Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a hot word these days. In this post, we cover artificial intelligence in detail – its meaning, scope, risks, ethics etc.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- To make it simple – Artificial Intelligence is intelligence exhibited by machines.
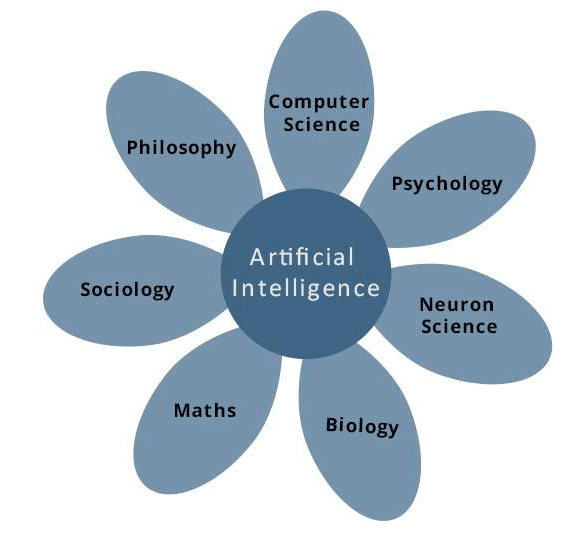
- It is a branch of computer science that deals with creating computers or machines as intelligent as human beings.
- The term was coined in 1956 by John McCarthy at the Dartmouth conference, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- It is a simulation of human intelligence processes such as learning (the acquisition of information and rules for using the information), reasoning (using the rules to reach approximate or definite conclusions), and self-correction by machines, especially computer systems.
- Nowadays it has become an umbrella term that encompasses everything from robotic process automation to actual robotics.
- Recently it has become widely popular and gained prominence due to its multifaceted application ranging from healthcare to military devices.
Is it possible for a computer to become completely Artificially Intelligent?

- Work is being done in this arena however except in some instances of computers playing games faster than the best human players no success has been achieved.
- For Example: In May 1997, an IBM super-computer called Deep Blue defeated world chess champion Gary Kasparov in a chess match.
- Another recent example of 2016 is, AlphaGo, a program driven by Google’s DeepMind AI, which has won Korean Lee Sedol, one of Go’s most dominant players.
What is the philosophy and ethics of Artificial Intelligence?
- The research and development of AI started with the intention of creating intelligence in machines that we find and regard as high in humans. Thus answering the big question which is can machines think and behave like humans do?
Three main philosophical questions related to Artificial Intelligence
- Are they dangerous to humanity? How can we ensure that machines behave ethically and that they are used ethically?
- Is artificial general intelligence probable? Can a machine decipher any problem that a human being can solve using intelligence? Or are there hard boundaries to what a machine can accomplish?
- Is it possible for machines to have a mind, consciousness, and mental state in the same sense that human beings do? Can a machine be sentient, and thus deserve certain rights? Can a machine intentionally cause harm?
Examples of Artificially Intelligent Technologies
- Robotic process automation: Automation is the process of making a system or process function automatically. Robots can be programmed to perform high-volume, repeatable tasks normally performed by humans and further, it is different from IT automation because of its agility and adaptability to the changing circumstances.
- Natural language processing (NLP) is the processing of human language and not computer language by a computer program. For Example, spam detection, which looks at the subject line and the text of an email and decides if it’s junk.
- Pattern recognition is a branch of machine learning that focuses on identifying patterns in data.
- Machine vision is the science of making computers visualize by capturing and analyzing visual information using a camera, analog-to-digital conversion, and digital signal processing. It is often compared to human eyesight, but machine vision isn’t bound by biology and can be programmed to see through walls. It is used in a range of applications from signature identification to medical image analysis.
- Machine learning: A field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed. Deep learning is a subset of machine learning and can be thought of as the automation of predictive analytics.
- Robotics is a field of engineering focused on the design and manufacturing of robots. Robots are often used to perform tasks that are difficult for humans to perform or perform consistently.
Applications of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Healthcare Sector: Machine learning is being used for faster, cheaper, and more accurate diagnosis thus improving patient outcomes and reducing costs. For Example, IBM Watson and chatbots are some of such tools.
- Business Sector: To take care of highly repetitive tasks Robotic process automation is applied which performs faster and effortlessly than humans. Further, Machine learning algorithms are being integrated into analytics and CRM platforms to provide better customer service. Chatbots are being used in websites to provide immediate service to customers. Automation of job positions has also become a talking point among academics and IT consultancies such as Gartner and Forrester.
- Education Sector: AI can make some of the educational processes automated such as grading, rewarding marks, etc. therefore giving educators more time. Further, it can assess students and adapt to their needs, helping them work at their own pace. AI may change where and how students learn, perhaps even replacing some teachers.
- Financial Sector: It can be applied to personal finance applications and could collect personal data and provide financial advice. Today software trades more than humans on Wall Street.
- Legal Sector: Automation can lead to faster resolution of already pending cases by reducing the time taken while analyzing cases thus better use of time and more efficient processes.
- Manufacturing sector: Robots have been used for manufacturing for a long time now, however, more advanced exponential technologies have emerged such as additive manufacturing (3D Printing) which with the help of AI can revolutionize the entire manufacturing supply chain ecosystem.
- Intelligent Robots − Robots can perform the tasks given by a human because of sensors to detect physical data from the real world such as light, heat, temperature, movement, sound, bump, and pressure. Moreover, they have efficient processors, multiple sensors, and huge memory, to exhibit intelligence. Further, they are capable of learning from their errors and therefore can adapt to the new environment.
- Gaming – AI has a crucial role in strategic games such as chess, poker, tic-tac-toe, etc., where the machine can think of a large number of possible positions based on heuristic knowledge.
