
The movement of ocean water is a complex and dynamic process driven by various factors, including wind, temperature, salinity, the Earth’s rotation, and the geography of the ocean basins. Ocean currents, tides, and waves are the primary manifestations of ocean water movement. Read here to learn more.
Our Geography notes continue. Having covered the most important concepts in the land, we are now dealing with the water (hydrosphere). In the last article, we have seen the ocean bottom topography.
In this comprehensive post, we will cover the movements of ocean water – waves, tides, and ocean currents. We hope the notes will be highly handy for quick learning and last-minute revision.
Also read: High Seas Treaty
Movements of ocean water
You all know that the ocean water is never still. There are different types of movements of ocean water under the influence of different physical characteristics like temperature, salinity, density, etc. Movements of ocean water are also affected by external forces like the sun, moon, and winds.
The major movements of the ocean waters can be classified into three. They are:
- Waves
- Tides
- Ocean Currents
Waves and ocean currents are horizontal movements of ocean waters while the tide is a kind of vertical movement of the ocean water.
Waves
- Waves are nothing but oscillatory movements that result in the rise and fall of water’s surface.
- Waves are a kind of horizontal movements of the ocean water.
- They are the energy, not the water as such, which moves across the ocean surface.
- This energy for the waves is provided by the wind.
- The size and strength of waves depend on factors like wind speed, duration, and fetch (the distance over which the wind blows).
- In a wave, the movement of each water particle is circular.
- A wave has two major parts: the raised part is called the crest while the low point is called the trough.
Read: Swell waves: What is Kallakadal?
Tides
- Tides are the periodical rise and fall of sea levels, once or twice a day, caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the sun, the moon, and the rotation of the earth.
- They are vertical movements of water and are different from movements of ocean water caused by meteorological effects like the winds and atmospheric pressure changes.
- Note: The water movements that are caused by the meteorological effects like the said above are called surges and they are not regular like tides.
- The moon’s gravitational pull to a great extent is the major cause of the occurrence of tides (the moon’s gravitational attraction is more effective on the Earth than that of the sun).
- Sun’s gravitational pull and the centrifugal force due to the rotation of the earth are the other forces that act along with the moon’s gravitational pull.
- The highest tides in the world occur in the Bay of Fundi in Canada.
- When the tide is channeled between islands or into bays and estuaries, they are termed Tidal Currents.
- The regular interval between two high or two low tides is 12 hours and 25 minutes.
Also read: Deep Water Circulation
Flow Tide and Ebb Tide
- A flow tide or a flood tide is a rising tide or incoming tide which results in a high tide.
- It is thus the period between a low tide and a high tide (i.e., the rising time).
- Ebb Tide is the receding or outgoing tide. It is the period between high tide and low tide during which water flows away from the shore.
Types of Tides
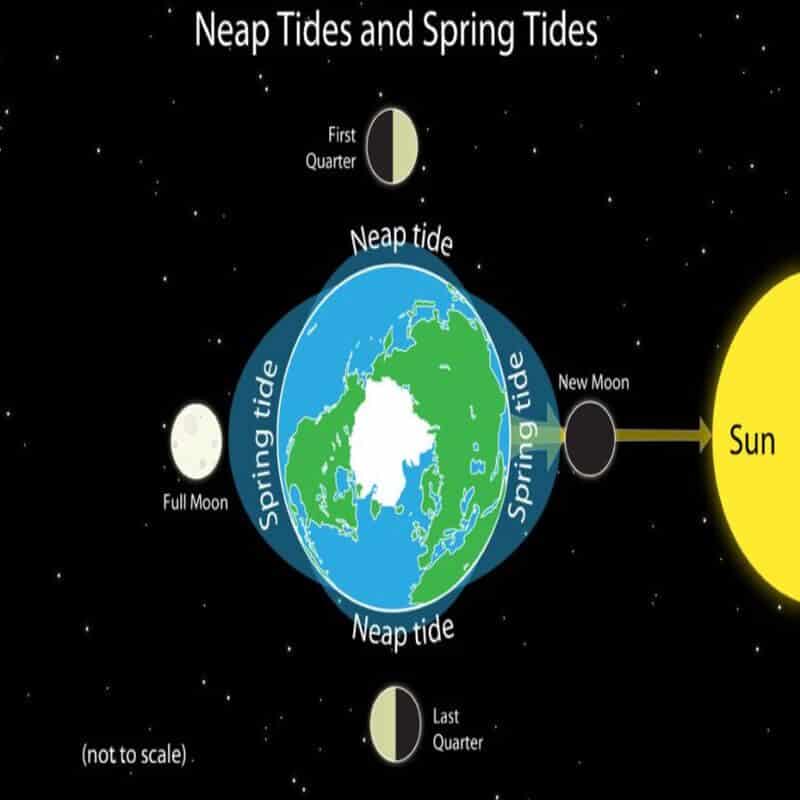
A. Tides based on the frequency
- Semi-diurnal Tide: They are the most common tidal pattern, featuring two high tides and two low tides each day.
