
We have seen the causes and consequences of the First World War in the last post. The First World War itself sowed the seeds for the Second World War, primarily because of the humiliating Treaty of Versailles. We shall see the causes and consequences of the Second World War (WWII) in this post.
The Second World War fundamentally reshaped the global order, setting the stage for the Cold War and dramatically altering the political, social, and economic landscapes of the 20th century.
The Two Groups: Allies vs Axis Powers
Causes of Second World War(1939-1945)
(1) Humiliation by the Treaty of Versailles
The harsh terms imposed on Germany by the Treaty of Versailles, including significant territorial losses, reparations, and military restrictions, led to widespread resentment in Germany. This environment of humiliation and economic hardship paved the way for the rise of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party, who promised to restore Germany’s former glory.
- War indemnity.
- The provision for disarming Germany.
- Saar coal mine to France for 15 years.
- Polish corridor was given to Poland.
- City of Danzing was made free.
(2) Growth of Fascism and Nazism
The interwar period saw the rise of fascist and totalitarian regimes in countries like Italy, Germany, and Japan. Leaders such as Benito Mussolini, Adolf Hitler, and the militaristic government of Japan pursued aggressive expansionist policies, seeking to overturn the post-World War I international order and establish dominance.
- Mussolini (Italy) and Hitler (Germany) strongly glorified war and violence.
- While the West was fighting communism, Germany and Italy started massive militarization.
(3) Rise of Japan
The League of Nations, established to maintain peace, was ineffective in preventing aggression by fascist powers. Its inability to enforce collective security, particularly in response to Japanese aggression in Manchuria (1931), the Italian invasion of Ethiopia (1935), and German reoccupation of the Rhineland (1936), emboldened these powers.
- Imperialism.
- Rome-Berlin-Tokyo axis (1936).
(4) Neglect of minority interests
European powers, particularly Britain and France, pursued a policy of appeasement in the 1930s, allowing Hitler to annex Austria (Anschluss, 1938) and the Sudetenland (Munich Agreement, 1938) without significant opposition. This emboldened Hitler to continue his expansionist agenda, ultimately leading to the invasion of Poland.
- New countries like Poland, Czechoslovakia and Austria were formed after the First World War. While drawing boundaries the interests of minority groups in each of these countries were neglected.
(5) Military Alliance
- Allies – Britain, France, USA, USSR and China vs Axis Powers – Germany, Italy and Japan
- Leaders – Churchill (Britain), Roosevelt (USA), Stalin (USSR)
(6) Germany’s attack on Czechoslovakia
- Despite the Munich Pact between Germany and Britain (1938), Germany re-attacked and sized Czechoslovakia.
(7) Immediate Cause: Germany’s invasion of Poland (1st September 1939)
- Germany annexed the Polish Corridor and Danzig city. The sudden attack on Poland is known as Blitzkrieg (lightning war).
- Britain and France declared war on Germany.
Also read: Imperialism and its History
The course of the War

- World War II officially began on September 1, 1939.
- Germany conquered – Poland, Norway, Denmark, Belgium, Holland and France.
- Battle of Britain – Germany vs Britain (air battle; German Air Force =Luftwaffe).
- Battle of Stalingrad – Germany vs USSR. (Operation of Barbarossa (1941 = Attack on Yugoslavia and Greece; Russia countered the attack on Moscow with Scorched Earth Policy).
- Atlantic Charter (August 1941) – Between Churchill (UK) and Roosevelt (USA).
