
The Mughal Crisis
- Emperor Aurangzeb had depleted the military and financial resources of his empire by fighting a long war in the Deccan.
- Nobles who were appointed as governors (subadars) controlled the offices of revenue and military administration (diwani and faujdari) which gave them extraordinary political, economic and military powers over vast regions of the Mughal Empire.
- Peasant and zamindari rebellions in many parts of northern and western India added to these problems.
Emergence of New States
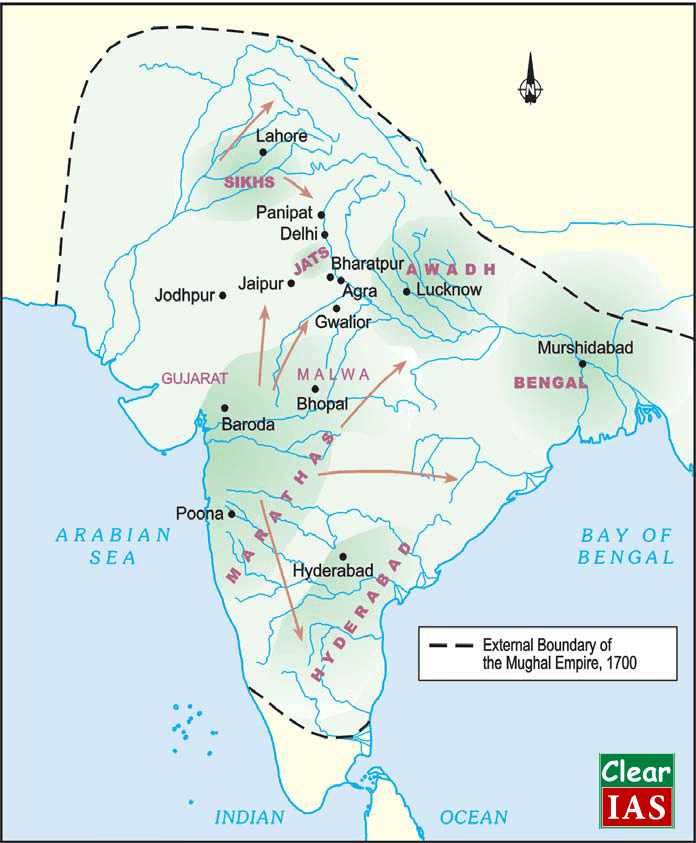
- Through the 18th century, the Mughal Empire gradually fragmented into a number of independent, regional states.
- It can be divided into three overlapping groups:
- States that were old Mughal provinces like Awadh, Bengal, and Hyderabad. Although extremely powerful and quite independent, the rulers of these states did not break their formal ties with the Mughal emperor.
- States that had enjoyed considerable independence under the Mughals as watan jagirs. These included several Rajput principalities.
- States under the control of Marathas, Sikhs and others like the Jats. They all had seized their independence from the Mughals after a long-drawn armed struggle.
Hyderabad
- Nizam-ul-Mulk Asaf Jah, the founder of Hyderabad state, was appointed by Mughal Emperor Farrukh Siyar.
- He was entrusted first with the governorship of Awadh, and later given charge of the Deccan.
- He ruled quite independently without seeking any direction from Delhi or facing any interference.
- The state of Hyderabad was constantly engaged in a struggle against the Marathas to the west and with independent Telugu warrior chiefs (nayakas)
Awadh
- Burhan-ul-Mulk Sa‘adat Khan was appointed subadar of Awadh in 1722.
- Awadh was a prosperous region, controlling the rich alluvial Ganga plain and the main trade route between north India and Bengal.
- Burhan-ul-Mulk held the combined offices of subadari, diwani and faujdari.
- Burhan-ul-Mulk tried to decrease Mughal influence in the Awadh region by reducing the number of office holders (jagirdars) appointed by the Mughals.
- The state depended on local bankers and mahajans for loans.
- It sold the right to collect the tax to the highest bidders. These “revenue farmers” (ijaradars) agreed to pay the state a fixed sum of money. So they were also given considerable freedom in the assessment and collection of taxes.
- These developments allowed new social groups, like moneylenders and bankers, to influence the management of the state’s revenue system, something which had not occurred in the past.
Bengal
- Bengal gradually broke away from Mughal control under Murshid Quli Khan who was appointed as the naib, deputy to the governor of the province and he was neither a formal subadar .
- Like the rulers of Hyderabad and Awadh, he also commanded the revenue administration of the state.
- In an effort to reduce Mughal influence in Bengal he transferred all Mughal jagirdars to Orissa and ordered a major reassessment of the revenues of Bengal.
- Revenue was collected in cash with great strictness from all zamindars.
- This shows that all 3 States Hyderabad, Awadh, Bengal richest merchants, and bankers were gaining a stake in the new political order.
