
Cellulose from plants accumulates in significant amounts on Earth’s surface each year. It undergoes various natural chemical processes through the carbon cycle in yielding carbon dioxide and water. Read here to understand the significance of cellulose.
The majority of organic compounds on earth are thought to be composed of cellulose.
(C6H10O5) n is the chemical formula for the polysaccharide in a chain.
Green plants, numerous types of algae, and oomycetes all have basic cell walls that contain cellulose as an essential structural element. It is secreted by some bacterial species in biofilms.
What is cellulose?
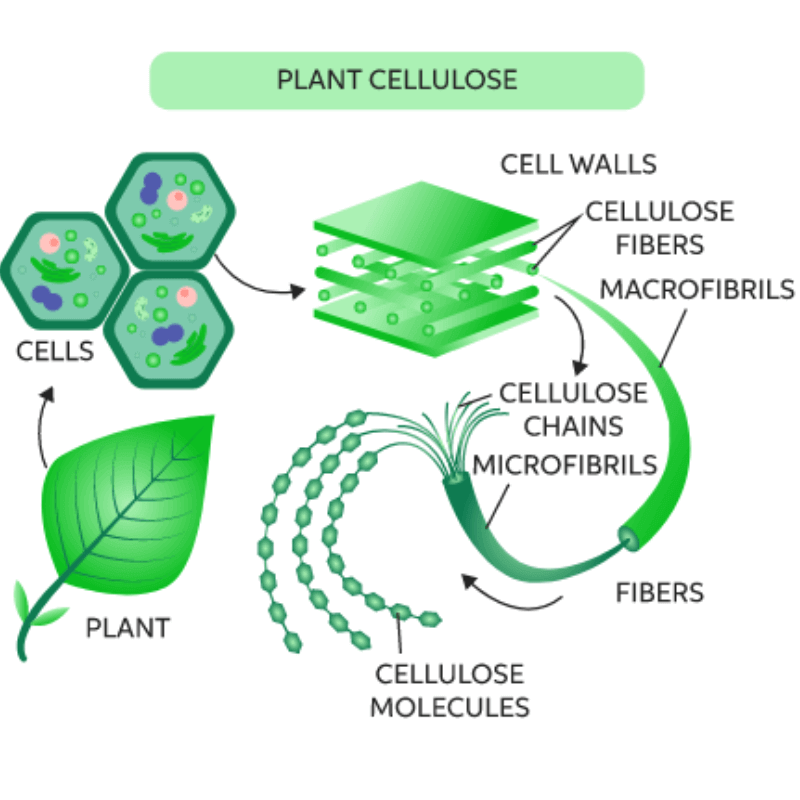
Glucose units make up the linear polymer (polysaccharide) known as cellulose. Plants typically produce it through synthesis.
The primary characteristics of this polysaccharide are biodegradability and hydrolysis resistance. Most plants contain this biopolymer, primarily in the leaves and stalks.
- It is the most abundant carbon input in soil. To access the glucose monomer, it must be cleaved by extracellular enzymes.
- These pieces are then transported into the cell for energy generation (catabolism) or production of biomass (anabolism).
- It is a biodegradable, chiral, tasteless compound without any odor.
- Cellulose is used by a diverse group of soil organisms including fungi such as Penicillium and Aspergillus and bacteria such as Streptomyces and Pseudomonas.
- Fungi and bacteria are important participants in the extracellular cleavage of the polysaccharide.
- Cotton fiber and wood are the principal industrial sources of polymer for industrial applications.
Hemicellulose is the next most common carbohydrate in plants. It is a branched polymer with varied sugar monomers (glucose, mannose, and galactose) and bonds.
- The decomposition of hemicellulose is similar to that of cellulose in that the initial cleavage step takes place outside of the cell, and the sugars produced are then transported into the cell for catabolism or anabolism.
(Catabolism involves breaking down complex molecules and releasing energy for the body to use. The anabolic process is the complete opposite of catabolism as it involves creating bigger, complex molecules from smaller, simpler molecules.)
- Even though hemicellulose decomposition is much quicker than cellulose decomposition, cells will utilize simple sugars as substrates before hemicellulose.
Photosynthesis and cellulose
When plants perform photosynthesis, carbon is primarily converted to cellulose, the form of carbohydrate that is one of the main building blocks for growing plants.
- In plants, cellulose is synthesized at the plasma membrane by Rosette Terminal Complexes (RTCs). The RTCs contain the cellulose synthase enzymes that synthesize the individual cellulose chains.
- The polysaccharide is synthesized by cellulose synthase complexes that are assembled in the Golgi apparatus and then delivered to the plasma membrane, where they actively synthesize cellulose.
- Cellulolysis is essentially the hydrolysis of cellulose. Cellulase is the enzyme that catalyzes the process of the breakdown of the polysaccharide into monosaccharides like β-glucose.
