
What is a tiger reserve? What is the number of tiger reserves in India? What is the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA)? When is International Tiger Day? Read further to know more.
A tiger reserve is made up of two areas: a “Core” or “Critical Tiger Habitat” that must be managed as a protected space, and a “Buffer” or “Peripheral” region that borders the Core area but may get less habitat protection. This is how a Tiger Reserve is typically zoned.
The National Tiger Conservation Authority, which oversees Project Tiger, is in charge of the Indian tiger reserves, which were established in 1973.
In India, tiger reserves have been established in 54 protected regions as of right now.
Tiger population in India
Note: Subscribe to the ClearIAS YouTube Channel to learn more.
- More than 70% of the tigers in the world are found in India. 15 different species of wild cats may be found in India, which is home to 40% of all known species. Nine of the fifteen cats are sadly threatened, vulnerable, or endangered.
- In the past 150 years, the global tiger population has decreased by approximately 95%, placing these magnificent animals in danger of going extinct.
- The International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) declared the tiger extinct in Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos in July 2022.
- The fourth iteration of India’s national tiger status assessment for the years 2018–19 included 381,400 km2 of forested habitats spread across 20 states.
- When consistently sampled areas were examined from 2006 to 2018, it was found that tigers were growing in India at a rate of 6% annually. The most recent estimate puts the number of tigers at 2967.
- Tiger became the national animal of India in 1973 as the lion was a national animal before.
- Jim Corbett National Park was created in 1936 for tiger conservation
- Classified as Endangered as per IUCN Red Databook
- Schedule 1 animal as per Wildlife Protection Act, 1972
- Tiger can be killed under two conditions- Diseased or disabled beyond recovery and the threat to human life
- In no case, the tiger can be declared vermin.
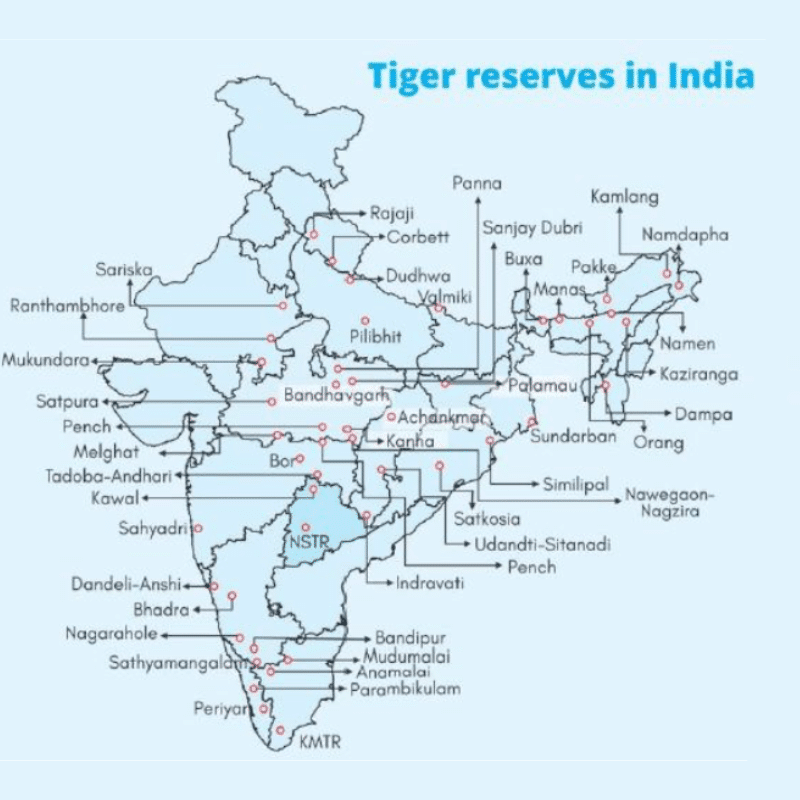
List of Tiger reserves in India
- In order to investigate the tiger population in India, the Indian government has divided the country’s territory into five zones. By classifying them into these zones, it is possible to study every tiger reserve in India.
- Shivalik Hills and Gangetic Plains
- Central India and Eastern Ghats
- Western Ghats
- NE Hills and Brahmaputra Plains
- Sundarban
- 2967 Tiger live in India, according to the most recent Tiger Census, which was done in 20 states across the country in 2018–19. Compared to the 2006 tiger census, the population growth rate of Tiger is 6% annually.
- Ranipur Tiger Reserve, in the Chitrakoot district of Uttar Pradesh, is the newest of India’s 54 Tiger Reserves, having been established on October 19, 2022.
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority has named the combined territory of Guru Ghasidas National Park (Sanjay National Park) and Tamor Pingla Wildlife Sanctuary in Chhattisgarh as India’s 53rd Tiger Reserve.
- Madhya pradesh with 6 tiger reserves (Maharashtra also have 6, because Pench tiger reserve is part of both Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra), but tiger population of MP is greatest in India.
- Bor tiger reserve in Maharashtra is the smallest tiger reserve in India with size of 138 sq km.
- Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve (NSTR) with size of 3,728 km2. In state of Andhra Pradesh is the Largest Tiger reserve in India.
What is National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA)?
- The Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972, as revised in 2006, gives the National Tiger Conservation Jurisdiction, a statutory agency under the Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change, authority over wildlife.
- The authority is headed by the Minister in charge of the Ministry of Environment and Forests, and its other members include three members of Parliament, the Secretary to the Ministry of Environment and Forests, and the Minister of State.
- The mandate includes Project Tiger implementation and monitoring, tiger preservation efforts on the ground, science-based tiger and habitat monitoring utilising cutting-edge technological techniques, and financial and technical support for tiger reserves in India.
