 What are Genetic disorders? What kinds of genetic abnormalities are there? What signs or symptoms indicate a genetic disorder? What are genetic illnesses treated with? To learn more about it, read on.
What are Genetic disorders? What kinds of genetic abnormalities are there? What signs or symptoms indicate a genetic disorder? What are genetic illnesses treated with? To learn more about it, read on.
Genetic disorders occur when a mutation affects your genes or chromosomes. Some genetic disorders are innate, i.e., present by birth, while others are acquired due to mutations in a particular gene.
Some disorders cause symptoms at birth, while others develop over time. Genetic testing can help you learn more about the likelihood of experiencing a genetic disorder.
What are Genetic Disorders?
Genetic disorders are due to alterations or abnormalities in the genome of an organism. A genetic disorder may be caused by a mutation in a single gene or multiple genes. It can also be due to changes in the number or structure of chromosomes.
First, we need to know about the genes before discussing genetic disorders.
So, genes are the unit of heredity. It contains genetic information in the DNA. It helps us carry out life processes by translating them into useful protein genes which are the basic unit of heredity. DNA or many times RNA is the genetic material in almost all living organisms. RNA is more unstable than DNA which is why DNA is the genetic component in all organisms except some.
Sometimes, under some faulty conditions, the genes undergo mutation causing falter the genetic code. Faulty genes produce faulty proteins that do not work properly. This leads to malfunctioning and genetic disorders.
Types of Genetic Disorders:
There are many types of genetic disorders. The most common genetic disorders are mendelian disorders and chromosomal disorders. Let’s know about them.
1. Mendelian Disorder
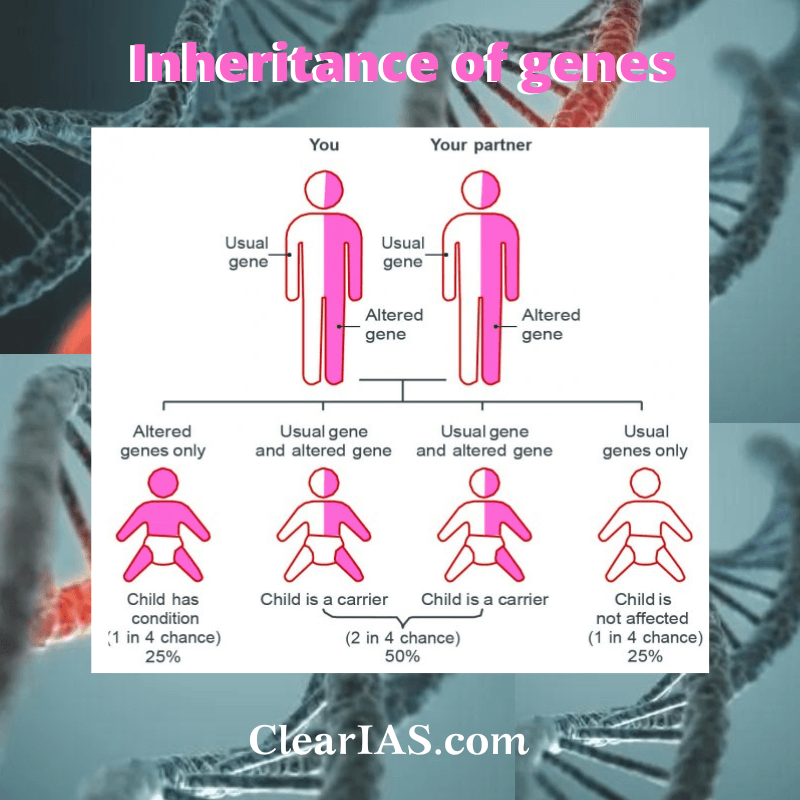
- Mendelian disorders are either autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, sex-linked dominant, sex-linked recessive, or mitochondrial and occur due to mutations in a single gene.
- These disorders can be detected by pedigree analysis.
- The genetic locus at which the mutation occurs may be a sex chromosome or an autosome and may be in a recessive or dominant mode.
- An autosomal recessive disease is articulated when the mutant gene is present in the homozygous state. In such cases, both parents are heterozygous, carrying one copy of the mutant gene and one copy of a normal functional gene.
- In autosomal traits, females and males are equally expected to be affected.
- Examples of Mendelian disorders are
- Sex Linked Disorders-Hemophilia.
- Autosomal Recessive Disorder- Cystic Fibrosis, Albinism, Sickle Cell Anemia.
