Stem cell therapy, stem cell banking, stem cell preservation etc are terms that are often in news.
Do you know what is a stem cell?
To know about stem cells, let’s start with the concept of cells in biology.
What is a cell?
A cell is the structural and fundamental unit of life. All organisms are made up of cells. They may be made up of a single cell (unicellular), or many cells (multicellular). Cells are the building blocks of all living beings. They provide structure to the body and convert the nutrients taken from the food into energy.
Cells are complex and their components perform various functions in an organism. Our body is made up of cells of different shapes and sizes. Cells are the lowest level of organization in every life form.
What are stem cells?
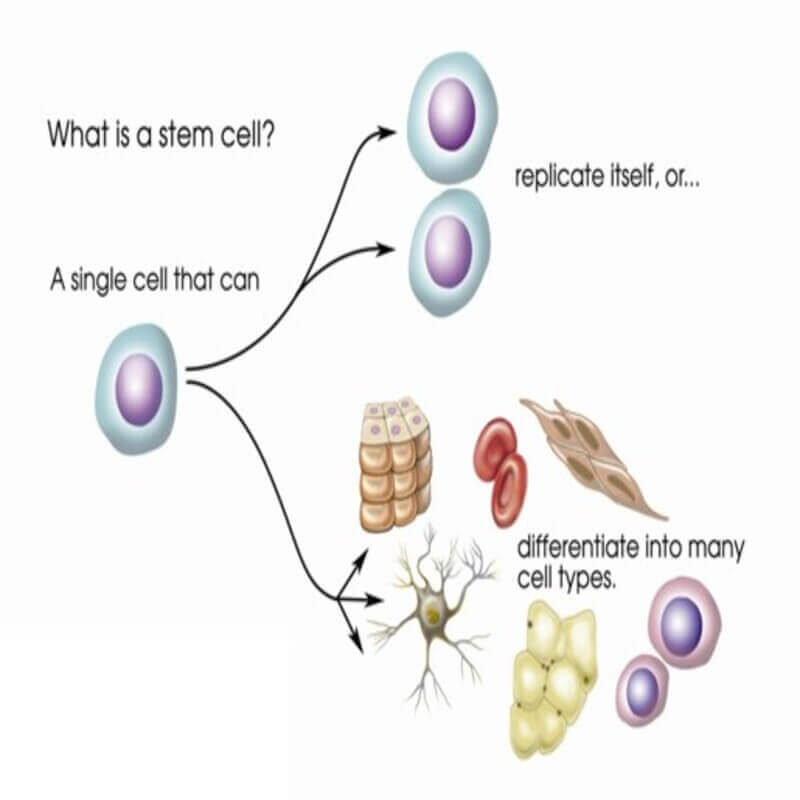
A stem cell is a cell with the unique ability to develop into specialized cell types in the body.
These cells provide new cells for the body as it grows, and replace specialized cells that are damaged or lost. In the future, they will be used to replace cells and tissues that have been damaged or lost due to disease. Our body is made up of numerous types of cells. Most cells are specialized for particular functions, like the red blood cells that carry oxygen in our bodies through the blood, but they are unable to divide.
All stem cells regardless of their source have three general properties:
- They are capable of dividing and renewing themselves for long periods
- They are unspecialized
- They can give rise to specialized cell types
Different types of stem cells:
Embryonic stem cells:
These types of cells supply new cells for an embryo as it grows and develops into a baby.
These cells are said to be pluripotent, which means they can change into any cell in the body.
Adult stem cells
Adult cells supply new cells as an organism grows and replace cells that get damaged.
These cells are said to be multipotent, which means they can only change into some cells in the body, not any cell, for example, blood cells and skin (epithelial) cells can replace their kind only.
Induced pluripotent stem cells
‘iPS cells’, are stem cells that scientists make in the laboratory.
‘Induced’ signifies that they are made in the lab by taking normal adult cells, like skin or blood cells, and reprogramming them to become stem cells.
Just like embryonic stem cells, they are pluripotent so they can develop into any cell type.
Also read: Commercial Cord Blood Banking
Stem cell therapy:
Stem cell therapy, also known as regenerative medicine, promotes the repair response of diseased, dysfunctional, or injured tissue using stem cells or their derivatives.
Stem cells may be one of the ways of generating new cells that can be transplanted into the body to replace the damaged or lost cells.
Adult stem cells are currently being used to treat some conditions, for example:
- Blood stem cells are used as a source of healthy blood cells for people with blood conditions, such as thalassemia, and cancer patients who have lost their blood stem cells during treatment.
- Skin stem cells can be used to generate new skin for people with severe burns.
- Some people with Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) lose their sight because cells in the retina of the eye called retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells stop working. Scientists are using induced pluripotent stem cells to produce new RPE cells in the lab that can be put into a patient’s eye to replace the damaged cells.
Stem cells could be used to generate new organs for use in transplants:
- Damaged organs are replaced by obtaining healthy organs from a donor, however, donated organs may be ‘rejected by the body as the immune system may detect it as a foreign body.
- Induced pluripotent stem cells generated from the patient could be used to grow new organs that would have a lower risk of being rejected.
Also read: Sickle Cell Disease
Regulations in India:
- In March 2019, the Union Health Ministry had notified the ‘New Drugs and Clinical Trial Rules, 2019’ which state that stem-cell-derived products are to be used as “new drugs”. This means that any doctor who uses stem-cell therapy needs to take permission from the government.
- In India as well as globally, only blood stem cells from bone marrow to treat blood cancers and different blood disorders are permitted. The clinical use in any other disease or use of any stem cells other than these is still in the research stage.
Also read: Cancer: Statistics, Causes and Types
Challenges faced and way forward:
Stem cells undoubtedly offer tremendous potential to treat many human diseases and to repair tissue damage resulting from injury or ageing.
The danger lies in the mix of desperate patients, enthusiastic scientists, ambitious clinicians, and commercial pressures.
Internationally agreed, and enforced, regulations are essential to protect patients from the dangers of stem cell tourism, whereby treatments that have not been approved in one country are freely available in another.





Leave a Reply