
What are Ballistic missiles?

- A ballistic missile/projectile follows a “ballistic trajectory”.
- The ballistic trajectory is the path followed by the projectile (missile) after thrust forces (propulsion) stop and the projectile is only acted upon by gravity and friction (drag forces).
- A ballistic missile thus is guided in the initial phase, i.e. lift off, while the rest of the trajectory is dependent on gravity and requires minimal guidance.
What are the advantages of Ballistic Missile?
- They have a very long range, as they travel above the atmosphere, experience less drag, and use gravity and earth’s rotation.
- They are highly fuel efficient. Only fuel requirements are during the lift-off phase and course correction measures.
- Multiple independent targetable re-entry vehicles (MIRV) capability can be achieved in ballistic missiles.
- Due to fuel efficiency, their payload-carrying capacity is significantly more than cruise missiles.
What’s a Ballistic Missile Defence (BMD) System?
- A Ballistic Missile Defence system (BMD) is a missile defence system that acts as a shield against ballistic missile attacks.
- You may not that the purpose is defence (by intercepting a ballistic missile) and not attack/offense.
A ballistic missile can be intercepted in three phases:
- Terminal phase: During the atmospheric descent phase.
- Mid-course interception (in-flight interception) – Most preferred interception.
- The lift-off phase– i.e. targeting at the launch point- requires advanced radars.
Generally, a BMD is a two-tier automated system that has:
- The advanced radar system, Early warning system ( Also called sensors system).
- Integrated command and control centre.
- Interceptor missile batteries- need to be agile, mobile, and strategically located on land and sea.
India’s Ballistic Missile Defence System
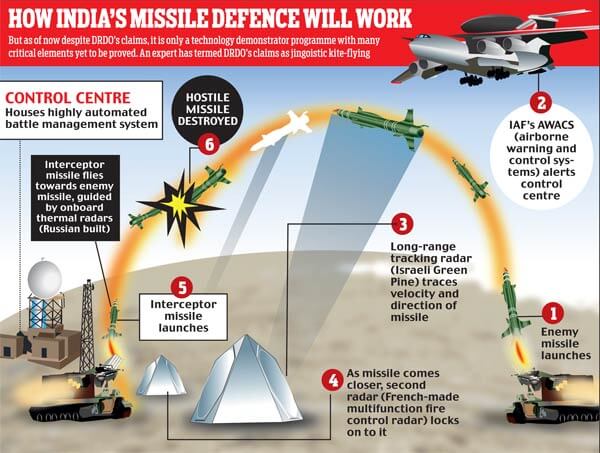
- India’s BMD development began in 1999, after the Kargil war.
- The primary aim was to bolster India’s defence against a possible nuclear attack from Pakistan. It holds a place of prime importance especially when India follows the ‘No first use’ policy.
- India seeks to deploy a functional ‘iron dome’ ballistic missile defence (BMD), incorporating both low-altitude and high-altitude interceptor missiles.
- India’s BMD is primarily developed by DRDO with the help of many public and private firms like BEL, Astra Microwave, L&T, etc.
India’s BMD is being developed in 2 phases:
- The first phase aims to develop a shield to intercept missiles with a range of up to 2000 km. 1st phase radar range is up to 600 km.
- The second phase will have an intercept missile with a 5000 km range. The radar range of this phase would be 1500 km.
Two- tiers of India’s BMD
They are Prithvi Air Defence (PAD) and Advanced Air Defence (AAD) respectively.
Prithvi Air Defence (PAD)

- Also referred to as Pradyumna Ballistic Missile Interceptor.
- It’s designed for High-altitude interception ( exo-atmospheric interception).
- Intercept missiles at altitudes between 50 – 80 km.
- The interceptor is a Prithvi Defence Vehicle ( PDV) which has two stages, both with solid propellants.
Advanced Air Defence (AAD)

- Also called Ashwin Ballistic Missile Interceptor.
- It’s an endo-atmospheric interception system ( for low-altitude interception).
- Altitude of interception is range up to 30 km.
- It has a single-stage solid-fueled missile.
Configurations of BMD
According to Lieutenant General Balraj Nagal (retired), director of the Centre for Land Warfare Studies. There are five possible configurations of BMD. These are:
- A land and sea-based defence system against all kinds of threats. This system is too expensive and requires too much technological and infrastructural development. Though it is the safest configuration, it still isn’t 100% secure.
- In the Second configuration, BMD is deployed to protect critical population centres, control, and command centres, critical infrastructure centres (including nuclear facilities), and major economic zones. It’s strategically and economically more pragmatic than the first configuration. Yet, it is too costly for a nation like India.
- In the third configuration, protection is provided to command and control centres, nuclear forces, and important citizen population centres.
- BMD will protect command and control centres nuclear forces and the capital in the fourth configuration. This is the most suitable candidate considering the nascent stage of India’s BMD and also the weak financial condition of the nation. It protects critical nodes of governance as well as of counter-attack.
- The final configuration would involve BMD deployment only around the command and control centre and the capital. Its purpose is only for total defence and not able to provide the ability to counterattack as nuclear forces are left out of it.
Why should India need BMD?
- India follows the ‘No First Use policy‘. A robust BMD provides an opportunity for the nation to strike back if a nuclear projectile is launched by an enemy state.
- In the past efforts have been made by radicalized non-state fractions in Pakistan to obtain Missile technology. BMD would shield from non-state actors initiated missile warfare and thus could avoid the Mutual Destruction trap.
- India has hostile, nuclear states in its north. It’s only practical for the nation to prepare in advance.
- China is developing new technologies to implement its Anti-Access/Area-Denial (A2/AD) strategy in the Western Pacific. It can impact the mainland in Indian water. A robust BMD is a proactive measure to tackle China’s A2/AD strategy.
- BMD reduces the incentive for the enemy state to launch a nuclear attack, Thus enhancing strategic stability.
- An indigenous system would reduce the import bill of defence systems from other nations.
- There are side benefits of BMD too, like better reconnaissance, detection, tracking, and situation awareness.
- Technology developed for BMD can be used in other sectors, especially in space technology.
Apprehensions regarding BMD
- It may start the arms race with Pakistan investing in more powerful missiles to thwart BMD’s disturbing strategic balance.
- BMD is ineffective against Cruise missiles. Both China and Pakistan have cruise missiles capable of delivering the nuclear payload.
- No BMD can have a 100% success rate in the interception of the projectile (ballistic missile).
- BMD is a very costly affair. For example, the U.S. Continental System is estimated to have cost around $100 bn from 2002 onwards.
- India has a wide and segregated geography. It creates a problem in the protection of all critical centres and the creation of land infrastructure for BMD in many areas.
- Even after interception, there remain chances of damage, especially if the interception is done in the terminal phase of the ballistic missile.
- BMD testing is done in a controlled atmosphere raising the question of its efficacy in wartime.
- DRDO has been criticized for not releasing whole data related to the BMD system. It evokes a sense of suspicion regarding BMD’s capability.
Also read: India’s Defence Exports
Conclusion
In the fast-changing geo-political scenario, strategic preparedness and self-reliance are the new currency of defence. BMD fulfils all such criteria and creates a protective shield that has not only physical but also psychological effects on hostile nations.
It bolsters India’s NO FIRST USE policy by providing the second strike capability.
Though there are issues related to its cost, effectiveness, and extent; nevertheless with development in technology and support from Make in India, it can augment over some time. As for now, BMD is an idea whose time has come and will remain so for a long.
Read:
Article by: Alok Singh






Thanks for the knowledge.
i am trying to drop some email to you bt it says d addres does not found..what is d email adres kindly tel me have certain queries