Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) represent a critical technology in the modern energy landscape, pivotal for enhancing the efficiency and reliability of the power grid and facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources. Read here to learn more about BESS.
India has set a target to achieve 50% cumulative installed capacity from non-fossil fuel-based energy resources by 2030 and has pledged to reduce the emission intensity of its GDP by 45% by 2030, based on 2005 levels.
The incorporation of a significant amount of variable and intermittent Renewable Energy into the energy mix presents a challenge for maintaining grid stability and uninterrupted power supply.
Energy Storage Systems (ESS) can be used for storing available energy from Renewable Energy and further can be used during peak hours of the day.
As the world increasingly shifts towards sustainable energy, BESS plays a vital role in addressing the variability and intermittency challenges associated with renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
What is a Battery Energy Storage System (BESS)?
A Battery Energy Storage System is a technology that allows for the storage of electrical energy within a battery system.
- It can store energy from the grid or from renewable energy sources, to be used at a later time when demand is high or generation is low.
- BESS can include various types of battery technologies, with lithium-ion batteries currently being the most prevalent due to their high energy density, efficiency, and decreasing cost.
The challenge with Renewable Energy (RE) sources arises due to their varying nature with time, climate, season, or geographic location.
- Energy Storage Systems (ESS) can be used for storing available energy from Renewable Energy and further can be used during peak hours of the day.
- The various benefits of Energy Storage are help in bringing down the variability of generation in RE sources, improving grid stability, enabling energy/ peak shifting, providing ancillary support services, enabling larger renewable energy integration, bringing down peak deficit and peak tariffs, reducing of carbon emissions, deferral of transmission and distribution capex, energy arbitrage, etc.
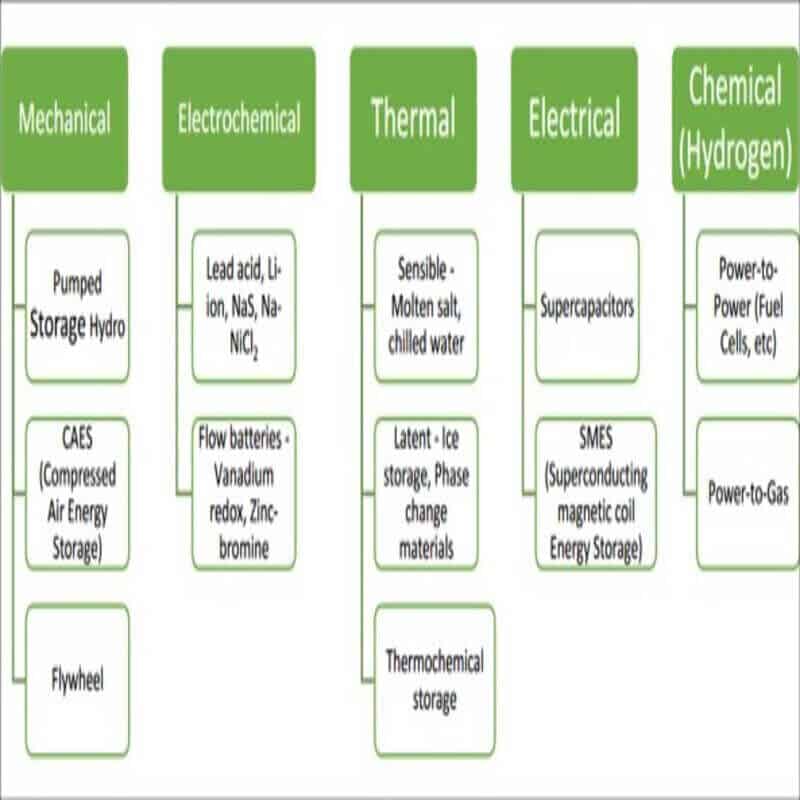
There are several energy storage technologies available, broadly – mechanical, thermal, electrochemical, electrical, and chemical storage systems, as shown above.
Components of BESS
A typical BESS includes:
- Battery cells: The basic units of the system where energy is stored chemically.
- Battery Management System (BMS): A system that manages the charging and discharging of batteries, ensuring the safety and efficiency of the storage system.
- Power Conversion System (PCS): Converts electrical energy from AC to DC and vice versa, facilitating the integration of the storage system with the grid.
- Control System: Manages the operation of the BESS, optimizing performance and interaction with the power grid.
Applications
- Energy Arbitrage: Buying energy when prices are low, storing it, and then selling it when prices are high.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Storing excess energy generated from renewable sources for use when generation is low or demand is high.
- Grid Stability and Reliability: Providing ancillary services such as frequency regulation, voltage control, and spinning reserves to support grid operation.
- Peak Shaving: Reducing peak demand charges for industrial and commercial energy users by supplying stored energy during peak demand periods.
- Emergency Backup: Offering power supply continuity during outages or disasters.
