
The news of the Coup in Niger has the world’s attention. This is the seventh coup in western and central Africa since 2020, including two each witnessed by Niger’s neighbors Burkina Faso and Mali. Read here to learn about the unrest in the Sahel region of Africa.
Niger is a key part of the African region known as the Sahel – a belt of land that stretches from the Atlantic Ocean to the Red Sea. The area is plagued by religious extremists and tormented by military regimes.
Niger is geographically the largest country in West Africa. It has been politically the most stable compared to its neighbors. It is a landlocked country bordered by Algeria, Libya, Chad, Nigeria, Benin, Burkina Faso, and Mali.
Niger has strategic importance as it hosts military bases of the US and France, hence playing a major part in the fight against religious extremists.
Niger is rich in uranium and produces 7% of all global supplies. The uranium industry plays a crucial role in Niger’s economy, contributing significantly to the country’s gross domestic product (GDP) and government revenue.
Coup in Niger
Niger was a French colony until it gained independence in 1960.
Since 2018, terrorist activity in Niger has increased steadily, with 2021 being a record year for violence as indicated by deaths.
Even though there were more instances of political violence in 2022, the violence’s severity has continuously decreased, with a notable overall drop in deaths in 2017.
- During this time, looting and property destruction cases predominated, indicating that terrorist groups like IS Sahel and JNIM are increasingly targeting Niger as a prime location for resource extraction.
- Despite a noticeable geographic movement from the north to the west, the western Tillaberi region remains the most afflicted by war.
Presently, the coup was launched by the Presidential Guard in Niger after detaining the democratically elected President Mohamed Bazoum and his family.
- Senior officers from various branches of the defense and security forces (FDS) formed a junta, named the National Council for the Safeguarding of the Homeland (CNSP), and announced the seizure of power.
Most nations have denounced the coup, including significant players like the United States, France, the European Union, and ECOWAS.
- At a session in Abuja, Nigeria, ECOWAS discussed the possibility of using sanctions and a one-week deadline to put pressure on the junta to restore Bazoum.
- The Nigerien government’s assets were immediately sanctioned and frozen by the West African Economic and Monetary Union (UEMOA).
- Mali, Guinea, and Burkina Faso have all stated that they would not impose any sanctions on Niger and that they back the Nigerien junta.
- In a separate joint statement, Burkina Faso and Mali cautioned that any military action in Niger would amount to a declaration of war on their nations.
- The junta-led governments’ responses in favor of Niger have created the conditions for a wider rift and probable dissolution of the West African bloc.
Following the coup, there is a significant likelihood of domestic unrest and regional war, a rise in militant activity, a reversal of democratic progress, and a limitation of civil freedoms, as well as serious socioeconomic repercussions because of sanctions.
The military junta also faces fierce criticism from a variety of foreign parties and has not yet solidified its grasp on power.
There are indications that Bazoum’s supporters are counter-mobilizing for large-scale protests against the junta in addition to receiving backing from the international community and a sizable portion of the Niger populace.
Unrest in the Sahel region
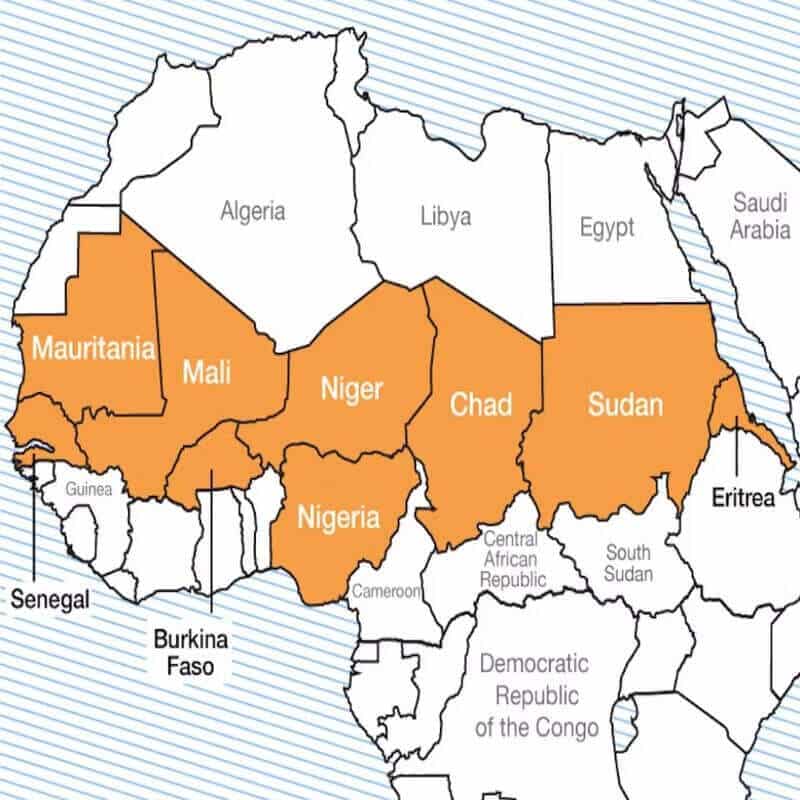
The Sahel region is a semi-arid belt of land located in Africa, stretching across the southern edge of the Sahara Desert.