- Diurnal Tides: Only one high tide and one low tide each day.
- Mixed Tide: Tides having variations in height are known as mixed tides. They generally occur along the west coast of North America.
B. Tides based on the sun, the moon, and the earth’s positions
- Spring Tides: When the sun, the moon, and the earth are in a straight line, the height of the tide will be higher than normal. These are called spring tides. They occur twice a month on the full moon (Poornima) and the other on the new moon (Amavasya).
- Neap Tides: Normally after seven days of a spring tide, the sun and the moon become at a right angle to each other concerning the earth. Thus, the gravitational forces of the sun and the moon tend to counteract one another. The tides during this period will be lower than the normal which are called the neap tides. They also occur twice in a month- during the first quarter moon and the last quarter moon.
Magnitude of Tides
Perigee: When the moon’s orbit is closest to the Earth, it is called a perigee. During this period, unusually high and low tides occur.
Apogee: When the moon’s orbit is farthest from the earth, it is called an apogee. Tidal ranges will be much less than the average during this period.
Perihelion: It is the position where the earth is closest to the sun (around January 3rd). Unusual high and low tides occur during this time.
Aphelion: It is the position where the earth is farthest from the sun (around July 4th). Tidal ranges are much less than the average during this period.
Tidal Bore
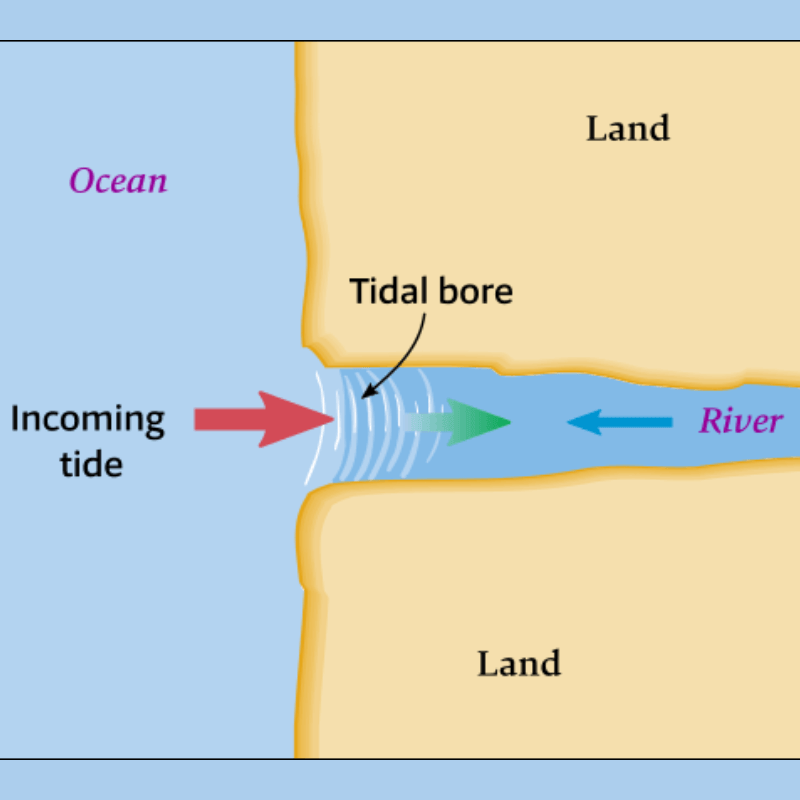
When the leading edge of the incoming tide forms a wave/ waves of water that travel up a river or a narrow bay against the direction of the river or bay’s current, it is called a tidal bore. The Indian rivers like the Ganges, Brahmaputra, Indus, etc. exhibit tidal bores.
Inter-Tidal Zone
The intertidal zone, also known as the foreshore and seashore and sometimes referred to as the littoral zone, is the area that is above water at low tide and under water at high tide (i.e., the area between the tide marks).
Effects of tides
- Tides act as a link between the port and the open sea. Some of the major ports of the world, such as London port on the river Thames and Kolkata port on river Hugli are located on the rivers away from the sea coast.
- The tidal current clears away the river sediments and slows down the growth of the delta.
- It increases the depth of water which helps ships to move safely to the ports.
- It also acts as a source for producing electricity.
