
ECOWAS has played a significant role in fostering peace, stability, and development in the West African region. Here’s a comprehensive overview of ECOWAS.
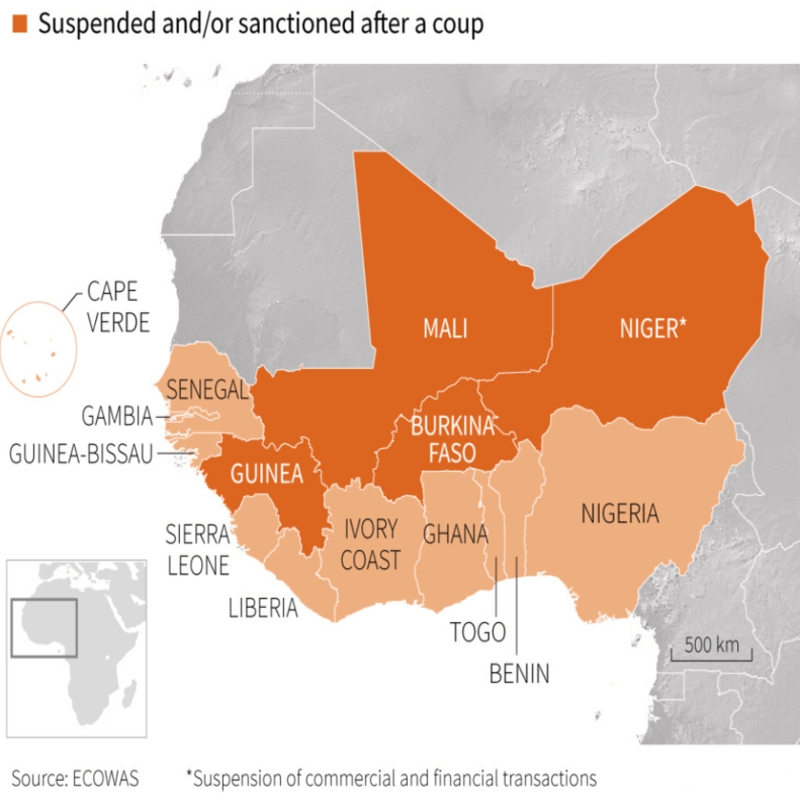
Recently, the military regimes in Burkina Faso, Mali and Niger announced their immediate withdrawal from the West African bloc Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS).
All three were suspended from ECOWAS with Niger and Mali facing heavy sanctions.
Analysts fear that this threatens to undermine Ecowas effort to overturn a series of violent military coups and risks the stability and unity of the entire 15-member union.
Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
The Atlantic Ocean forms the western as well as the southern borders of the West African region. The northern border is the Sahara Desert, with the Ranishanu Bend generally considered the northernmost part of the region. The eastern border lies between the Benue Trough, and a line running from Mount Cameroon to Lake Chad.
Colonial boundaries are still reflected in the modern boundaries between contemporary West African states, cutting across ethnic and cultural lines, often dividing single ethnic groups between two or more states.
The Economic Community of West African States is a regional intergovernmental organization to promote economic integration and cooperation among West African countries.
- The ECOWAS Treaty was signed on the 28th of May 1975 in Lagos, Nigeria.
- The Treaty of Lagos was signed by the 15 Heads of State and Government of Benin, Burkina Faso, Côte d’Ivoire, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea Bissau, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Sierra Leone, Sénégal and Togo, with its stated mission to promote economic integration across the region.
- The only Arabic-speaking Member Mauritania withdrew in December 2000. Mauritania recently signed a new associate membership agreement in August 2017.
The headquarters of ECOWAS is in Abuja, Nigeria.
Member States
The Economic Community of West African States consists of 15 member states, each with its government. The member states are:
- Benin
- Burkina Faso
- Cape Verde
- Ivory Coast (Côte d’Ivoire)
- Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Liberia
- Mali
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Senegal
- Sierra Leone
- Togo
Objectives of ECOWAS
- Promoting Economic Integration: The organisation seeks to create a common market and a customs union to facilitate the free movement of goods, services, and capital among member states.
- Peace and Security: The organization aims to promote political stability and prevent conflicts within the region. ECOWAS has been involved in conflict resolution and peacekeeping efforts, notably in Liberia, Sierra Leone, and Ivory Coast.