- The term “Sahel” is derived from the Arabic word “Sahil,” which means “coast” or “shoreline.”
- The region extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east.
- The Sahel is characterized by a semi-arid climate, with distinct wet and dry seasons. Rainfall is relatively scarce and unreliable, and droughts are common. The region experiences hot temperatures during the dry season and mild temperatures during the wet season.
- The vegetation in the Sahel is mainly composed of grasslands, shrubs, and acacia trees. The landscape is a transition zone between the arid Sahara Desert to the north and the more humid savannas to the south.
- The Sahel region is prone to desertification, which is the process of fertile land turning into desert due to various factors, including climate change, overgrazing, deforestation, and unsustainable agricultural practices. Desertification poses significant challenges to agriculture, food security, and the livelihoods of the people in the region.
The Sahel region is home to a diverse range of ethnic groups and cultures. It is inhabited by various pastoralist and agricultural communities, as well as nomadic groups.
- The region faces various socio-economic and political challenges, including poverty, unemployment, and ethnic tensions.
- These factors have contributed to the movement of people within the region and towards neighboring countries, leading to migration and occasional conflicts.
- The region has been affected by recurrent humanitarian crises, including food insecurity and displacement of populations due to conflicts and environmental factors.
The Sahel region has gained international attention due to its complex challenges, and various international organizations, including the United Nations, the African Union, and regional bodies, are actively engaged in providing assistance and support for development, peacekeeping, and humanitarian efforts.
The Sahel region’s environmental and socio-economic challenges, combined with its strategic location as a transit route for migration and potential threats from extremist groups, have made it an area of focus for regional and global policymakers in terms of development, security, and humanitarian efforts.
Also Read: Sudan Crisis
What led to the coup in Niger?
Niger faces a variety of security challenges-
- The Sahelian insurgency led by IS Sahel and the al-Qaeda-affiliated JNIM in the west
- The ISWAP and Boko Haram insurgency in the southeastern Diffa region, a mix of IS Sahel militancy and banditry in the central Tahoua region
- Organized bandit gangs in Maradi along the southern border with Nigeria, and the gold-rich Agadez.
- The Agadez region lies along the border with Libya, Algeria, and Chad, and has become a smuggling route for armed groups, among them Chadian and Sudanese rebels, drug traffickers, and organized criminal gangs.
Although Niger was handling the insurgencies considerably better than Mali and Burkina Faso before their coups, the mutinous Niger soldiers have cited this deteriorating security situation as the cause of their rebellion.
Because of the escalating turmoil, some people now think that the only way to put an end to it is by severe military repression; this is why the coup appears to have widespread support in some areas.
Desertification is spreading from the Sahara into the Sahel as a result of climate change, which exacerbates the instability in the area. According to experts, the Sahel region is seeing the fastest global temperature rise.
Consequences
Globally, the coup in Nigeria has implications as many of the actions against trafficking and migration by the Nigerian government become futile.
- By agreeing to accept hundreds of migrants from Libyan detention facilities, President Bazoum’s administration has worked alongside European nations to curb the flow of migrants over the Mediterranean Sea.
- In what used to be a crucial transit area between neighboring nations in West Africa and those farther north, he has also clamped down on people traffickers.
Regionally, the coup will make the Sahel region already bereft of instability more fragile.
Also Read: European Refugee Crisis
Previous year question
Q. In recent years Chad, Guinea, Mali, and Sudan caught international attention for which one of the following reasons is common to all of them? (2023)
- Discovery of rich deposits of rare earth elements
- Establishment of Chinese military bases
- The southward expansion of the Sahara Desert
- Successful coups
Also read:
- Colonization of Africa – How did the Scramble for Africa lead to Decolonization?
- West Africa: India’s strategic focus and Relations with Nigeria
-Article by Swathi Satish





Leave a Reply