Advantages of BESS
- Flexibility: Can be deployed at various points in the energy system, from residential applications to utility-scale projects.
- Rapid Response: Capable of responding to changes in demand or supply within milliseconds, providing a critical resource for balancing grid operations.
- Emissions Reduction: Facilitates the increased use of renewable energy, contributing to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
- Energy Independence: Enhances energy security by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and imported energy.
Challenges
- Cost: While the cost of battery storage has been declining, the initial investment remains significant, especially for large-scale applications.
- Battery Lifespan and Degradation: The efficiency and capacity of batteries degrade over time, impacting the performance and economics of BESS.
- Recycling and Sustainability: Developing efficient recycling processes for battery materials is crucial to address environmental concerns.
Ongoing research into alternative battery technologies, such as solid-state batteries, aims to improve performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
Why in the news?
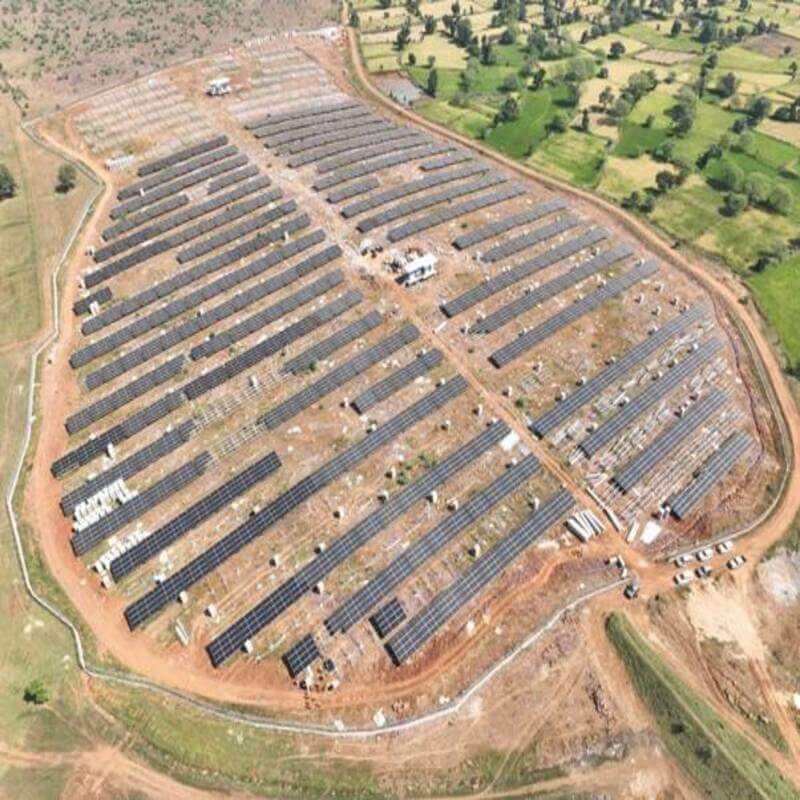

The Solar Energy Corporation of India Limited (SECI), under the aegis of the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, has successfully commissioned India’s largest Battery Energy Storage System (BESS), which stores energy using solar energy.
- The 40 megawatts (MW) / 120MWh BESS with a solar photovoltaic (PV) plant which has an installed capacity of 152.325-megawatt hour (MWh)and dispatchable capacity of 100MW AC (155.02 MW peak DC) is located in Rajnandgaon, Chhattisgarh.
- The energy would be purchased by the state of Chhattisgarh, thus contributing to meeting the peak energy demand of the state using green electrons and also towards its renewable purchase obligations.
The project using solar panels and battery storage represents a monumental leap forward in the generation and use of renewable energy.
- The project utilizes battery storage for storing solar energy when the sun is shining and using it later during hours of peak demand in the evening, for meeting the electricity demand in the state.
- The project has deployed bifacial modules, which reflect the light from the ground, thus generating more electricity than mono-facial modules, hence setting a new standard for large-scale renewable energy projects.
This project is estimated to save tonnes of carbon dioxide emissions annually. SECI’s long-term power purchase agreement with the state electricity distribution company (CSPDCL) underscores the economic viability of the project and support for such renewable energy endeavors.
The project has been constructed with funding from the World Bank and Clean Technology Fund under the Innovation in Solar Power & Hybrid Technologies Project as well as leveraged financing from domestic lending agencies.
This further highlights the collaborative efforts to drive sustainable financial arrangements, making the project commercially attractive and viable.
Conclusion
Battery Energy Storage Systems are at the forefront of the energy transition, providing a key solution to the challenges posed by the integration of renewable energy sources into the power grid.
As technology advances and costs continue to decrease, BESS is set to play an increasingly important role in achieving a sustainable, reliable, and efficient energy future.
Related articles:
-Article by Swathi Satish






Leave a Reply