
Geomorphic processes are natural mechanisms that shape and alter the Earth’s surface over time, forming various landforms such as mountains, valleys, plains, and plateaus. These processes are driven by forces originating within the Earth (endogenic processes) or from external sources (exogenic processes). Read here to learn more.
It is time to know in detail about the surface of the earth on which we live. We know that the surface of the earth is not a plain platform. It is distributed unevenly with a variety of landforms like mountains, hills, plateaus, plains, ravines, cliffs etc.
Why is the surface of the earth uneven? What makes changes in the earth’s surface? What process makes mountains and hills? The answer to all the questions above is geomorphic Processes.
Also read: Geologic Time Scale
Geomorphic Process
The formation and deformation of landforms on the surface of the earth are a continuous process which is due to the continuous influence of external and internal forces.
The internal and external forces causing stresses and chemical action on earth materials and bringing about changes in the configuration of the surface of the earth are known as geomorphic processes.
Also read: Geohazards and their Management
Mind Map to Study Geomorphic Processes/Earth Movements
The below mind map will help to study geomorphic processes and their sub-classification in a matter of minutes.
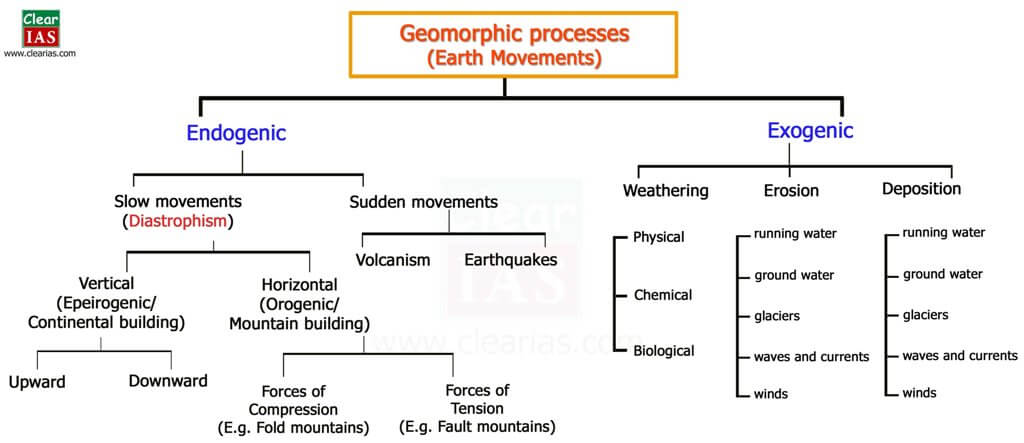
Endogenic Forces
- Endogenic forces are those internal forces that derive their strength from the earth’s interior and play a crucial role in shaping the earth’s crust.
- Examples – mountain-building forces, continent-building forces, earthquakes, volcanism etc.
- The endogenic forces are mainly land-building forces.
The energy emanating from within the earth is the main force behind endogenic geomorphic processes. This energy is mostly generated by radioactivity, rotational and tidal friction and primordial heat from the origin of the earth.
These are internal processes that derive their energy from within the Earth, mainly from tectonic and volcanic activity.
Tectonic Processes:
- Folding: When Earth’s crust is compressed, it bends and forms folds, leading to the creation of mountain ranges, such as the Himalayas.
- Faulting: When the crust is subjected to stress, it may fracture, creating faults. Movements along these faults can result in earthquakes, forming rift valleys or blocking mountains.
- Volcanism: The movement of molten rock (magma) from beneath the Earth’s surface to above it, leading to the formation of volcanic landforms like volcanoes, lava plateaus, and volcanic islands.
Also read: Marginal seas of the world
Exogenic Forces
Exogenic forces can take the form of weathering, erosion, and deposition. Weathering is the breaking of rocks on the earth’s surface by different agents like rivers, wind, sea waves and glaciers. Erosion is the carrying of broken rocks from one place to another by natural agents like wind, water, and glaciers.
The actions of exogenic forces result in wearing down (degradation) of relief/elevations and filling up (aggradation) of basins/ depressions, on the earth’s surface. The phenomenon of wearing down of relief variations of the surface of the earth through erosion is known as gradation.
These are external processes driven by forces like gravity, water, wind, and ice, which gradually wear down the Earth’s surface.
- Weathering:
- Physical Weathering: The mechanical breakdown of rocks into smaller pieces without changing their chemical composition, often due to temperature changes (freeze-thaw cycles), pressure release, or biological activity.