- Speech Recognition – There are intelligent systems that are capable of hearing and grasping the language in terms of sentences and their meanings while humans talk to it. It can handle different accents, slang words, noise in the background, changes in human noise due to cold, etc.
- Cyber Security: In the 20th conference on e-governance in India it was discussed that AI can provide more teeth to cyber security and must be explored.
Read: AI in Elections
What are the downsides and risks of Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- The decrease in demand for human labour is due to machines and intelligent robots taking over the jobs in the manufacturing and services sectors. For Example: In China, some customs officers are now robots, In Japan robots such as housemaids is an emerging trend.
- Existential risks: Stephen Hawkins once said “The development of full artificial intelligence could spell the end of the human race. Once humans develop artificial intelligence, it will take off on its own and redesign itself at an ever-increasing rate. Humans, who are limited by slow biological evolution, couldn’t compete and would be superseded”.
- AI technologies falling into terrorist hands may unleash modern terror networks including machines and therefore vulnerability of humans may magnify.
- It may lead to moral degradation in society due to decreased human-to-human interactions.
In such an era of rapid and disruptive changes, many questions arise:
- Will these technological changes be accompanied by equally profound economic, social, and cultural changes?
- Will technology destroy jobs at a faster rate than the rate of creation of jobs?
- Will future governments be forced to fork out Universal Basic Income?
- How could education be redefined with artificial intelligence, big data, augmented reality, and personalized learning pathways?
- Are conventional manufacturing plants under threat with the advent of additive manufacturing?
- What will be the impact on the skills required?
- After all these changes, do people-to-people communication and socio-economic activities remain the same?
Possible areas for AI applications in Indian conditions
- It can complement Digital India Mission by helping in the big data analysis which is not possible without using AI.
- Targeted delivery of services, schemes, and subsidies can be further fine-tuned.
- Smart border surveillance and monitoring to enhance security infrastructure.
- Weather forecasting models may become proactive and therefore preplanning for any future mishaps such as floods, and droughts and therefore addressing the farming crisis, farmer’s suicide, crop losses, etc.
- By analyzing big data of road safety data and NCRB (National Crime Record Bureau) data for crimes, new policies can be formulated.
- Disaster management can be faster and more accessible with the help of robots and intelligent machines.
- In the counterinsurgency and patrolling operations, we often hear the loss of CRPF jawans which can be minimized by using the robotic army and lesser human personnel.
- AI can be used to automate government processes, therefore, minimizing human interactions and maximizing transparency and accountability.
- It can be applied to study ancient literature on medicines and therefore help in modernizing health care with the juxtaposition of modern machines and ancient techniques.
- In the remotest areas where the last leg of governance is almost broken, AI can do the job. For Example: in the tribal areas and the hilly areas of the northeast.
Which is the nodal organization of the government for the research work on Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- Centre for Artificial Intelligence and Robotics (CAIR), is the primary laboratory of DRDO for research and development in different areas of defense, Information and Communication Technology (ICT) and is located in Bangalore. It is involved in the Research & Development of high-quality Secure Communication, Command, and Control, and Intelligent Systems.
- CAIR came into existence in 1986.
- Projects: NETRA- software to intercept online communication, SECOS- Secure operating system.
What are the challenges India’s Artificial Intelligence Development is facing?
- AI-based applications are mostly driven largely by the private sector and have been focused largely on consumer goods.
- Public-private funding model which is a success in the United States, China, South Korea, and elsewhere may be considered good for India. Presently it is not present in India.
- Our educational system is not updated to modern technologies and is outdated in today’s economic environment as the nature of jobs shifts rapidly and skills become valuable and obsolete in a matter of years.
- The debate of poverty vs. technology and where to spend the most is more likely to persist until the political class takes a higher interest in real issues than trivial ones.
Latest Developments
March 2024: The UN General Assembly adopted a landmark resolution to promote “safe, secure and trustworthy” artificial intelligence (AI) systems that will also benefit sustainable development for all.
- The Assembly resolved to bridge the artificial intelligence (AI) and other digital divides between and within countries and promote safe, secure and trustworthy AI systems to accelerate progress towards the full realization of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
- The United States is spearheading the first United Nations resolution on artificial intelligence, aimed at ensuring that the new technology is “safe, secure and trustworthy” and that all countries, especially those in the developing world, have equal access.
- The resolution aims at closing the digital divide between countries and making sure they are all at the table in discussions on AI — and that they have the technology and capabilities to take advantage of its benefits, including detecting diseases, predicting floods and training the next generation of workers.
Conclusion
Despite these threats and challenges, it would be stupid to argue that Artificial Intelligence (AI) is not the future and it’s only a matter of time before machines replace most jobs. It does not mean the end of the road for humanity and we have a history of technological revolutions causing social and political changes in society.
There were bound to be some fears and challenges in the early years, but so was the case with the French Revolution, steam engines, industrial revolutions, and most recently the computers.
Nevertheless, there will be more opportunities in the fields not yet known and there will be more jobs to cater to human needs. In the case of India, Innefu is one such Artificial Intelligence (AI) based company that is still in its nascent phase but soon may challenge global companies and therefore can create an AI ecosystem in India.
Also read:
Article by: Nishant Raj. The author is an IIT Kharagpur Alumnus.






Thank you Team for this article.
nice article
Nice one..
Nice Article. Especially liked the Possible areas for AI application in Indian conditions. In particular about how weather forecasting models may become proactive and therefore preplanning for any future mishaps such as floods, droughts and therefore addressing the farming crisis, farmer’s suicide, crop losses etc.
your Article is also very important for the UPSC (AC) exam 2.
thanks to clearIAS team