The Watan Jagirs of the Rajputs
- Many Rajput kings, particularly those belonging to Amber and Jodhpur, were permitted to enjoy considerable autonomy in their watan jagirs.
- In the 18th century, these rulers now attempted to extend their control over adjacent regions.
- So Raja Ajit Singh of Jodhpur held the governorship of Gujarat and Sawai Raja Jai Singh of Amber was governor of Malwa.
- They also tried to extend their territories by seizing portions of imperial territories neighbouring their watans.
Seizing Independence
The Sikhs
- The organisation of the Sikhs into a political community during the seventeenth century helped in regional state-building in the Punjab.
- Guru Gobind Singh fought against the Rajaput and Mughal rulers, after this death, it was under Banda Bahadur’s the fight continued.
- The entire body used to meet at Amritsar at the time of Baisakhi and Diwali to take collective decisions known as “resolutions of the Guru (gurmatas)”.
- A system called rakhi was introduced, offering protection to cultivators on the payment of a tax of 20 per cent of the produce.
- Their well-knit organization enabled them to put up a successful resistance to the Mughal governors first and then to Ahmad Shah Abdali who had seized the rich province of the Punjab and the Sarkar of Sirhind from the Mughals.
- The Khalsa declared their sovereign rule by striking their own coin in 1765. The coin was same as that of Band Bahadur’s time.
- Maharaja Ranjit Singh reunited the groups and established his capital at Lahore in 1799.
The Marathas
- Another powerful regional kingdom to arise out of a sustained opposition to the Mughal rule.
- Shivaji (1627-1680) carved out a stable kingdom with the support of powerful warrior families (deshmukhs). Groups of highly mobile, peasant- pastoralists (kunbis) provided the backbone of the Maratha army.
- Poona became the capital of the Maratha kingdom.
- After Shivaji, Peshwas[principal ministers] developed a very successful military organisation by raiding cities and by engaging Mughal armies in areas where their supply lines and reinforcements could be easily disturbed.
- By the 1730s, the Maratha king was recognised as the overlord of the entire Deccan peninsula. He possessed the right to levy chauth[25 per cent of the land revenue claimed by zamindars]. and sardeshmukhi[9-10 per cent of the land revenue paid to the head revenue collector in the Deccan] in the entire region.
- The frontiers of Maratha domination expanded, after raiding Delhi in 1737, but these areas were not formally included in the Maratha empire but were made to pay tribute as a way of accepting Maratha sovereignty.
- These military campaigns made other rulers hostile towards the Marathas. As a result, they were not inclined to support the Marathas during the third battle of Panipat in 1761.
- By all accounts cities[Malwa, Ujjain etc] were large and prosperous and functioned as important ant commercial and cultural centers show the effective administration capacities of Marathas.
The Jats
- Jats too consolidated their power during the late 17th and 18th-centuries.
- Under their leader, Churaman, they acquired control over territories situated to the west of the city of Delhi, and by the 1680s they had begun dominating the region between the two imperial cities of Delhi and Agra.
- The Jats were prosperous agriculturists, and towns like Panipat and Ballabhgarh became important trading centers in the areas dominated by them.
- When Nadir Shah (Shah of Iran) sacked Delhi in 1739, many of the city’s notables took refuge there.
- His son Jawahir Shah had troops and assembled some another from Maratha and Sikh to fight Mughal.
Emergence of British as a Supreme Power

By 1765, the British had successfully grabbed major chunks of territory in eastern India. We shall learn about the emergence of British and the resistance from Indians to British in the coming posts.
Article by: Vibin Lakshmanan






Very short knowledge but excellent info
Too much good.. thkxx
It is very useful..thanks
Happy to help :-).
Learn and practice GK,TET, Aptitude questions and answers with explanation for interview https://www.gkindiaonline.com/
Thanks clearias.com. It’s really helpful.
Now I am going to join b. Tech. My aim is civil service. Please tell me the way to study now onwards
Please do not waste your time on btech
My age is 27 as on date n I want to start preparing for IAS.. I know it’s late but I would want some guidance for this.. Please help clearing.com
I am student of bca then how we will start preparation for ias
I am a student of class 11. I wish to begin my preparation for IAS now so please guide me how to go about it
Thanks a lot….very informative yet short
I am a plus two student and an IAS aspirant. Pls tell me the way to start the preparations now onwards….
I want to become an ias I am in 8th std. Give me some guidance that I have to follow to pass civil service and please tell me which is the best degree I have to pass to clear civil service exam easily
sir i’m a ba sociology graduate my aim is to become an ias officer ….. i wanna prepare it on my own effort …. please
give me suggestions on planning and priority
SIR in hindi notes are provided by you…
actually i am very thankful to u guys because this short information helped a lot in my history school project
My son want to creck IAS after 6years .He is in 10th.what should he join?
Good
Nice work
I’m truly excited to delve further into the content. I will definitely continue reading with anticipation.