 Energy is defined as the ability to do work. People uses energy to walk, cook, communicate, read, etc. Do you know how this energy is transported in the world around us? Is the terms light and electromagnetic waves referring to the same phenomenon? Read the article to answer these questions.
Energy is defined as the ability to do work. People uses energy to walk, cook, communicate, read, etc. Do you know how this energy is transported in the world around us? Is the terms light and electromagnetic waves referring to the same phenomenon? Read the article to answer these questions.
Energy is moved around the world in two main ways: mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves.
Moving charged particles, such as electrons and protons, produce electromagnetic fields that carry the energy type known as electromagnetic radiation, or light.
What are Mechanical Waves?
Mechanical waves include water and air waves caused by sound. A disruption or vibration in matter, whether solid, gas, liquid, or plasma, is what generates mechanical waves. A medium is considered as a material through which waves are propagating.
Sound waves are created by vibrations in a gas (air), while water waves are created by vibrations in a liquid. By causing molecules to collide with one another, similar to dominoes knocking each other, these mechanical waves move across a medium and transfer energy from one to the next. Since there is no channel for these mechanical vibrations to be transmitted, sound cannot travel in the vacuum of space.
What are Electromagnetic Waves?
Electricity can be static which can cause your hair to stand on end. A refrigerator magnet is an example of static magnetism. A changing magnetic field will cause a changing electric field, and vice versa. When this changing electric field couples with changing magnetic field, electromagnetic waves are formed. Magnetic and electric fields of an electromagnetic wave are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of the wave.
In contrast to mechanical waves, electromagnetic waves can travel without a medium. This implies that electromagnetic waves can pass not only through solid objects like air and rock but also through empty space.
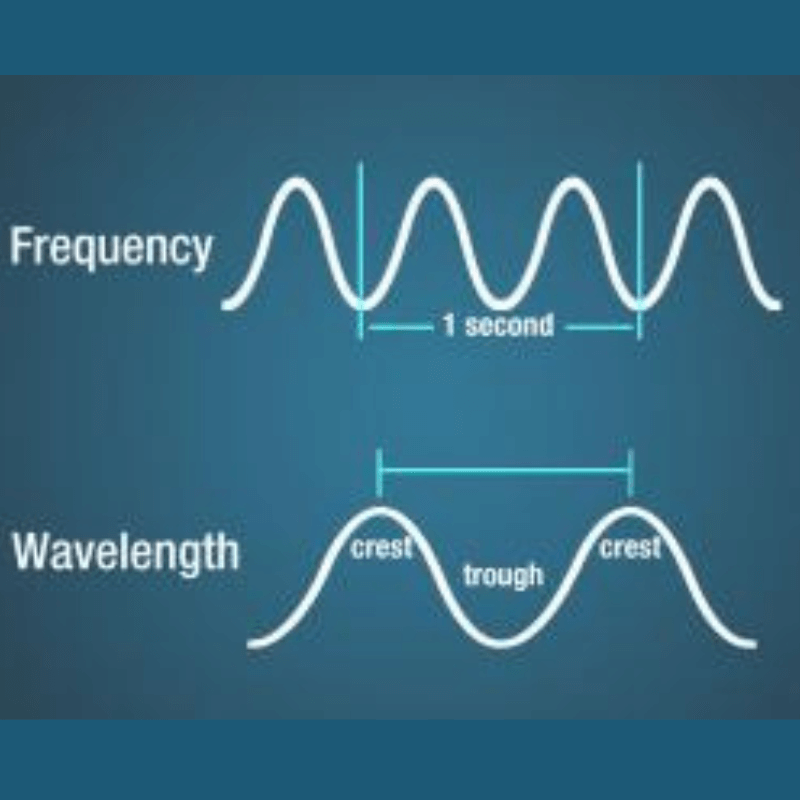
Electromagnetic waves are used whenever you watch television, listen to the radio, or cook food in a microwave. Electromagnetic waves include radio waves, television waves, and microwaves. The only thing that differentiates them is wavelength. The distance between each wave’s crest and the next is called the wavelength.
The energy increases with decreasing wavelength. For example, visible light wave lengths are blocked by brick walls. Brick walls can be penetrated by smaller, more energetic x-rays, but these rays are themselves prevented by denser materials like lead.
Although it is possible to say that certain materials “block” waves, the right terminology is “wave lengths of energy are absorbed” by objects. In other words, certain materials can absorb wave length energy.
Since the atmosphere also absorbs some wave lengths while allowing others to flow through, we employ this knowledge in weather satellites.
Related topics: Learn about Nuclear energy and Geothermal energy
Different Electromagnetic Waves
Either an electromagnetic wave’s frequency of oscillation or its wavelength can be used to describe its location within the electromagnetic spectrum. Because they originate from different sources and have distinct effects on matter, electromagnetic waves of different frequencies are referred to by various names.
In sequence of increasing frequency and decreasing wavelength are:
- Radio waves
- Microwaves
- Infrared radiation
- Visible light
- Ultraviolet radiation
- X-rays
- Gamma rays
Uses of Electromagnetic Waves
They transfer energy over distances or through solid objects. Certain electromagnetic waves are usually safe. An excellent illustration is the light we use to see. Other electromagnetic waves have the potential to be quite hazardous, thus caution must be taken to limit exposure. X-rays are a common example.
What causes these variations in electromagnetic waves? It is based on their characteristics. Electromagnetic waves have wavelength, frequency, and speed characteristics just like other waves.
Different parts of the EM spectrum have different uses. They are as follows:
Radio waves
Radio and television employ radio waves for communication. Air simply allows for the transmission of radio waves. If the human body absorbs them, they do not harm the body, and they can be reflected to reverse direction. They are excellent for communicating because of these qualities.
Read: Fast Radio Bursts
Microwaves
Both food preparation and satellite communication employ microwaves. Food molecules readily absorb the frequencies of high frequency microwaves. When molecules absorb microwaves, their internal energy rises, which leads to heating. Since microwaves may easily travel through the atmosphere, they can connect ground stations and satellites in orbit.
Infrared
Electric heaters, food-cooking appliances, and infrared cameras which can see individuals in the dark all employ infrared light. The wavelengths of infrared light are absorbed by some chemical bonds. When infrared light is absorbed, the internal energy of bonds rises, which results in heating. Infrared light can thus be used to cook food and power heaters. All materials emit infrared light. This light is invisible to the human eye, but infrared cameras can see it. The term “thermal imaging” refers to a technique for finding people in the dark.
Visible light
The light we can see is known as visible light. It is employed in fibre optic communications, where coded pulses of light are sent from a source to a receiver through glass fibres.
Ultraviolet
Water that has bacteria in it can be sterilised and made safe to drink by the use of ultraviolet radiation. Due to its role in the production of vitamin D, ultraviolet radiation benefits skin as well. However, excessive UV exposure can result in skin problems.
X-rays
Bone breaks are found through X-rays. It can pass through flesh but not through bone or other hard materials. X-rays harm cells and result in cancer. To reduce exposure, radiologists take precautions including donning lead aprons and positioning themselves behind a lead screen.
Gamma rays
Cancer is caused and treated by gamma rays. Gamma radiation can damage healthy cells in large amounts and result in cancer. But mutated cells can also be eliminated using gamma radiation.
Article written by: Krishnapriya JR






Leave a Reply