 Non-constitutional bodies or Extra Constitutional bodies are authorities or agencies that are not defined in the Indian Constitution.
Non-constitutional bodies or Extra Constitutional bodies are authorities or agencies that are not defined in the Indian Constitution.
We have learned about Constitutional Posts and Constitutional Bodies in our Indian Polity notes.
Non-constitutional bodies in India refer to organizations or institutions that are not explicitly mentioned in the Constitution of India but play a significant role in the governance and functioning of the country. These bodies are typically established by the government through executive orders or legislation.
In this post, we shall learn about Non-Constitutional Bodies in India.
What is meant by a Non-Constitutional Body?
A non-constitutional body is an organization or institution which is not mentioned in the Constitution of India.
Unlike a Constitutional Body, a non-constitutional body does not derive its powers from the Indian Constitution.
Usually, a non-constitutional body derives powers from corresponding laws passed by the Indian Parliament.
There are also non-constitutional bodies that derive power based on Indian Government Orders (Executive Resolution).
Classification of Non-Constitutional Bodies
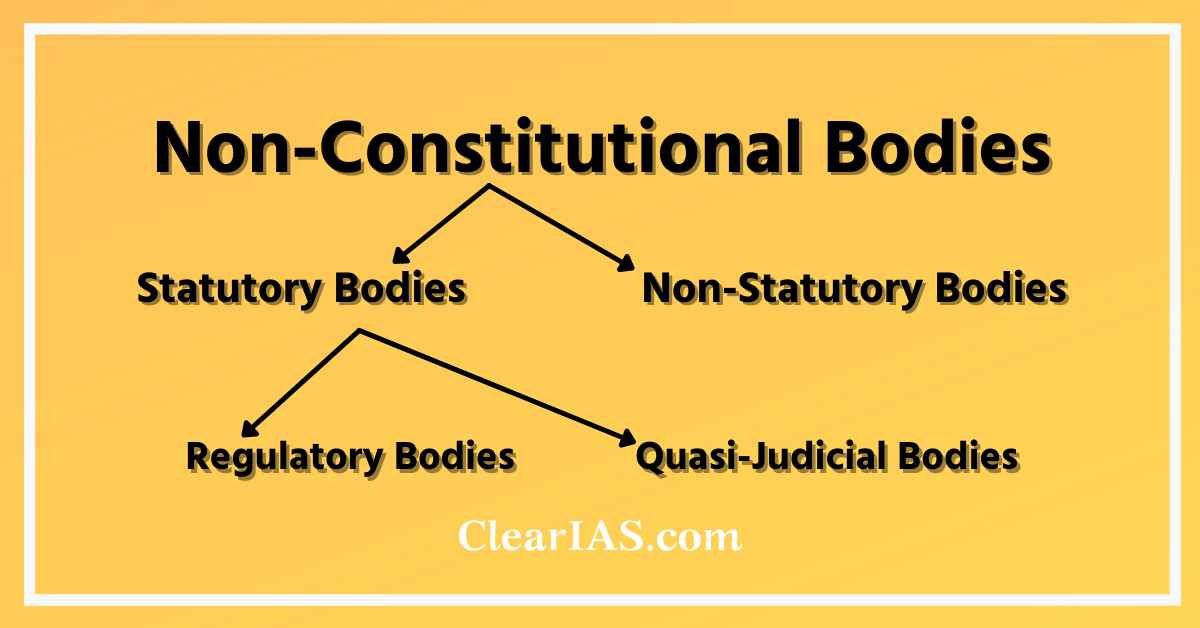
Based on how the body derives its power, non-constitutional bodies can be broadly classified into two – (1) Statutory Bodies (2) Non-Statutory Bodies.
- Statutory Bodies – They get the power from a statute (ie an Act enacted by the Legislature). Eg: National Investigation Agency (NIA), National Human Rights Commission (NHRC), Lokpal and Lokayukta, etc.