2. Chromosomal Disorders
- Genetic disorders arising due to mutation in the chromosome are chromosomal disorders.
- Alteration in the number and functioning of the chromosomes leads to chromosomal disorders.
- A chromosomal disorder affects many genes at a time and can be fatal.
- It may occur due to the loss or gain of a whole chromosome.
- Examples of Chromosomal Disorders are as follows:
- Down’s syndrome- the addition of a chromosome 21 (trisomy)
- Turner’s syndrome-absence of an X chromosome (XO)
- Kleinfelter’s syndrome-addition of an X chromosome (XXY
3. Multifactorial Genetic Inheritance
- This is also known as polygenic inheritance.
- These are caused as a result of environmental factors and gene mutations.
- Examples of Multifactorial Diseases are as Follows:
- Heart Disease
- High Blood Pressure
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Cancer, Arthritis
4. Mitochondrial Inheritance
- These kinds of genetic disorders arise as a result of mutations in the non-nuclear mitochondrial DNA.
- Generally, in such cases, each mitochondrion has 5 to 10 pieces of DNA.
- These anomalies are inherited from the mother.
- Examples of Mitochondrial Diseases are,
- Leber’s Hereditary Optic Atrophy (LHON).
- Myoclonic epilepsy with ragged red fibres.
- Mitochondrial encephalopathy.
- Lactic acidosis.
Genetic Disorders in India
- Common genetic disorders in India are Beta-Thalassemia, Cystic Fibrosis, Sickle Cell Anaemia, Spinal Muscular Atrophy and Haemophilia.
- Beta thalassemia is a blood disorder that reduces the production of haemoglobin.
Cystic fibrosis is a disorder that causes severe damage to the lungs, digestive system and other organs in the body. - Sickle cell anaemia, or sickle cell disease (SCD), is a genetic disease of the red blood cells (RBCs).
Spinal muscular atrophy is a disorder characterized by weakness and wasting in muscles used for movement (skeletal muscles).
Symptoms of Genetic disorders
- There are some symptoms to know about common genetic disorders. But the symptoms change with different disorders and affected organs.
- We can observe breathing problems and Behavioural changes or disturbances.
- The brain can not process information properly. We call it Cognitive deficits.
- Development issues, here, the person faces challenges with social skills.
- A digestive problem in a person. They are unable to process nutrients.
- Muscle stiffness, weakness, and movement disorders. Poor growth, vision, and hearing loss.
Also read: Sickle Cell Disease
How can we identify Genetic Disorders?
So, if you have a family history of genetic disorders, you can take some steps to start a family. It will help you know the conditions responsible for gene mutations through lab tests.
- Genetic counselling:- Genetic counselling is the process of communication to help individuals or families understand and adapt to the medical implications of genetic disorders. It is the way of detecting if the child before birth will have a genetic disease or can develop any genetic disorder.
- Carrier testing:- This is a blood test that helps you to know whether parents carry a mutation linked to genetic disorders or not.
- Prenatal diagnostic testing:- This test will help you to know whether your unborn child has the risk of genetic disorders or not. This test uses fluid samples from the womb.
- Prenatal screening:- This test is used in pregnant women. It says unborn children could have a common chromosome condition.
- Newborn screening:- This test uses a sample of newborn blood. It detects genetic disorders early in life. It will help children to receive timely care. And cure genetic disorders in children.
Previous Year UPSC Questions from Topic
Qn) Which one of the following genetic disease is sex-linked? (PYQ-2019 CSE Prelims)
A) Royal Haemophilia
B) Tay- Sachs disease
C) Cystic fibrosis
D) Hypertension
Solution: The correct option is A Royal Haemophilia
- Sex-linked genetic disorders are any diseases or abnormal conditions that are caused by a defective gene on the X chromosome, one of the sex chromosomes. These disorders may also involve a deviation in the number of X or Y chromosomes.
- Examples of sex-linked disorders caused by a single gene defect on the X chromosome include:
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy, progressive degeneration of muscle tissue.
Turner Syndrome, a disorder in which all or part of one of the female’s X chromosomes is missing, is an example of this.
Hemophilia, is a deficiency in one of several blood-clotting factors and causes uncontrollable bleeding
Fragile-X syndrome, a problem with the FMR1 gene on the X chromosome, can cause mental retardation
Article written by: Aseem Muhammed





Leave a Reply