What is Project Tiger?
- In order to protect our national animal, the TIGER, India started the Project Tiger initiative in 1973.
- Project Tiger keeps an eye on 54 tiger reserves in India, which makes up roughly 2.21% of the nation’s total land area.
- The Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change’s Project Tiger is a centrally sponsored programme that offers tiger reserve states in India centralised support for tiger conservation. The NTCA oversees project tiger’s execution.
- Tiger reserves in india are declared by the NTCA, constituted with two components.
- Core Area– the core areas have the legal status of a national park or a sanctuary, exclusive tiger agenda is followed in the core areas.
- Buffer Area- buffer or peripheral areas are a mix of forest and non-forest land, managed as a multiple use area, an inclusive people oriented agenda is followed in the buffer zone.
Tiger Density In India
- The density of tigers in the Sunderbans, India, may have reached the carrying capacity, according to a new study on the area’s tiger population. The Wildlife Institute of India undertook the survey in order to determine the population density in the Sunderbans.
- The Sunderbans is a sizable region of wetlands and mangrove trees that lies on the border between Bangladesh and India. Numerous tigers and other animals reside there. Human growth and activities like fishing and timber harvesting are putting more pressure on the forests.
- Tiger Density in India: Only a fixed number of tigers can coexist in a given ecosystem. Carrying capacity is the largest population that an ecosystem can sustain. The number of tigers that can coexist peacefully in a region is constrained by a variety of factors, such as food availability, habitat size, and human-tiger conflict. The number of tigers that can coexist in a given location depends on the amount of available prey.
- The ecosystem’s carrying capacity is determined by limiting constraints.
Limiting considerations include things like food, water, oxygen, and space. - Each ecosystem has a limited quantity of area and resources that can support life. When a species’ population grows faster than its environment can support it, the ecosystem may no longer be suited for the species to exist.
- As people and animals struggle for dwindling resources, this may result in increasing levels of human-wildlife conflict in the reserve’s peripheral areas. Ecosystems must be managed in a way that doesn’t drive species above their ecological limits in order to prevent such a situation from occurring.
International Tiger Day
- Since 2010, the 29th of July is celebrated as Global Tiger Day.
- At the Saint Petersburg Tiger Summit in Russia in 2010, the first International Tiger Day was established.
- The purpose of the day is to increase public awareness of the wild tiger population’s decline and to support efforts to conserve them.
- Governments of countries with tigers pledged to double the tiger population by 2022 in a statement issued during the Saint Petersburg Tiger Summit.
- Over 70% of the world’s tigers are found in India, which has 54 tiger reserves distributed over 18 states, as indicated in the article above.
- The population of tigers increased, according to India’s most recent tiger census from 2018.
Notably, India beat the St. Petersburg Declaration on Tiger Conservation’s goal of doubling the number of tigers by 4 years.
St Petersburg Declaration
- The first “Tiger Summit” took place in St. Petersburg, Russia, in November 2010.
- At the conference, the Global Tiger Recovery Program was announced with the goal of halting the tigers’ rapid population decline and tripling their numbers by 2022.
- One of the 13 nations in the tiger range that attended the conference was India.
- The 13 Tiger range countries are:-Bangladesh, Bhutan, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Lao PDR, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nepal, Russia, Thailand and Vietnam.
- The leaders of these nations committed to drawing up action plan to –
- India’s tiger reserves
- Strikes against poachers
- Financial support should be made available to sustain a healthy tiger population.
Tiger Reserves in India
UPSC Previous Year Questions on Environmental Conventions & Protocols
Kind of questions that are asked in Prelims with reference to Tiger reserves in India
1. Which of the following Protected Areas are located in the Cauvery basin?
- Nagarhole National Park
- Papikonda National Park
- Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
- Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary
Select the correct answer using the code given below:(UPSC Prelims 2020 Question)
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
2. Among the following Tiger Reserves, which one has the largest area under “Critical Tiger Habitat”? (UPSC Prelims 2020 Question)
(a) Corbett
(b) Ranthambore
(c) Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam
(d) Sunderbans
3. Which of the following are in Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve? (UPSC Prelims 2019 Question)
(a) Neyyar, Peppara and Shendurney Wildlife sanctuaries; and Kalakad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve
(b) Mudumalai, Sathyamangalam and Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuaries; and Silent Valley National Park
(c) Kaundinya, Gundla Brahmeswaram and Papikonda Wildlife Sanctuaries; and Mukurthi National Park
(d) Kawal and Sri Venkateswara Wildlife Sanctuaries; and NagarjunasagarSrisailam Tiger Reserve
4. The term M-STrIPES’ is sometimes seen in the news in the context of (UPSC Prelims 2017 Question)
(a) Captive breeding of Wild Fauna
(b) Maintenance of Tiger Reservoirs
(c) Indigenous Satellite Navigation System
(d) Security of National Highways
5. In India, if a species of tortoise is declared protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, what does it imply? (UPSC Prelims 2017 Question)
(a) It enjoys the same level of protection as a tiger
(b) It no longer exists in the wild; a few individuals are under captive protection, and now it is impossible to prevent its extinction
(c) It is endemic to a particular region of India
(d) Both (b) and (c) stated above are correct in this context
6. Consider the following statements :(UPSC Prelims 2014 Question)
- Animal Welfare Board of India is established under the Environments (Protection) Act, 1986
- National Tiger Conservation Authority is a statutory body
- National Ganga River Basin Authority is chaired by the Prime Minister
Which if the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Article written by Aseem Muhammed





Leave a Reply