
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) has been in the news for some time. Read here to know the history of NATO.
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is in global headlines due to the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict. The NATO membership of Ukraine is the thorn in the whole issue; hence it is pertinent to know the history and formation of NATO.
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization was created in 1949 by the United States, Canada, and several Western European nations to provide collective security against the Soviet Union.
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) treaty
The North Atlantic Treaty also known as the Washington Treaty was the first peacetime military alliance between the United States and non-western countries.
After the Second World War, the European nations were struggling to rebuild their economies and security. The economic advancement required a huge amount of aid to help the war-torn landscapes. Help was also needed to establish industries and produce food, while the threat from Germany and the Soviet Union prevailed.
The Marshall Plan (1948): The US viewed the new Europe as economically strong, rearmed, and integrated which was important to prevent the communist expansion across the continent.
Hence, the Secretary of State George Marshall proposed a plan of huge economic aid to Europe known as the Marshall Plan or European Recovery Program, which facilitated European economic integration and promoted the idea of shared interests and cooperation between the United States and Europe.
However, the Soviet Union refused to participate in the Marshall Plan and did not even allow its satellite states in Eastern Europe to accept economic assistance. This led to more division between the East and the West.
Members of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
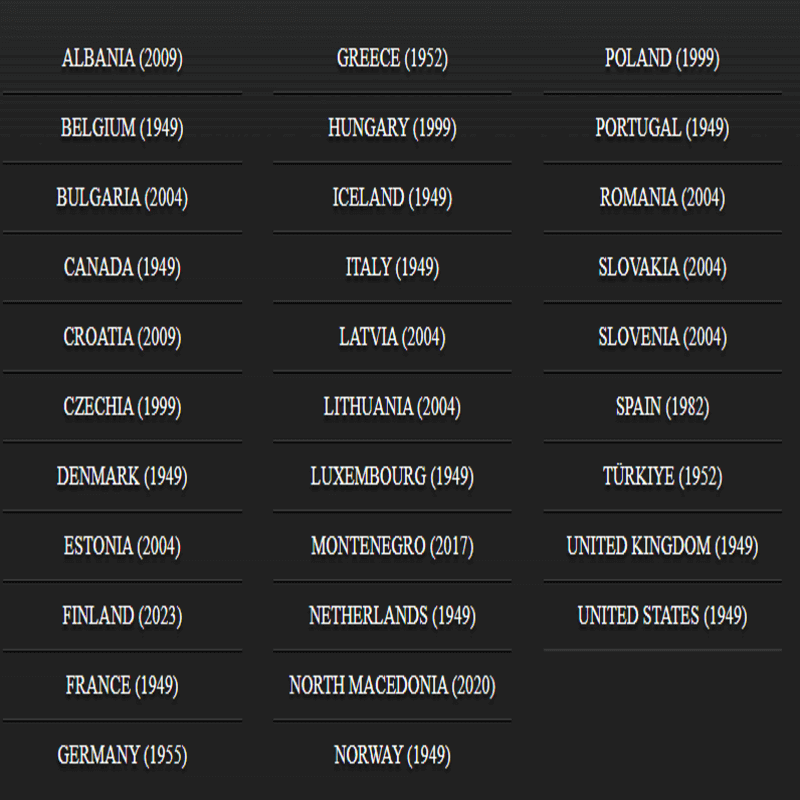
The original members were Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the UK, and the US.
Later the original signatories were joined by Greece and Turkey (1952), West Germany (1955; Germany from 1990); Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia, and Slovenia (2004); Albania and Croatia (2009); Montenegro (2017); and North Macedonia (2020).
France withdrew from the integrated military command of NATO in 1966 but remained a member of the organization; it resumed its position in NATO’s military command in 2009.
Articles 5 and 6 of the North Atlantic Treaty:
Article 5: An armed attack against one or more of them in Europe or North America shall be considered an attack against them all; and consequently they agree that, if such an armed attack occurs, each of them, in the exercise of the right of individual or collective self-defense recognized by Article 51 of the Charter of the United Nations, will assist the Party or Parties so attacked by taking forthwith, individually and in concert with the other Parties, such action as it deems necessary, including the use of armed force, to restore and maintain the security of the North Atlantic area.
Article 6 defines the geographic scope of the treaty as covering “an armed attack on the territory of any of the Parties in Europe or North America.” Other articles commit the allies to strengthening their democratic institutions, building their collective military capability, to consulting each other, and remaining open to inviting other European states to join.