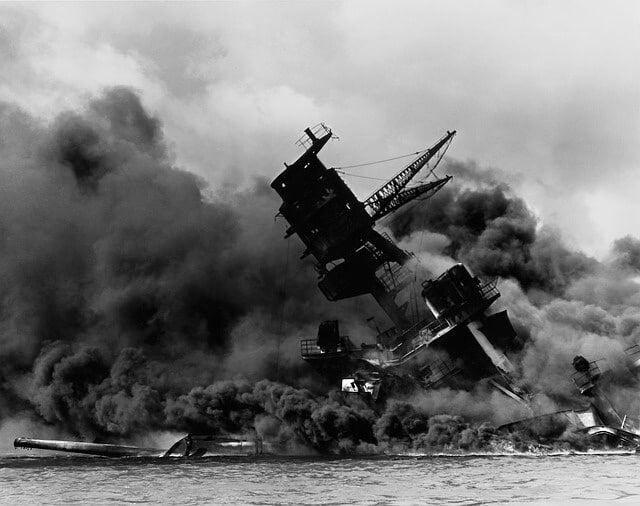
- Pearl Harbor Attack (7th December 1941) – Japan on USA.
- Italy vs UK in Africa (1942) – Ethiopia, Kenya, Sudan, British Somaliland, Eritrea.
- France was conquered by Germany in 1940, but British and American troops liberated France in 1944.
- Atom bomb – Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Consequences of Second World War
- Human and Economic Cost: World War II was the deadliest conflict in human history, resulting in an estimated 70-85 million deaths, including civilians and military personnel. The war caused widespread destruction, particularly in Europe and Asia, leading to massive economic and infrastructure devastation.
- Redrawing of National Borders: The war led to significant changes in national borders, especially in Europe. Germany was divided into four occupation zones controlled by the Allies (the U.S., the UK, France, and the Soviet Union), eventually leading to the creation of West Germany and East Germany.
- Rise of the United States and the Soviet Union as Superpowers: The United States and the Soviet Union emerged as the two dominant superpowers in the post-war world, leading to the Cold War. Their ideological conflict between capitalism and communism shaped global politics for the next several decades.
- Decolonization: The war weakened the colonial powers, particularly Britain and France, leading to a wave of decolonization in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. Countries like India, Indonesia, and numerous African nations gained independence in the years following the war.
- Creation of the United Nations: In response to the failure of the League of Nations and the devastation of World War II, the United Nations was established in 1945 to promote international cooperation and prevent future conflicts. The UN played a central role in shaping the post-war international order.
- Cold War and Division of Europe: The ideological and political rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union led to the division of Europe, with Eastern Europe falling under Soviet influence and Western Europe aligning with the United States. This division was symbolized by the Iron Curtain and culminated in the fall of the Berlin Wall (1961-1989).
- Holocaust and Genocide Awareness: The Holocaust, in which six million Jews were murdered by Nazi Germany, highlighted the horrors of genocide. This led to increased global awareness of human rights and the establishment of conventions against genocide and crimes against humanity.
- Nuclear Arms Race: The use of atomic bombs by the United States on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945 introduced nuclear weapons to the world, leading to an arms race during the Cold War. The threat of nuclear warfare became a central issue in international relations.






It’s good but in very short…
it’s a very nice one, but you should should have explain more for the benefit of those that don’t know history
it is very good but students need a much information other than these briefly
Yas
This mssage is not quite good for ICSE students!!!😝😝
true
This massage is good but no more information briefly
This is good for ordinary school students
Explain the anwers in a long term with more words
this is not massage it is message
That Is Great Bt Explain It Further
It’s very meaningful in short….better for projects . it helped me a lot in this.thanx 😇
Thank you so much for this
without history you don’t no who are you
It is knowledgeable but in short extent it
You have a concrete histosty I like it
Thnks
Eradane mahayudh parinamagalu
Nice one, but students need more Elaboration upon this second world war
Thnx a lot, it was really helpful for me bcz it has explained a lot of things in very short paragraphs………😇😇😇
Very helpful to project
thanks so much
Can I do it there mean ?
This is very best information I got from through internet thank you,,😊
Is good but it needs to be in a long term i means well elaborated for advanced level students right
it is good but can you do more longer
Thank you for information 😇😇😇
the more u now the more u know
true