- Strengthening Cooperation: It promotes cooperation in various fields, including agriculture, health, education, and infrastructure, to enhance the overall development of the region.
- Facilitating Free Movement of People: The Economic Community of West African States works towards allowing the free movement of people across member states by harmonizing immigration and residency policies.
- Promoting Economic Development: The organization seeks to foster economic development through initiatives that support industrialization, agriculture, and infrastructure development.
Fundamental Principles
- Equality and inter-dependence of Member States;
- Solidarity and collective self-reliance;
- Inter-State cooperation, harmonization of policies, and integration of programs;
- Non-aggression between Member States;
- Maintenance of regional peace, stability, and security through the promotion and strengthening of good neighbourliness;
- Peaceful settlement of disputes among Member States, active cooperation between neighbouring countries, and promotion of a peaceful environment as a prerequisite for economic development;
- Recognition, promotion, and protection of human and people’s rights by the provisions of the African Charter on Human and Peoples’ Rights;
- Accountability, economic and social justice, and popular participation in development;
- Recognition and observance of the rules and principles of the Community;
- Promotion and consolidation of a democratic system of governance in each Member State as envisaged by the Declaration of Political Principles adopted in Abuja on 6 July 1991; and
- Equitable and just distribution of the costs and benefits of economic cooperation and integration.
Institutions of ECOWAS
- The Commission: The ECOWAS Commission serves as the executive arm, responsible for implementing policies and programs. It is headed by a President and supported by Commissioners.
- The Parliament: The ECOWAS Parliament is a consultative body that provides input on regional policies. Its members are drawn from national parliaments of member states.
- The Court of Justice: The ECOWAS Court of Justice adjudicates legal disputes and ensures the interpretation and application of the ECOWAS Treaty.
- The Mediation and Security Council: This council is responsible for conflict prevention, management, resolution, and post-conflict peace-building within the region.
Achievements and Challenges
Considered one of the pillars of the African Economic Community, ECOWAS was set up to foster the ideal of collective self-sufficiency for its member states. As a trading union, it is also meant to create a single, large trading bloc through economic cooperation.
- Peacekeeping: It has successfully intervened in conflicts, contributing to the restoration of peace in countries like Liberia and Sierra Leone.
- Economic Integration: The organization has made progress in economic integration, with the adoption of a common external tariff and efforts to create a single currency.
- Security Concerns: Persistent security challenges, including terrorism and transnational organized crime, continue to pose threats to the stability of the region.
- Economic Disparities: Wide economic disparities among member states and structural challenges hinder the full realization of economic integration.
- Political Instability: Some member states face political instability and governance issues, impacting the overall cohesion of the organization. The military coups in different member states are a major concern.
Future Prospects
- Single Currency: ECOWAS aims to establish a single currency, the “Eco,” to promote further economic integration.
- Infrastructure Development: Investments in regional infrastructure projects, such as transportation and energy, are critical for enhancing connectivity and economic development.
- Institutional Strengthening: Strengthening the institutions of ECOWAS is essential for the effective implementation of policies and programs.
India and ECOWAS
ECOWAS and India have strong ties with the latter achieving the status of Observer to ECOWAS in 2004.
After becoming an observer, India extended Line of Credit (LOCs) to ECOWAS in 2006.
- It was intended to supplement India’s Focus Africa program along with aiding regional integration for ECOWAS while offering additional opportunities for Indian companies to contribute in sectors such as energy, telecom, and transportation in West Africa.
In 2010, the Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI) and ECOWAS embarked upon a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to enable better trade ties and to accelerate investment prospects.
ECOWAS has supported India’s claim to a seat in the United Nations Security Council.
Read: African free trade: Opportunities for India-ORF
Conclusion
ECOWAS has played a pivotal role in shaping the economic and political landscape of West Africa. Despite facing challenges, the organization continues to work towards fostering regional integration, peace, and development. As it navigates the complexities of the evolving geopolitical landscape, ECOWAS remains a key player in addressing the collective aspirations and challenges of West African nations.
Related articles:
- Coup in Niger
- West Africa: India’s strategic focus and Relations with Nigeria
- Sudan Crisis 2023
- Desertification (Sahel region)
- Children and armed conflict
-Article by Swathi Satish






Leave a Reply