Organization of North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
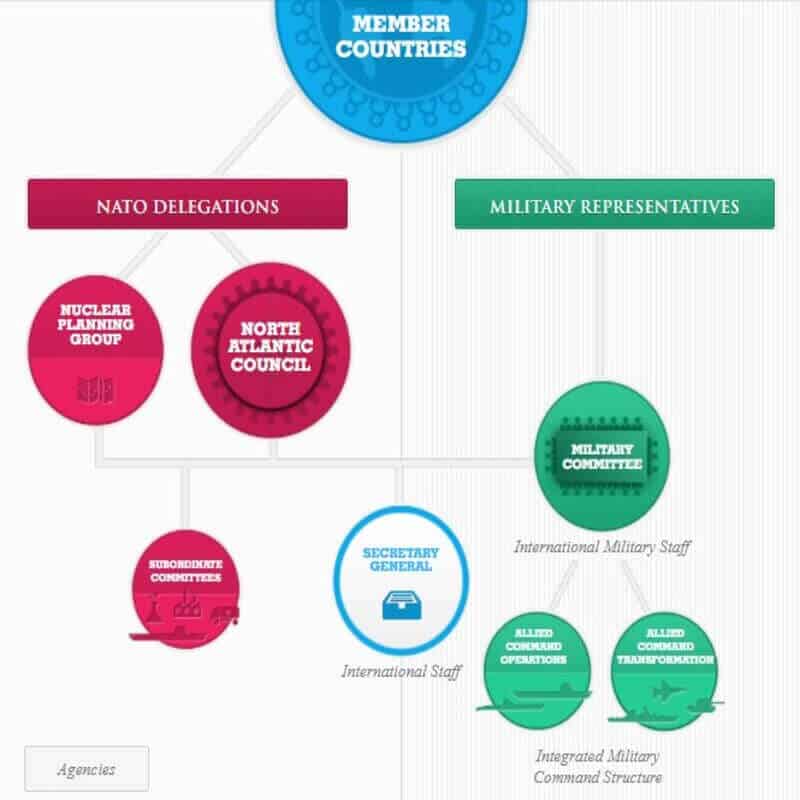
The North Atlantic Council was established soon after the treaty came into effect. It is composed of ministerial representatives of the member states, who meet at least twice a year. At other times the council, chaired by the NATO secretary-general, remains in permanent session at the ambassadorial level.
Supreme Allied Commander Europe (SACEUR) by the North Atlantic Council (NATO’s governing body) was formed after World War II in December 1950.
The position of SACEUR has always been held by an American, the secretary-generalship has always been held by a European.
The Military Committee, consisting of representatives of the military chiefs of staff of the member states, subsumes two strategic commands: Allied Command Operations (ACO) and Allied Command Transformation (ACT). ACO is headed by the SACEUR and located at Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe (SHAPE) in Casteau, Belgium.
The Warsaw Pact
The Paris Agreement admitted the membership of West Germany to NATO in 1950 prompting the soviet union to form the Warsaw Pact alliance in central and eastern Europe the same year.
Warsaw Pact, formally Warsaw Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation, and Mutual Assistance, (May 14, 1955–July 1, 1991) treaty establishing a mutual-defence organization (Warsaw Treaty Organization) composed originally of the Soviet Union and Albania, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Hungary, Poland, and Romania (Albania withdrew in 1968, and East Germany in 1990.)
The treaty (which was renewed on April 26, 1985) provided for a unified military command and the maintenance of Soviet military units on the territories of the other participating states.
After the democratic revolutions of 1989 in Eastern Europe, the Warsaw Pact became moribund and was formally declared “nonexistent” on July 1, 1991, at a final summit meeting of Warsaw Pact leaders in Prague, Czechoslovakia. Deployed Soviet troops were gradually withdrawn from the former satellites, now politically independent countries.
The decades-long confrontation between Eastern and Western Europe was formally rejected by members of the Warsaw Pact, all of which, except the Soviet successor state of Russia, subsequently joined NATO.
Russia-NATO Relations
Russia has constantly raised the issue of the eastward expansion of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). Over the years Russia-NATO relations have seen many ups and downs.
1994: Russia joined the partnership for peace program with NATO.
2002: the Russia-NATO council was established to handle security issues and other joint projects.
2014: The annexation of Crimea by Russia caused the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) to unanimously end all cooperation with Russia. But the NATO-Russia council was not suspended.
2021: Eight Russian diplomats were expelled from Brussels where the Russian mission to NATO was present. Russian President Vladimir Putin stated his displeasure with the North Atlantic Treaty Organization’s expansion into Ukraine which in the end led to the present Russia-Ukraine conflict.
Recent developments
- Finland became NATO’s 31st member on 4 April 2023, upon depositing its instrument of accession to the North Atlantic Treaty.
- Hungary’s parliament approved Sweden’s NATO accession on February 26, 2024, clearing the last hurdle before the historic step by the Nordic country whose neutrality lasted through two world wars and the simmering conflict of the Cold War.
- Sweden is leaving 200 years of neutrality and military non-alignment behind and joining NATO.






👍