics” is the abbreviation for “biological informatics.”
Information technology is used in bioinformatics to research living things, typically at the molecular level in order to gather, organise, and interpret biological data to provide answers in areas like evolutionary biology, bioinformatics uses computers.
Due to the huge amounts of data that have been accumulated as a result of the sequencing of genomes and the solution of crystal structures, the growth of biotechnology has accelerated, especially over the past ten years. The growth of genomics, biotechnology and other molecular research technologies, along with the growth of information technology, paved the way for this new field of study, Bioinformatics.
The two Dutch biologists Ben Hesper and Paulien Hogeweg originally used the word “bioinformatics” in 1960. Their studies and discoveries led to the definition of bioinformatics as the study of information processes in biotic systems.
Need a scientific and authoritative definition?
According to the NCBI- National Center for Biotechnology Information, Bioinformatics is defined as the analysis, collection, classification, manipulation, recovery, storage and visualization of all biological information using computation technology.
How does Bioinformatics work?
It is an interdisciplinary field of research that creates strategies and computer programmes to comprehend biological data .It analyses and interprets biological data by combining computer science, biology, chemistry, mathematics, engineering and statistics into one discipline. This industry focuses mostly on the creation of new software with biological instruments.
Mapping and analysing DNA and protein sequences, matching various DNA and protein sequences to compare them, and building and examining 3D models of protein structures are typical bioinformatics tasks. Bioinformatics is now more important than ever because of the Human Genome Project.
Sequence alignment, protein structure prediction, gene expression and protein-protein interaction prediction, genome-wide association studies, and many other fields will benefit from the research’s advancement and success.
The sciences of biological computation and bioinformatics are related yet separate from one another. Bioinformatics employs computation to learn more about biology, whereas biological computation uses bioengineering and biology to construct biological computers.
Although their scopes are different, computational biology and bioinformatics share similar goals and methods. The former organises and analyses fundamental biological data, while the latter creates theoretical models of biological systems, much like mathematical biology does with mathematical models.
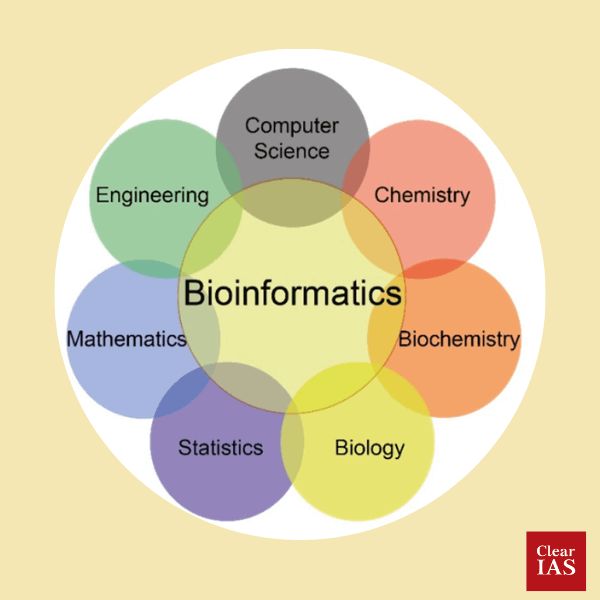
Applications
A collection of data that has been set aside to be turned into valuable information must be selected for bioinformatics and its applications to function. The fields of 3D image processing, 3D modelling of living cells, image analysis, drug development, and many more are the focus of bioinformatics.
- Microbial analysis and computing.
- Recognizing and modelling protein structure.
- Treatments for contagious and dangerous diseases
- Data storage and retrieval related to biotechnology.
- Search for new medicines.
- Understanding agricultural trends, pest management, and crop management in agriculture.
- Finds relevance in evolutionary theory.
- To understand the function of genes and gene therapy.
- Cell organizations and function.
- Analysis of drug targets.
- Examine the characteristics of various diseases.
- Integration and development of various tools for the management of biological databases.