Digestion of cellulose
By Animals
Cattle are made to digest cellulose. They can consume grasses and other plants that are high in cellulose and, through enteric fermentation, digest the carbon that is stored in the polysaccharide.
Cattle can use that carbon, upcycling the cellulose, for growth, milk production, and other metabolic processes.
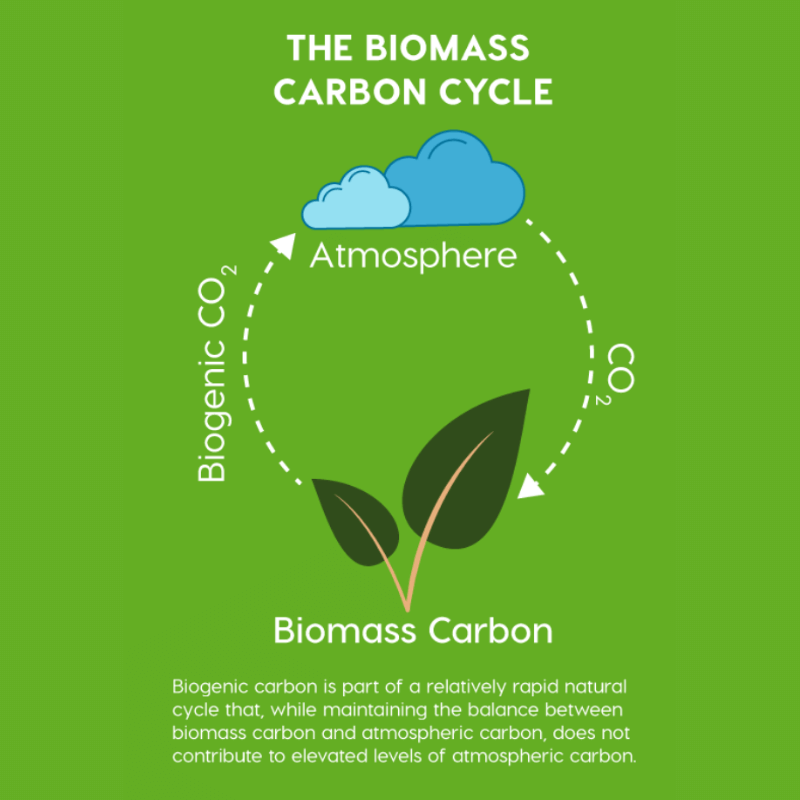
- As a by-product of consuming cellulose, cattle belch out methane, thereby returning that carbon sequestered by plants back into the atmosphere.
- After about ten years, that methane is broken down and converted back to CO2.
- Once converted to CO2, plants can again perform photosynthesis and fix that carbon back into cellulose.
- From here, cattle can eat the plants and the cycle begins once again.
In essence, the methane belched from cattle is not adding new carbon to the atmosphere. Rather it is part of the natural cycling of carbon through the biogenic carbon cycle.
By Humans
Cellulose is an indigestible plant fiber that is thought to be difficult for humans to use as energy.
Because of the lack of the right enzymes to dissolve the beta-acetal connections, cellulose cannot be broken down in the human body.
- The digestive system of the human body is unable to dissociate the cellulose’s monosaccharide linkages.
- Despite being indigestible, this polysaccharide aids in the smooth operation of the intestinal tract.
- But because it is a good source of fiber, it has a crucial function in the human body.
- The digestive enzymes produced by the human mouth, liver, and stomach can break down all types of sugar except cellulose.
- Some foods, such as fermented foods, cereals, and vegetables, are indigestible or difficult to digest.
Fruits and vegetables contain cellulose in small amounts which are easily digestible. Fibers contain cellulose which acts as roughage, adding bulk to consumed food and helping in the smooth passage of the food efficiently and at a much faster pace. A high-fiber diet reduces the risk of colon cancer as fiber in the diet helps reduce the time the feces stay in the colon wall.
Uses of cellulose in industry
This natural polymer has versatile uses in many industries such as veterinary foods, wood and paper, fibers and clothes, and cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries as excipients.
The polymer has very semi-synthetic derivatives which are extensively used in pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries.
Paper and paperboard are the two main products made from polymer. Smaller amounts are transformed into a wide range of derivative goods, including rayon and cellophane.
As a renewable fuel source, cellulosic ethanol and other biofuels made from cellulose from energy crops are currently being developed.
Previous year questions
- Each year a large amount of plant material, cellulose is deposited on the surface of Planet Earth. What are the natural processes this cellulose undergoes before yielding carbon dioxide, water, and other end products? (Answer in 150 words) 10 marks (GS Paper 3, 2022)
- Which of the following statements are correct regarding the general difference between plant and animal cells? (Prelims 2020)
1. Plant cells have cellulose cell walls whilst animal cells do not.
2. Plant cells do not have plasma membranes, unlike animal cells which do.
3. Mature plant cell has one large vacuole whilst animal cell has many small vacuoles.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
-Article written by Swathi Satish





Leave a Reply