Read: Tidal Energy
Ocean Currents
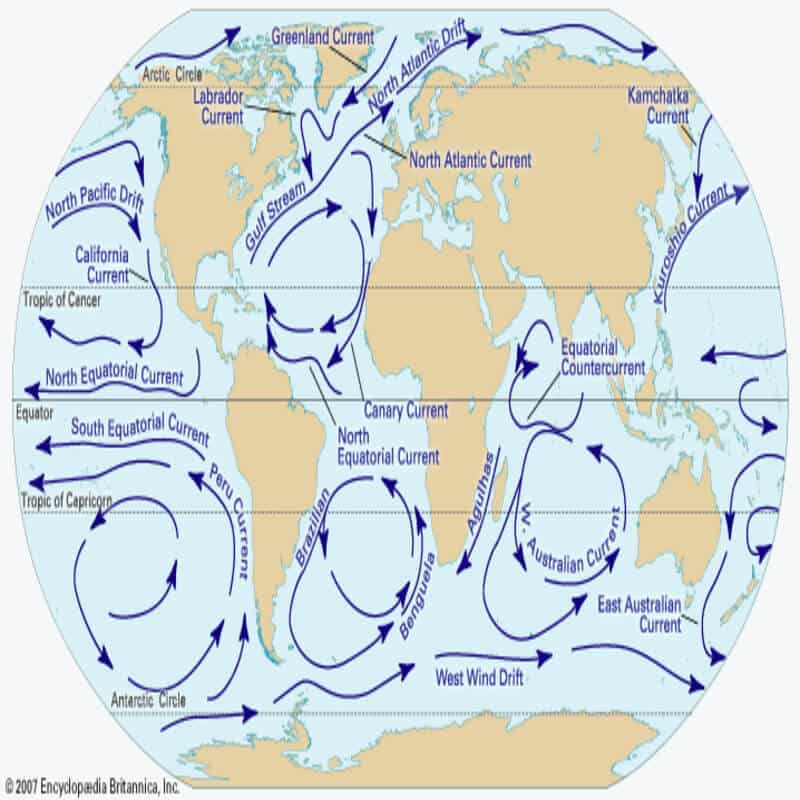
- The ocean currents are the horizontal flow of a mass of water in a fairly defined direction over great distances.
- They are just like a river flowing in an ocean.
- Ocean currents can be formed by the winds, density differences in ocean waters due to differences in temperature and salinity, gravity, and events such as earthquakes.
- The direction of movement of an ocean current is mainly influenced by the rotation of the earth (due to the Coriolis force, most ocean currents in the northern hemisphere move in a clockwise manner, and ocean currents in the southern hemisphere move in an anti-clockwise manner).
Gyre, Drift, and Stream
- Any large system of rotating ocean currents, particularly those involved with large wind movements is called a Gyre. They are caused by the Coriolis force.
- When the ocean water moves forward under the influence of prevailing wind, it is called Drift (The term ‘drift’ is also used to refer to the speed of an ocean current which is measured in knots). E.g. North Atlantic Drift.
- When a large mass of ocean water moves in a definite path just like a large river on the continent, it is called a Stream. They will have greater speed than drifts. E.g. Gulf Stream.
- Ocean eddies are swirling, rotating masses of water that can occur within ocean currents. They can have a significant impact on local oceanic and atmospheric conditions.
Types of Ocean Currents
Warm Ocean Currents:
- Those currents that flow from equatorial regions towards poles which have a higher surface temperature and are called warm current.
- They bring warm waters to the cold regions.
- They are usually observed on the east coast of the continents in the lower and middle latitudes of both hemispheres.
- In the northern hemisphere, they are also found on the west coast of the continents in the higher latitudes (E.g. Alaska and Norwegian Currents).
Cold Ocean Currents:
- Those currents that flow from polar regions towards the equator have a lower surface temperature and are called cold currents.
- They bring cold waters into warm areas.
- These currents are usually found on the west coast of the continents in low and middle latitudes of both hemispheres.
- In the northern hemisphere, they are also found on the east coast in the higher latitudes (E.g. Labrador, East Greenland, and Oyashio currents).
The ocean currents can be also classified as:
- Surface Currents: They constitute about 10% of all the water in an ocean. These waters are occupied at the upper 400m of an ocean or the Ekman Layer. It is the layer of ocean water which moves due to the stress of blowing the wind and this motion is thus called Ekman Transport.
- Deep Water Currents: They constitute about 90% of the ocean water. They move around the ocean basin due to variations in the density and gravity.
Read: Marine cold waves
Factors influencing the origin and nature of ocean currents
Difference in density
- As we all know, the density of seawater varies from place to place according to its temperature and proportion of salinity.
- The density increases with an increase in salinity and decreases with a decrease in salinity.
- But when the temperature increases, density decreases, and when the temperature decreases density increases.
- This increase and decrease in density due to the differences in temperature and salinity causes the water to move from one place to another.
