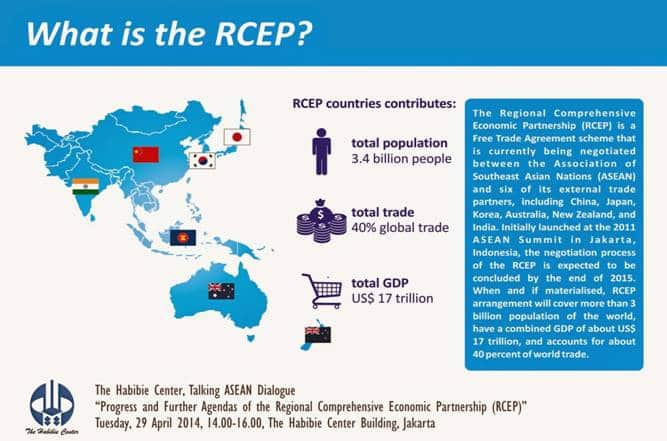
Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) is a proposed free trade agreement (FTA) between the countries of Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN) namely Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam and the six states with which ASEAN has free trade agreements (Australia, China, India, Japan, South Korea and New Zealand).
RCEP is considered as an alternative to the other important multilateral treaty named Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP). The TPP agreement excludes two of the important Asian powers – China and India.
The Potential of RCEP
Note: Subscribe to the ClearIAS YouTube Channel to learn more.
- RCEP member states accounted for a population of 3.4 billion people and a total Gross Domestic Product of $49.5 trillion.
- It is seen that the total GDP in RCEP could grow over to $100 billion by 2050 if the growth of the countries like China, India and India continues to be high.
- On Jan 23, 2017, US President Trump signed a memorandum stating the withdrawal of the US from the TPP, a move which has turned the focus of the world towards RCEP.
- RCEP will cover trade in goods, trade in services, investment, economic, technical cooperation, intellectual property, dispute settlement and other issues.
Importance of RCEP for India

- The RCEP provides an opportunity for the success of India’s Act East policy and will also influence the economic stature of India among the other South Asian countries.
- Also in comparison with the TPP & TTIP groups of countries, India’s trade with the RCEP group of countries as a percentage of its total trade has increased over the past decade. This shows the importance of RCEP to India.
The three immediate benefits of RCEP to India are::
- RCEP agreement would complement India’s existing free trade agreements with ASEAN nations and some of its member countries. The goal of greater economic integration with the countries of South East Asia and East Asia can be achieved through RCEP. India will have access to vast regional markets of these countries thereby helping its economy.
- RCEP will facilitate India’s Integration into regional production networks harmonizing trade-related rules. India is not a party to two other important regional economic blocs namely Asia- Pacific Economic Cooperation and Trans-Pacific partnership and thus RCEP would play an important role in strengthening its trade ties with these countries.
- India enjoys a comparative advantage in areas such as ICT, IT-enabled services, healthcare, and education services. RCEP would help in attracting greater FDI into these areas.
Importance of RCEP for China
Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership is the key point of accelerating the implementation of the FTA strategy in China.
- The members of the RCEP are all important trade partners of China.
- The establishment of the RCEP is in the strategic interest of China. It is the largest FTA China has ever negotiated on.
- China is fighting hard for establishing a new set of economic and trade rules outside the influence of USA and RCEP will help in this endeavour.
- This would help in the domestic economic development further strengthening China’s position in the global arena.
- China was excluded from the other important agreement TPP and thus RCEP provides an opportunity for better economic and peaceful relations with the neighbouring countries necessary for China’s rise.
New Delhi’s Challenges

For New Delhi, four challenges lie ahead.
- Tariff barriers which have been a matter of discontent in bilateral FTAs, particularly in the case of ASEAN-India FTA will be central to the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership negotiations.
- Non-trade issues such as environment and labour are likely to be a cause of concern. Some of the countries are stressing on stricter labour and environmental protection steps which India feels go far beyond the World Trade Organisation’s Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS)
- India must take steps to strengthen its medium small and micro enterprises (MSME) sector so as to make it withstand the free flow of trade. Higher investments in R&D and achieving international standards in terms of delivery are needed for this purpose.
- India must work tirelessly on capacity building of its domestic industries.
- Also, the negotiation services are not moving on par with that of trade in goods. India wants liberalised service trade so as to leverage its pool of skilled workforce providing them easier movement across the borders.
Also read: CPTPP (Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership)
Why is India worried about the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership?
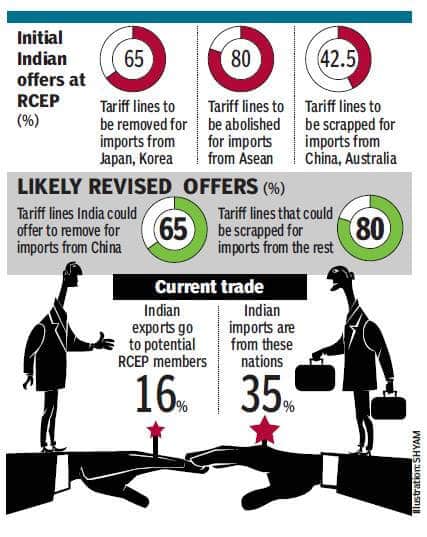
- Sources say India could put forward a two-tier proposal on foods that will treat China differently from the remaining RCEP countries.
- This proposal on China will include a larger negative list (goods that will be protected from tariff cuts) and longer time frame for reducing/eliminating tariffs on the remaining goods.
However, India is under pressure to offer similar tariff cuts to all the member states and proposals are being opposed.
Contentions of Civil Society Organizations (CSOs)
- Medecins Sans Frontieres (MSF) along with other CSOs are pushing for the removal of harmful intellectual property provisions that could potentially increase drug costs by creating new monopolies and delaying the entry of affordable generics into the market.
- Two of the most worrying proposals in the trade deal are the demand for Data exclusivity and patent term extensions, both Intellectual Property obligations that least developed countries oppose.
- India is considered the Pharmacy of the World due to its provision of generic drugs to countries all over and thus agreeing to such proposals in the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership would severely undermine India’s position among the least developed countries.
Also read: India’s Free Trade Agreements – The ‘present’ and the ‘future’
Conclusion
India needs to maintain a balance between the opening of its economy and protecting its domestic manufacturing industry. In the current scenario of growing protectionism, Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership provides an opportunity for the countries to prosper by increasing trade, creating jobs and other economic opportunities and India should make use of such an agreement.
India, as it has done in the latest round of negotiations need to step its effort for negotiations on liberalizing services and should also convince the member states to take a humanitarian view regarding the provision of generic medicines. A win-win situation in which the interests of all the parties are taken into concern is what is required to make Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership successful.
Article by: Pullela Ujwala






Leave a Reply