Cocoa cultivation in India is an intriguing chapter in the country’s agricultural landscape, offering a blend of challenges and opportunities. Read here to learn more.
Although India is not among the world’s largest producers of cocoa, the cultivation of this crop has been steadily growing, primarily due to the increasing demand from the domestic chocolate industry and the export potential.
Cocoa cultivation in India
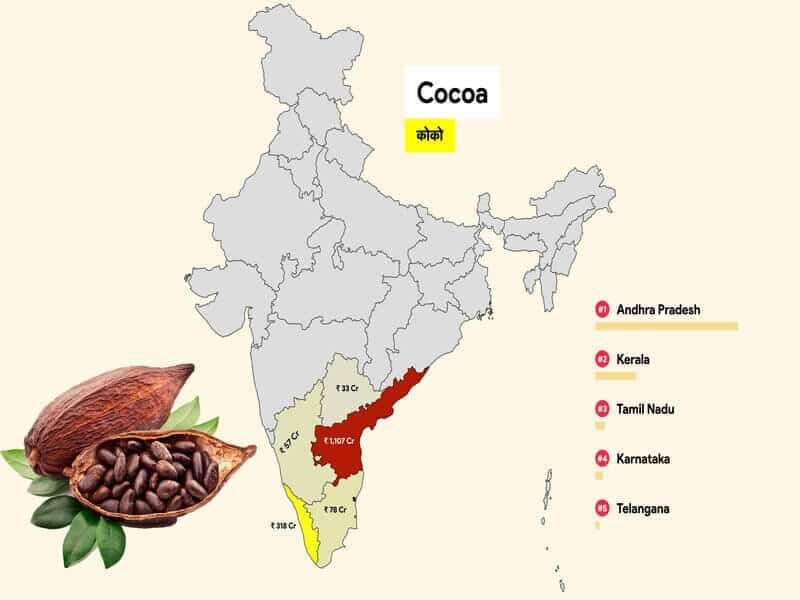
Cocoa is primarily grown in the southern states of India, with Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu being the major producers.
- These areas offer the ideal climatic conditions required for cocoa cultivation, which include a warm and humid climate with well-distributed rainfall throughout the year.
- Cocoa is cultivated both as a mono-crop and more commonly as an intercrop with coconut and arecanut, which are predominant in these regions.
- This intercropping system benefits farmers by maximizing the use of their land and providing an additional source of income.
Cultivation Practices
The cultivation of cocoa in India is characterized by a variety of practices aimed at optimizing yield and ensuring the sustainability of production. These include:
- Selection of Suitable Varieties: Cocoa variety is crucial for yield and quality. In India, varieties that are resistant to pests and diseases and suitable for the specific climatic conditions of the cultivation area are preferred.
- Agroforestry and Intercropping: As mentioned, cocoa is often grown as an intercrop. This practice optimises land use helps maintain soil health and reduces the impact of pests and diseases.
- Irrigation and Drainage: Proper irrigation is crucial, especially in areas where the rainfall is not sufficient or well-distributed. At the same time, good drainage systems are necessary to prevent root rot diseases.
- Pest and Disease Management: Cocoa cultivation in India faces challenges from various pests and diseases. Integrated pest management practices, including the use of biological control agents and disease-resistant varieties, are important.
- Harvesting and Post-harvest Handling: Timely harvesting and proper post-harvest handling are crucial for ensuring the quality of the cocoa beans. Fermentation and drying are vital processes that significantly affect the flavour profile of cocoa.
Challenges
Despite the potential, cocoa cultivation in India faces several challenges:
- Limited Awareness and Technical Knowledge: There is a need for greater awareness and technical support for farmers regarding best practices in cocoa cultivation and post-harvest handling.
- Market Fluctuations: The global cocoa market is highly volatile, and fluctuations in prices can significantly affect the income of cocoa farmers.
- Climate Change: Changes in weather patterns, including irregular rainfall and rising temperatures, pose a significant risk to cocoa cultivation, affecting yields and quality.
Opportunities
- Growing Domestic Market: The increasing consumption of chocolate and cocoa-based products in India presents a significant opportunity for expanding cocoa cultivation.
- Export Potential: With the right strategies and support, India has the potential to increase its share in the global cocoa market.
- Sustainable Practices: There is a growing interest in sustainable and organic cocoa production, which can open up niche markets and potentially offer higher returns to farmers.
Cocoa cultivation regions of the world
Cocoa cultivation is a critical agricultural activity worldwide, deeply intertwined with the global chocolate industry.
- The main belt of cocoa cultivation lies within 20 degrees north and south of the Equator, where the climate is suitable for growing cocoa trees.
- The top cocoa-producing countries are primarily located in West Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America.
West Africa
- Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana are the top cocoa-producing countries, together accounting for more than 60% of the world’s cocoa supply. The cocoa sector in these countries is vital for their economies, supporting millions of smallholder farmers and their families.
- Nigeria and Cameroon are also significant producers in the region, contributing substantial quantities to the global cocoa market.
Southeast Asia
- Indonesia is the leading cocoa producer in Asia, with a significant portion of its production coming from the island of Sulawesi. However, the country has faced challenges such as ageing trees, diseases, and fluctuating global cocoa prices.
- Malaysia and Papua New Guinea also contribute to the region’s cocoa production, though to a lesser extent compared to Indonesia.