- Such a movement of water due to the differences in density as a function of water temperature and salinity is called the Thermohaline Circulation.
- In polar regions, due to a lower temperature, the waters will be of high density. This causes the waters to sink to the bottom and then to move towards the less dense middle and lower latitudes (or towards the equatorial regions).
- They rise (upwelling) at the warm region and push the already existing less dense, warm water towards the poles.
- While considering the equatorial region, the high temperature in those regions causes the water to expand. Thus, the waters in these regions will be at a higher level than that of the middle and upper latitudes. This also creates a gradient and results in the movement of waters from the equatorial region to the middle and upper latitudes.
The earth’s rotation
- Earth’s rotation causes Coriolis force which deflects the air to its right in the northern hemisphere and its left in the southern hemisphere.
- Similarly, ocean water is also affected by the Coriolis force and follows Ferrel’s Law.
- Hence, ocean currents in the northern hemisphere move in a clockwise (towards right) direction, and ocean currents in the southern hemisphere move in an anti-clockwise (towards left) direction (In the Indian Ocean due to the impact of the Asian monsoon, the currents in the northern hemisphere do not follow this pattern of movements all time).
The winds
- The winds like trade winds and westerlies drive the ocean water in a steady flow in front of them.
- When the direction of the winds changes, the direction of the current also gets changed.
The movement of ocean water is a critical component of Earth’s climate system and has far-reaching effects on weather patterns, marine ecosystems, and global climate regulation. Scientists continue to study and monitor these processes to better understand their impacts on our planet.
Article by: Jijo Sudarsan






Excellent explanation regarding waves currents winds and tides
Great. Explained in a very systematic way. Keep it up
Tq
Fantastic article
Good and Easy explaination
thank you very much ……..clear ias
Very specifically explained. Thanks CLEARIAS.
Lucid and crisp info. Keep it up
Thanks for providing free study material for poor students one who does not purchase books.this is good study material for ias pre and mains and pcs.
Dear sir I am 3rd year mechanical engineering student I am requesting you to Please explain the syllabus separate for a mechanical engineering student so that I can understand in a good way.Thankyou
Very helpful information for all times. Very appreciative. Thanks
Thank u very much .
This helped me a lot for my Geography Exam.
In-depth knowledge of ocean water and it’s subsequent formations collected through this extensive artical can help a lot in preparation of any competitive exam..
Mind-blowing article with depth knowledge
I was in Mozambique last week…at or about 11am I found the sea shore muddy as if the sea was dried up..at or about 12pm the water started coming to the shore until 4pm.i could not understand the physics
bade bade shehro m choti choti bate hoti rhti h victor.hahahaha
that is a great explanation about the movements of ocean water and what causes so i would say to you thank you and hope you good health
its very useful but i need a brief notes of waves
Neap tides should 1st and 3rd quarter of moon that had been written as 1st and last quarter….
There are 2 mismatched info in “Magnitude of Tides” section:
1. You stated: “Perihelion: It is the position where the earth is closest to the sun (around January 3rd). Unusual high and low tides occur during this time.”
My understanding: When the earth is closest to the sun, it must be mid summer (around July).
2. You stated: “Aphelion: It is the position where the earth is farthest from the sun (around July 4th). Tidal ranges are much less than the average during this period.”
My understanding: When the earth is farthest from the sun, it must be mid winter (around January).
Summers and winters occur due to the tilt of Earth’s axis and not due to its distance from the sun. The seasons occur due to apparent movement of sun and not its distance from the Earth or aphelion or perihelion.
Good stuff for faster revision thanks clear ias
Wow!! Amazing, notes are very systematically arranged easy to read and learn. Thank you so much for these notes.🙏
it should be Sathya sai baba
these notes are amazing! thankyou so much.
How much is made up and assumptions. We need to take a closer look at natural phenomena.
Here is a simple example of another approach
We know that in any vessel, if it is filled with substances of different specific weights, their separation will occur. The heaviest will precipitate, lighter above and very light at the top. A simple example is an aquarium. Rocks and sand at the bottom, then toys, fish, and a feeder at the top and all this in the water.
Our planet, for the Sun, is the same aquarium. And why should she have the hardest part in the center?
The heavy part should be on the sunny side all the time. After all, if we tilt the aquarium, then the stones and sand will slide towards the Earth?
a short list of phenomena that are explained by this model –
Mountain formation,
the magnetic field of the planets – is understandable even to a schoolboy,
The main Ocean currents are the real reasons
Tides in the ocean are another mechanism,
The movement of the planets- for example, why the Moon comes to us all the time with one side,
the change in the time of the Earth’s revolution
Other physics of earthquakes.
Solar. 11 year old, active
Gravitational waves
, etc.