
The U.S. H1B visa program, which plays a pivotal role in facilitating the movement of skilled foreign professionals, has been under heightened scrutiny, particularly due to its significant impact on Indian workers who are its primary beneficiaries. The program allows U.S. employers to hire skilled professionals from abroad for specialized roles, fostering innovation and filling gaps in the domestic labour market. Read here to learn more.
A series of events has brought renewed attention to the program, including a viral post by Chennai-born techie Sriram Krishnan, recently appointed as an AI advisor to the U.S. government by President-elect Donald Trump.
Krishnan’s appointment and insights on the H1B program reflect the importance of skilled migration in advancing technological innovation in the U.S.
His journey underscores how the H1B visa facilitates career opportunities for foreign professionals, enabling them to contribute to the U.S. economy significantly.
Key Issues and Discussions
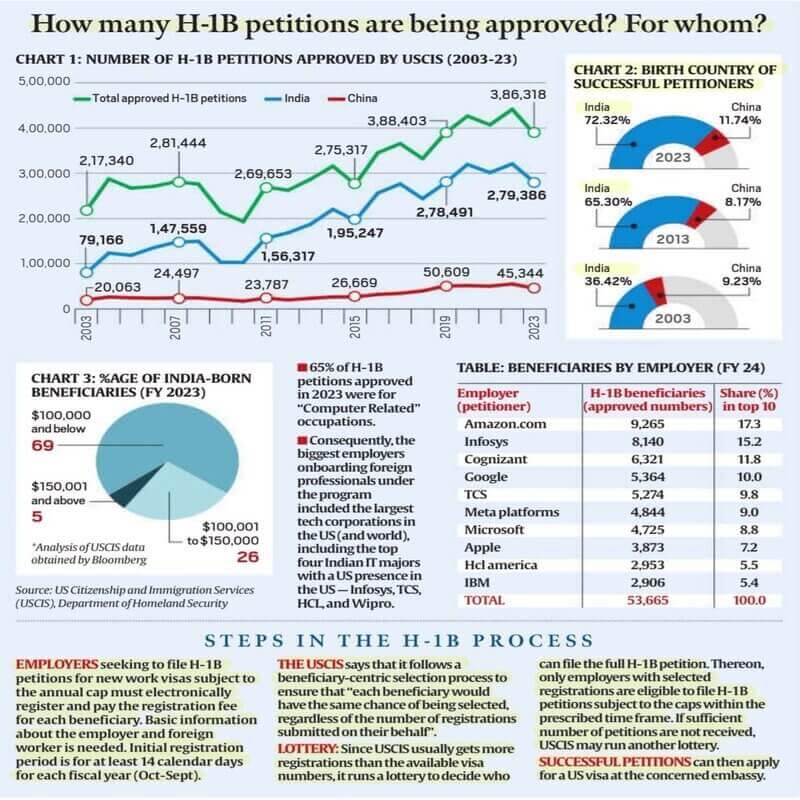
- Indian Dominance in the Program: Indian nationals constitute the largest group of H1B beneficiaries, particularly in technology and IT services.
- Criticism and Reforms: Critics argue that the program is sometimes misused, leading to the exploitation of foreign workers or displacing U.S. workers. Recent years have seen calls for stricter regulations, transparency, and fairness in the visa allocation process.
- Economic and Strategic Importance: The H1B visa is crucial for maintaining the U.S.’ competitive edge in tech and other high-demand sectors, especially amid global advancements in fields like artificial intelligence.
- Implications of High-Profile Appointments: Appointments like Sriram Krishnan’s signal the U.S. administration’s acknowledgement of the global talent pool’s contributions. However, they also bring to light the challenges faced by H1B visa holders, such as job insecurity, dependence on employers, and visa backlogs.
The debate among Americans
The debate over H1B immigration has highlighted differences between Republican Party supporters and former President Donald Trump’s team, underscoring broader divides within U.S. political discourse on legal immigration.
- Public Opinion Among Republicans vs. Democrats
- 30% of Republicans support reducing legal immigration levels, including H1B visas, reflecting concerns over job competition and national security.
- By contrast, only 14% of Democrats favour a decrease, aligning with their party’s broader pro-immigration stance.
- Trump’s Stance on H1B Immigration
- Donald Trump and his administration historically supported tighter restrictions on H1B visas, citing the need to prioritize American workers.
- However, Trump’s campaign rhetoric often clashed with the interests of major business entities reliant on skilled foreign workers, creating internal tensions.
