 What is Oxygen Cycle? How is it vital for sustaining life on earth? Read to know more about the importance of the oxygen cycle.
What is Oxygen Cycle? How is it vital for sustaining life on earth? Read to know more about the importance of the oxygen cycle.
Oxygen is one of the most vital elements on Earth and the most common element of the human body. Oxygen constitutes about 65% of the mass of the human body and most of this is in the form of water. Oxygen also makes up about 30% of the Earth and 20% of the atmosphere.
Free in the air and dissolved in water, oxygen is second only to nitrogen in abundance among elements in the atmosphere.
The oxygen cycle helps move oxygen through the Atmosphere, the Biosphere, and the Lithosphere.
- The Atmosphere is the region that lies above the Earth’s surface and it is one of the largest reservoirs of free oxygen on earth.
- The Biosphere is the sum of all the Earth’s ecosystems and also has some free oxygen produced from photosynthesis and other life processes.
- The largest reservoir of oxygen is the lithosphere. But most of this oxygen is not free moving rather it is a part of chemical compounds such as silicates and oxides.
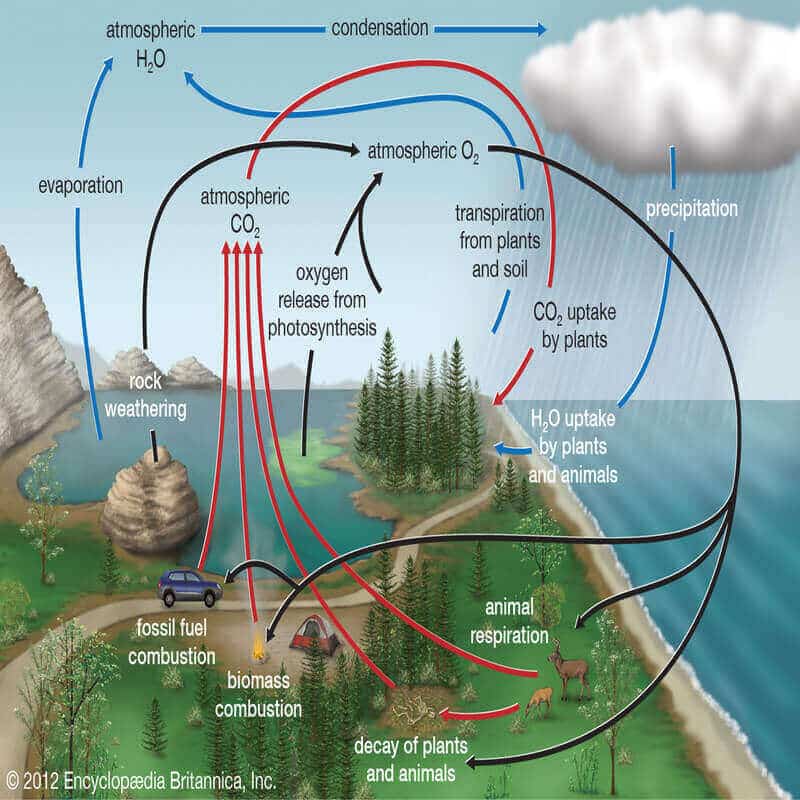
Plants and animals use oxygen to respire and return it to the air and water as carbon dioxide (CO2). This CO2 is then taken up by algae and terrestrial green plants and converted into carbohydrates through the process of photosynthesis of which oxygen is a by-product.
The water systems on earth are the main oxygen generators of the biosphere; their algae are estimated to replace about 90 percent of all oxygen used. Oxygen is involved to some degree in all the other biogeochemical cycles also.
The Oxygen Cycle:
The oxygen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle of oxygen atoms between different oxidation states in ions, oxides, and molecules through redox reactions within and between the reservoirs of the planet Earth.
The cycle incorporates biological, geological, and chemical aspects to circulate the oxygen molecule in the atmosphere.
Atmosphere:
Photolysis is the process by which oxygen is released in the atmosphere. In the process, high-energy sunlight breaks apart oxygen-bearing molecules to produce free oxygen.
The ozone cycle is an outcome of the photolysis process. An oxygen molecule (O2) is broken down to atomic oxygen by the ultraviolet radiation of sunlight. This free oxygen then recombines with existing O2 molecules to make O3 or ozone. This cycle is important because it helps to shield the Earth from the majority of harmful ultraviolet radiation by turning it into harmless heat before it reaches the Earth’s surface.
Biosphere:
In the biosphere, the main processes in the oxygen cycle are respiration and photosynthesis. During respiration animals and humans breathe by consuming oxygen to be used in the metabolic process and exhale carbon dioxide. Photosynthesis is the reverse of this process and is done by plants and plankton.
Lithosphere:
In the lithosphere, oxygen is fixed and trapped in minerals such as silicates and oxides. This is the natural process of oxidation, when a pure element comes in contact with oxygen it gets oxidized.
A portion of the oxygen is freed by chemical weathering. When an oxygen-bearing mineral is exposed to the elements a chemical reaction occurs that wears it down and in the process produces free oxygen.
The processes that produce oxygen:
- Photosynthesis is a biological process by which all green plants synthesize their food in the presence of sunlight. During photosynthesis, plants use sunlight, water, carbon dioxide to create energy, and oxygen gas is liberated as a by-product of this process.
- Sunlight also produced oxygen through reaction with water vapor in the atmosphere.
The processes that consume oxygen:
- Breathing is the physical process, through which all living organisms, including plants, animals, and humans inhale oxygen from the environment into the cells and exhale carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere.
- Decomposition is an important part of the oxygen cycle and occurs after the death of an organism. The dead organism decays and the organic matter with carbon, oxygen, water, and other components are returned into the soil and air. This process is carried out by decomposers like invertebrates (fungi, bacteria, and some insects. The entire process consumes oxygen and releases carbon dioxide.
- Combustion occurs when the organic and inorganic matter is burned in the presence of oxygen.
- Rusting is the process of oxidation of metals and alloys.
Human influence on the oxygen cycle:
The anthropogenic activities are affecting the oxygen cycle also along with other biogeochemical cycles.
Fossil fuel combustion, respiration of humans and livestock, and wildfire are significant high Oxygen consumption activities. Areas like East Asia, India, eastern North America, Europe, and central Africa have high consumption rates due to dense population. While in regions of central Africa, the wildfire accounts for the majority of local Oxygen consumption.
Even after the excessive burning of fossil fuel and the reduction of the natural vegetation on both land and in the sea, the level of atmospheric oxygen seems to be relatively stable which may be because of the increase in plant productivity due to agricultural advances worldwide.






Leave a Reply