Latin America
- Ecuador is renowned for its fine-flavoured cocoa, which is highly sought after by chocolate makers around the world. The country has a long history of cocoa cultivation and has been focusing on quality and sustainability.
- Peru and the Dominican Republic are noted for their growth in the cocoa sector, emphasizing organic and fair-trade cocoa beans.
- Brazil once a leading cocoa producer, has been working to rebuild its cocoa sector after being hit hard by the witches’ broom disease in the 1990s.
Why in the news?
A new dwarf coconut variety named ‘Kalpa Suvarna’ and two new hybrid varieties of cocoa developed by the Central Plantation Crops Research Institute (CPCRI) were released.
- Kalpa Suvarna, the coconut variety is ideal for tender coconut and copra production, with specific characteristics like large-sized fruits, high water content, and oil content.
- The cocoa varieties, VTL CH I and VTL CH II have high fat and nutrient contents, with VTL CH II being tolerant to black pod rot.
- Black pod rot is a fungal disease that affects Cocoa Trees. It is majorly caused by fungal species belonging to the genera Phytophthora.
- VTL CH I is suitable for growing in Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh, while VTL CH II is recommended for high rainfall regions in Karnataka, Kerala, Gujarat, and Tamil Nadu.
- Both cocoa varieties yield 1.5 kg to 2.5 kg of dry beans per tree per year.
Coconut cultivation in India
Coconut cultivation in India is a significant part of the country’s agriculture, contributing to the livelihoods of millions of people, especially in the coastal regions.
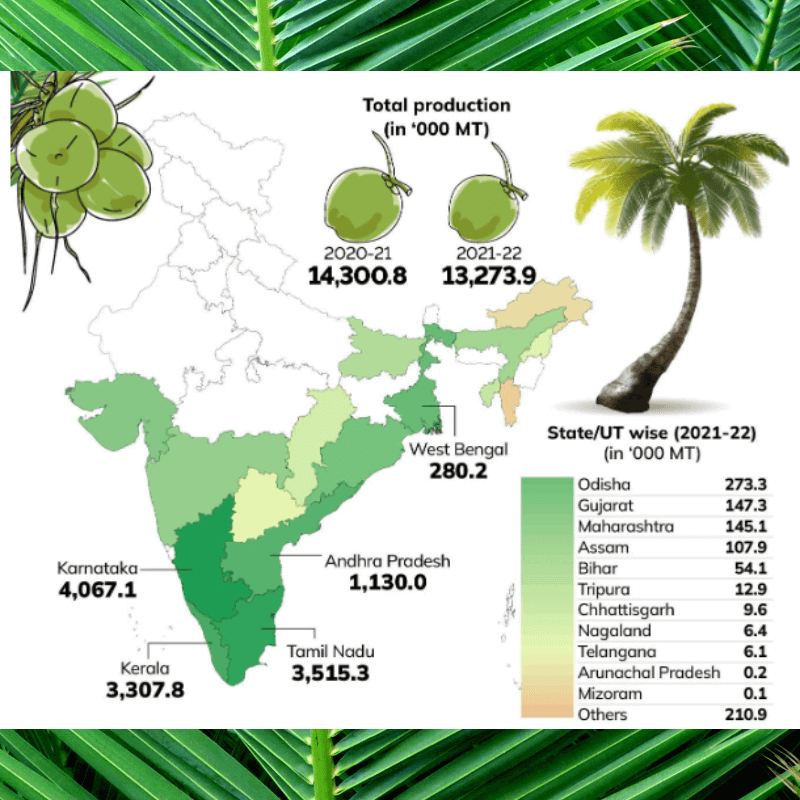
- India is one of the leading countries in coconut production, standing only behind countries like Indonesia and the Philippines in terms of volume.
- The coconut palm thrives in the coastal areas of India because of the tropical climate, which provides the ideal conditions of high humidity, abundant rainfall, and sunshine.
Key Coconut Producing States
- Kerala has been the leading state in coconut production, but in recent years, other states have started to contribute significantly to the country’s coconut output.
- Tamil Nadu and Karnataka are also major producers, with vast areas under coconut cultivation.
- Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal, Odisha, Maharashtra, and Gujarat contribute considerably to the national production.
Varieties
India cultivates a variety of coconuts, including the traditional tall varieties, which are known for their high-quality nuts and copra, and the dwarf varieties, which are preferred for tender coconut water. Hybrid varieties, developed for specific qualities like disease resistance, high yield, and early maturation, are also popular among farmers.
Uses and Market
The coconut tree is often called the “Tree of Life” because of its versatile uses. Every part of the coconut palm is used in various forms:
- Coconut Water: A refreshing drink rich in electrolytes.
- Coconut Meat: Used in cooking and for extracting coconut oil.
- Coconut Oil: Widely used in cooking, cosmetics, and hair care products.
- Coir: Made from the husk, used in making ropes, mats, and as a soil additive.
- Coconut Shell: Used for crafts, as charcoal, and for utensils.
Conclusion
In summary, cocoa cultivation in India is poised for growth, driven by domestic demand and the potential for sustainable production. Addressing the existing challenges and leveraging the opportunities can help in the development of this sector, benefiting farmers and contributing to the diversification of agricultural practices in the country.
Related articles:
-Article by Swathi Satish






Leave a Reply