- Republican Party Divide
- A significant portion of Republican business interests advocates for the continuation or expansion of the H1B program due to its importance to industries like tech and healthcare.
- Grassroots Republicans, however, often express scepticism, fearing job displacement and wage suppression for American workers.
- Broader Implications
- The debate reflects the broader struggle within the Republican Party to balance populist sentiments with the interests of the business community.
- It also points to the potential for immigration to remain a divisive issue in the 2024 elections, influencing both policy decisions and voter alignments.
H1B Visa Program
The H1B visa is a non-immigrant visa introduced in 1990 that allows U.S. companies to employ foreign workers in speciality occupations requiring theoretical or technical expertise.
It is widely used by technology firms to recruit skilled workers from countries like India and China.
It encompasses speciality jobs like science, technology, engineering, mathematics (STEM), and IT (High skills and at least a bachelor’s degree).
Key Features of the H1B Visa:
- Eligibility Criteria
- The applicant must hold a bachelor’s degree or higher in a speciality field.
- The employer must demonstrate that the position requires specialized skills and qualifications.
- Duration: Initially issued for 3 years, extendable up to a maximum of 6 years.
- Employer Sponsorship: Employers must sponsor H1B visa applicants and file a Labor Condition Application (LCA) with the U.S. Department of Labor.
- Lottery System: Due to high demand, a lottery system is used when applications exceed the annual cap.
- Annual Cap
- 65,000 visas for general applicants.
- Additional 20,000 visas for those holding a U.S. master’s degree or higher.
- Certain categories, such as universities and research institutions, are exempt from the cap.
Advantages of the H1B Visa Program
- Work Authorization: Allows skilled professionals to work in specialized fields in the U.S.
- Pathway to Permanent Residency: This can lead to Green Card eligibility if the employer sponsors the worker.
- Dependents: H1B holders can bring dependents (spouses and children under 21) on H4 visas, some of whom may obtain work authorization.
Criticisms of the H1B Visa Program
- Worker Exploitation: Critics argue that some employers misuse the system to pay lower wages or exploit workers.
- Displacement of Local Workers: Accusations that it displaces U.S. workers in favour of cheaper foreign labour.
- Dependence on Lottery: High demand creates uncertainty for applicants due to the lottery-based allocation.
Recent Developments and Policy Changes
- Proposed Reforms
- Increasing wage thresholds to ensure fair pay for foreign workers.
- Prioritizing advanced degree holders in the lottery system.
- Remote Work Impact: The rise of remote work during the pandemic has led to a re-evaluation of work visa policies.
- Global Competition: Countries like Canada and Australia have introduced more accessible visa programs, drawing skilled workers away from the U.S.
Impact of H1B on the U.S. and Global Economy
- For the U.S.
- Supports industries like technology, healthcare, and academia with skilled labour.
- Drives innovation and contributes to economic growth.
- For Sending Countries
- Encourages remittances and skill development.
- The risks brain drain of talented professionals.
Future of the H1B Program
With ongoing debates about immigration and labour market policies, the program is likely to see further reforms aimed at balancing the needs of U.S. employers, foreign professionals, and domestic labour.
High-profile cases and the role of Indian professionals will continue to shape this discourse.
This focus on the H1B visa program highlights broader discussions about immigration, economic growth, and the global movement of talent.
Other US Non-immigrant Visa Categories
Visa Category |
Purpose |
O |
Foreign national with extraordinary ability in Sciences, Arts, Education, Business or Athletics |
H-2A |
Temporary agricultural worker |
H-2B |
Temporary worker performing other services or labour of a temporary or seasonal nature |
B-2 |
Tourism, vacation, pleasure visitor |
V |
Nonimmigrant Visa for Spouse and Children of a Lawful Permanent Resident |
Conclusion
The H1B visa program plays a crucial role in bridging skill gaps in the U.S. workforce while fostering global mobility of talent. However, its challenges highlight the need for comprehensive reform to balance domestic employment concerns with the benefits of skilled immigration.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. Who is eligible for the H-1B visa?
Ans: H-1B status is available to a person who has been offered a temporary professional position by a U.S. employer. A bachelor’s degree or higher in a related area is the minimum educational level required for a position to qualify for H-1B status, and the H-1B employee must have this degree (or higher).
Q. What is the difference between H-1B and green card?
Ans: While an H-1B visa can be used to live and work in the United States, a Green Card allows for permanent resident status and can be renewed every 10 years – it will also enable its holder to pursue US citizenship, which no visa currently offers.
Related articles:
-Article by Swathi Satish






Leave a Reply