
What is the Global Food Security Index? What is the significance of the report? How has India fared in the index? Read to know more.
The Global Food Security Index 2021 was released and has been news. India ranked 71st on the Global Food Security index 2021 of 113 nations. Pakistan (with 52.6 points) scored better than India (50.2 points) in the category of food affordability. Sri Lanka was even better with 62.9 points in this category on the GFS Index 2021.
Global Food Security Index
The GFS Index was designed and constructed by London-based Economist Impact and is sponsored by Corteva Agriscience.
It is an annually published index with the 2021 GFSI being the tenth edition of the index.
The GFS Index measures the underlying drivers of food security in 113 countries, based on the factors of-
- Affordability
- Availability
- Quality and safety
- Natural resources and resilience.
It considers 58 unique food security indicators including income and economic inequality.
It calls attention to systemic gaps and actions needed to accelerate progress toward the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal of Zero Hunger by 2030.
The 2021 GFSI indicates four arenas for focus- agricultural resiliency, food systems integrity, smart tech innovation, and empowering farmers.
Agricultural Resilience
The 2021 Index shows that threats from climate change and declining natural resources pose a threat to future prosperity. Ensuring long-term commitment to sustainability ensures farmers will be equipped with the solution they need to produce what our food system and global population demand.
Smart Agriculture
The 2021 Index highlights the importance of connecting farmers to information and markets. The agricultural tools, products, and services empower farmers with data that can help them stay abreast of crucial market developments and better manage their farms.
Empowering Farmers
The 2021 GFSI shows that farmers are facing more threats to their livelihoods than ever before. It is necessary to enable farmers to improve their livelihoods and operations while conserving resources and sustaining the land.
Food Systems Integrity
The 2021 Index highlights how new technologies and more connected and responsive supply chains can support farms and improve food security. Improving the supply chain partners and farmers to help ensure a reliable supply of nutritious food.
India and neighbors in Global Food Security Index 2021
India held the 71st position with an overall score of 57.2 points on the GFS Index 2021 of 113 countries.
India performed better than-
- Pakistan (75th position)
- Sri Lanka (77th Position)
- Nepal (79th position)
- Bangladesh (84th position)
- But are way behind China (34th position).
In the case of availability of food, quality, and safety as well as protecting natural resources for food production, India scored better than Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka.
In the food affordability category, Pakistan (52.6 points) and Sri Lanka (62.9 points) scored better than India (50.2 points).
But over the past 10 years, India’s incremental gains in overall food security score were lagging behind that of Pakistan, Nepal, and Bangladesh:
- India’s score improved only by 2.7 points (57.2 in 2021 from 54.5 in 2012).
- While Pakistan improved by 9 points (54.7 in 2021 from 45.7 in 2012).
- Nepal by 7 points (53.7 points in 2021 from 46.7 points in 2012).
- Bangladesh by 4.7 points (49.1 in 2021 from 44.4 points in 2012)
- China’s score improved by 9.6 points (71.3 in 2021 from 61.7 in 2012).
Key findings of the Global Food Security Index 2021
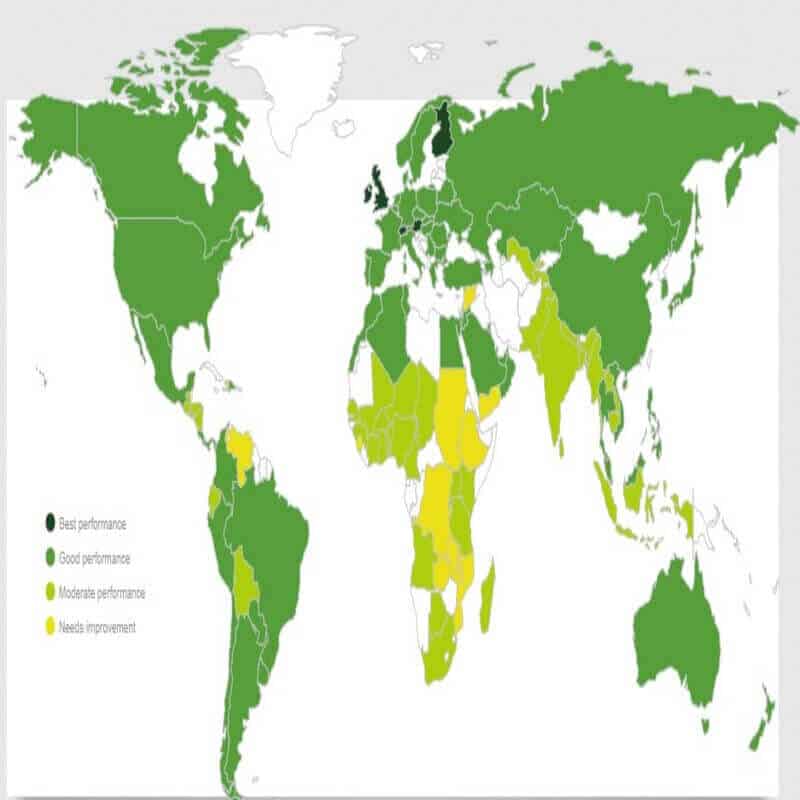
Ireland, Austria, the UK, Finland, Switzerland, the Netherlands, Canada, Japan, France, and the US shared the top 10 ranks with the overall GFS score in the range of 77.8 and 80 points on the index.
Burundi, Yemen, Mozambique, Sudan, Malawi, Ethiopia, and Syria are among the worst performers according to the index. Data from several other countries were unavailable for comparison.
However, the findings of the GFS Index 2021 also showed that global food security has decreased for the second year in a row after seven years of progress towards the Sustainable Development Goal of achieving zero hunger by 2030.
It shows that the countries did make significant improvements in addressing food insecurity in the past 10 years, yet the food systems remain vulnerable to economic, climatic, and geopolitical shocks.
More action is needed at all levels, local, national, and international, to bring an end to hunger and malnutrition, and to ensure global food security- which is a basic right of every human.
The Index goes on to show that to meet these emerging and future challenges, investments in food security need to be sustained – from innovation in climate-resilient crop yields to investing in programs to assist the most vulnerable.
Also read: Mosaic Viruses: Impact on Food Security
India’s efforts towards Food Security
The government has come out with several schemes and initiatives as action such as
- Eat Right India Movement
- POSHAN Abhiyan
- Food Fortification
- National Food Security Act
- Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) Scheme
- National Innovations Climate Resilient Agriculture (NICRA)
Also read: Food Security in India