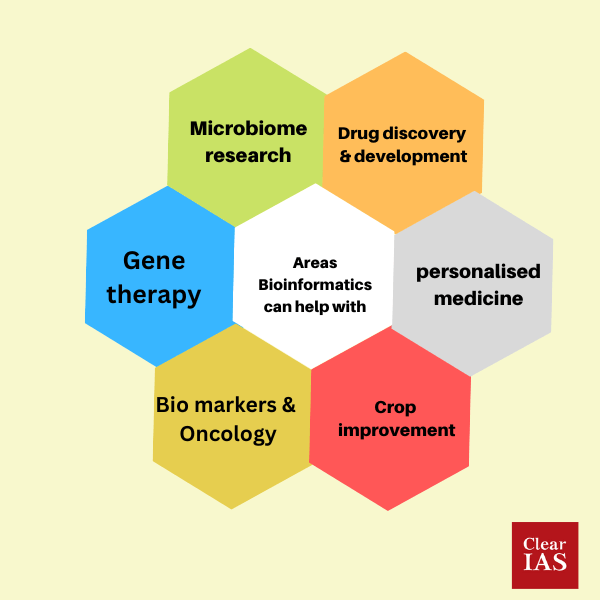
Uses of Bioinformatics in biomedicine
- Drug discovery: By combining Bioinformatics and structure-based drug design, researchers can create potent drugs for a wide range of acute and chronic conditions.
- Customized medicine: It is possible to create personalised medicine, which would be significantly more successful, by evaluating the genetic structure of the patient and their individual medical histories.
- Medicines for the prevention of diseases: This is primarily accomplished by combining data from bioinformatics, bioanalytics, and epidemiology. Preventive medications, as their name implies, can stop the spread of a disease or treat any acute illness before it manifests.
- Genome therapy: It is the process of replacing damaged genes with new ones in a living organism’s gene structure. Large amounts of data may be necessary because the gene structures of each creature vary greatly.
Milestones of India in the Bioinformatics sector
- India was a pioneer in the field of genomics. Through the successful conclusion of the Human Genome Project in 2009, the nation joined the ranks of the US, the UK, Canada, China, and Korea.
- The Department of Bio-Technology is also a regulatory body for bioinformatics.
- The 1987 creation of the Biotechnology Information System Network (BTISnet) is attributed to DBT. India was the first nation to create such a network.
- DBT created the Bioinformatics Policy of India (BPI) in 2004.
- DBT created a system to facilitate the sharing of bioinformatics knowledge among SAARC members.
- India has more trained bioinformaticists than any other country in the world.
- Double-digit growth in the bioinformatics sector.
- India is considered a good location for drug development low-cost R&D and cheap availability of knowledge resources.
India’s capacity and advancements
- Major Indian government agencies including the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) and the Biotechnology Information System (BTIS) are pushing bioinformatics.
- For the 10th plan period, DBT had deemed bioinformatics a high-priority issue (2002-2007). Along with IT, the Indian government is supporting the growth of the bioinformatics industry with a variety of tax benefits.
- By constructing a Bio-IT park, India has combined its strengths in biotechnology and IT to entice outsourcing deals in bioinformatics. These parks will be a collection of academic-industry-research activities, opening up fresh perspectives and revitalising the Indian bioinformatics sector, making it a future sunrise industry.
- India’s Department of Biotechnology has been collaborating with other departments on the establishment of Bio-IT parks and new biotech regulations which are projected to establish India as the world’s centre for bioinformatics and to serve as a growth accelerator for the bioinformatics industry.
- India’s bioinformatics industry has expanded quickly as a result of IT businesses’ increased attention to the life sciences industry.
- Indian enterprises offering these services including data mining, mapping, DNA sequencing, functional genomics, proteomics, and molecular design modelling can anticipate capturing a sizable portion of the global market. The bioinformatics sections of Indian IT firms like Tata Consultancy Services (TCS), Cognizant Technologies, Infosys, and Wipro are already functioning in the bioinformatics sector.
- In the field of bioinformatics, Indian pharmaceutical firms like GVK Biosciences, Dr Reddy’s Laboratories, Biocon, AstraZeneca, Ranbaxy, Biological E, and Nicholas Piramal are moving quickly. The growth of pure-play bioinformatics businesses like Strand Genomics is also happening in India.
Conclusion
Bioinformatics avail central, globally accessible databases that allow scientists to submit, search and analyze the information provided to them making it very important for the analysis of data in modern biology and medicine.
The field is expanding on its own, greatly accelerating the development of biotechnology. Its ultimate objective is to unearth the vast amount of biological knowledge that is concealed in the bulk of data and to gain a greater understanding of the basic biology of organisms.
The study of biology, which is often regarded as the defining scientific enterprise of the twenty-first century, relies heavily on bioinformatics, which has emerged as a frontline applied science.
Without the use of bioinformatics, the growth of whole genome sequencing, structural genomics, proteomics, micro-array, etc. will be very slow. The ability of these fields to address challenging biological issues will be limited without bioinformatics and thus gives very high importance to bioinformatics.
Article Written By: Atheena Fathima Riyas






Leave a Reply