- Non-Statutory Bodies – They usually get the power from an Executive order. Eg: NITI Aayog, National Development Council (NDC) etc
Statutory Bodies can be further classified into two based on their roles and responsibilities. They are (1) Regulatory Bodies and (2) Quasi-Judicial Bodies.
- Regulatory Bodies – A regulatory body is a government agency that is accountable for exercising autonomous authority over some area of human activity in a regulatory or supervisory capacity. However, their regulatory interventions are outside executive observation. Eg: the Biodiversity Authority of India (BAI), Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA), etc.
- Quasi-Judicial Bodies – Quasi-Judicial bodies are non-judicial bodies like Commissions or Tribunals which can interpret the law. They are different from judicial bodies in that their field is limited compared to a court. Eg: National Green Tribunal, National Human Rights Commission, Central Information Commission.
Note: One statutory body can be both regulatory as well as quasi-judicial in nature. Eg: RBI, SEBI, etc.
Non-Constitutional Bodies in India (Video Class)
Note: Subscribe to ClearIAS YouTube Channel to learn from more free videos.
List of Extra Constitutional Bodies in India that are regulatory
- RBI – Reserve Bank of India
- SEBI – Securities and Exchange Board of India
- IRDAI – Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India
- PFRDA – Pension Fund Regulatory & Development Authority
- NABARD – National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development
- SIDBI – Small Industries Development Bank of India
- NHB – National Housing Bank
- TRAI – Telecom Regulatory Authority of India
- CBFC – Central Board of Film Certification
- FSDC – Financial Stability and Development Council
- FSSAI – Food Safety and Standards Authority of India
- BIS – Bureau of Indian Standards
- ASCI – Advertising Standards Council of India
- BCCI – Board of Control for Cricket in India
- AMFI – Association of Mutual Funds in India
- EEPC – Engineering Export Promotional Council of India
- EICI – Express Industry Council of India
- FIEO – Federation of Indian Export Organisation
- INSA – Indian National Shipowners’ Association
- ICC – Indian Chemical Council
- ISSDA – Indian Stainless Steel Development Association
- MAIT – Manufacturers’ Association for Information Technology
- NASSCOM – National Association of Software and Service Companies
- OPPI – Organisation Of Plastic Processors of India
- PEPC – Project Exports Promotion Council of India
- PNGRB – Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board
Also read: Lokpal and Lokayukta
List of Non-Constitutional Bodies in India which are quasi-judicial
- National Human Rights Commission
- National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
- Competition Commission of India
- Income Tax Appellate Tribunal
- National Company Law Tribunal
- Appellate Tribunal for Electricity
- Railway Claims Tribunal
- Intellectual Property Appellate Tribunal
- Banking Ombudsman
- National Green Tribunal
- Central Information Commission
- SEBI
- RBI
Note: ‘Quasi’ is Latin for “as if.” Quasi-judicial bodies have a partly judicial character.
They possess the right to hold hearings and conduct investigations into disputed claims and alleged infractions of rules and regulations. They similarly make decisions as courts.
UPSC CSE Questions from the topic
Q.Consider the following statements: (2019)
1. Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board (PNGRB) is the first regulatory body set up by the Government of India.
2. One of the tasks of PNGRB is to, ensure competitive gas markets.
3. Appeals against the decisions of PNGRB go before the Appellate Tribunals for Electricity.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 only
Q. In India, which of the following reviews the independent regulators in sectors like telecommunications, insurance, electricity, etc.? (2019)
- Ad Hoc Committees set up by the Parliament
- Parliamentary Department-Related Standing Committees
- Finance Commission
- Financial Sector Legislative Reforms Commission
- NITI Aayog
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 1, 3 and 4
(c) 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2 and 5
Answer: (a) 1 and 2





Is quasi judicial judgement challenge in supreme court?
Why not, sc is guardian of law
Yes
Information provided in precise and sorted manner.Definitely helpful study material for upcoming aspirants
Thank you
Thank you very much for such an insightful and comprehensive article.
Great thank