- Chemical Weathering: The decomposition of rocks due to chemical reactions, often involving water, acids, or gases. This process leads to the formation of features like karst landscapes (e.g., limestone caves).
- Biological Weathering: The breakdown of rocks by living organisms, such as plants and microbes, which can accelerate both physical and chemical weathering processes.
- Erosion: The process of wearing away and transporting rock material by natural agents like water, wind, ice, and gravity.
- Fluvial Erosion: Erosion caused by rivers and streams, leading to the formation of valleys, canyons, and deltas.
- Aeolian Erosion: Wind-driven erosion, which shapes features like dunes and desert pavements.
- Glacial Erosion: The movement of glaciers erodes the underlying rock, creating U-shaped valleys, fjords, and moraines.
- Mass Wasting: The movement of rock and soil downslope under the influence of gravity, including landslides, rockfalls, and debris flows.
- Deposition: The accumulation of sediment in new locations, creating landforms such as deltas, alluvial fans, dunes, and glacial moraines.
Other geomorphic processes
Coastal Processes
- Wave Action: The continuous impact of ocean waves erodes coastlines, forming features like cliffs, arches, and sea stacks.
- Tides and Currents: These influence the deposition of sediments along coastlines, leading to the formation of beaches, spits, and barrier islands.
Fluvial Processes
- River Action: Rivers play a crucial role in shaping landscapes by eroding, transporting, and depositing sediments, which leads to the formation of valleys, floodplains, meanders, and oxbow lakes.
Glacial Processes
- Glacial Movement: Glaciers erode the landscape through plucking and abrasion, carving out deep valleys and shaping mountain ranges. The deposition of glacial till creates landforms such as drumlins, eskers, and terminal moraines.
Wind Processes (Aeolian Processes)
- Wind Erosion: Wind picks up and transports fine particles, leading to the formation of landforms like dunes and loess plains.
Biotic Processes
- Vegetation and Animals: The roots of plants and the activities of animals contribute to the breakdown of rocks and the stabilization of soil, influencing erosion and deposition.
Geomorphic Processes vs Geomorphic Agents
Geomorphic agents are natural forces that drive the processes of weathering, erosion, transportation, and deposition, which collectively shape the Earth’s surface over time.
These agents play a crucial role in the formation and evolution of landscapes, and they can be classified into several categories based on their nature and effects.
These geomorphic agents interact with each other, and their combined effects are responsible for the continuous reshaping of the Earth’s surface, creating diverse landscapes across the planet.
Earth Movements
- They are the movements in the earth’s crust caused by endogenic or exogenic forces. These movements are also termed as Tectonic movements.
- The term ‘Tectonic’ is derived from the Greek word ‘Tekton’ which means builders.
- As the word means, these movements are mainly builders and have been responsible for building up different types of landforms.
Next in the series: Endogenic Forces and Evolution of Land Forms.
Article by: Jijo Sudarshan






Thanx
Thanks…..
Thanks a lot.. It is a very useful post.
Hello sir
Can provide all study material in hindi
Weathering is the breaking of rocks on the earth’s surface by different agents like rivers, wind, sea waves and glaciers.
I have doubt in these lines , I think weathering is a static process , i.e . The in-Situ decomposition and disintegration of rocks by atmospheric-climatic elements, chemical and biological agents. viz Isolation ,
Freezing-thawing , etc
Weathering +transportation=erosion
Weathering-static process
Erosion -dynamic process
You are right bro. The other one is erosion.
It was nice. Thanks. But it could have been a simpler yet fancier way. On essay basics this was a hard website to refer to.
Thank you.
it is also a off situ process
thanks
Thank you so much
Thanks
how to next page
Thanks sir…. this is very very useful for our last time studies
thank u
Thanks team…keep supporting
thank you
thank u
The best website.. For preparing
this is really helpful. how can I join
Very informing
Kindly post the “concepts of geomorphology ” please
I have a question which said “in geomorphology weathering described to be as means of an a
End” justfy this statement.
Thank you sir
thank u so much
Very good sir, please keep this publishing regular for the upsc examination.
Nice and great website ,thank u your contribution.
Can you provide it in Hindi
Tnqqq Sir
Very educating
I love it.
Is this material Full or we have to pay some amount to get access to complete material?
Great !!!it helped me a lot
thankyou sir
Under exogenic geomorphic process, we can add one more sub division “anthropogenic causes” along with weathering, erosion, deposition. Recently human impact can be greatly seen on land features through activities such as mining, building etc. which comes under anthropogenic causes.