 In the global search for clean and renewable energy sources, green hydrogen has emerged as a promising solution to address the pressing challenges of climate change and energy security.
In the global search for clean and renewable energy sources, green hydrogen has emerged as a promising solution to address the pressing challenges of climate change and energy security.
The time is right to tap into hydrogen’s potential to play a key role in tackling critical energy challenges.
The recent successes of renewable energy technologies and electric vehicles have shown that policy and technology innovation have the power to build global clean energy industries.
As the world increasingly recognizes the urgency to transition away from fossil fuels, India has taken bold steps to position itself as a global leader in the production, utilization, and export of green hydrogen.
Green Hydrogen
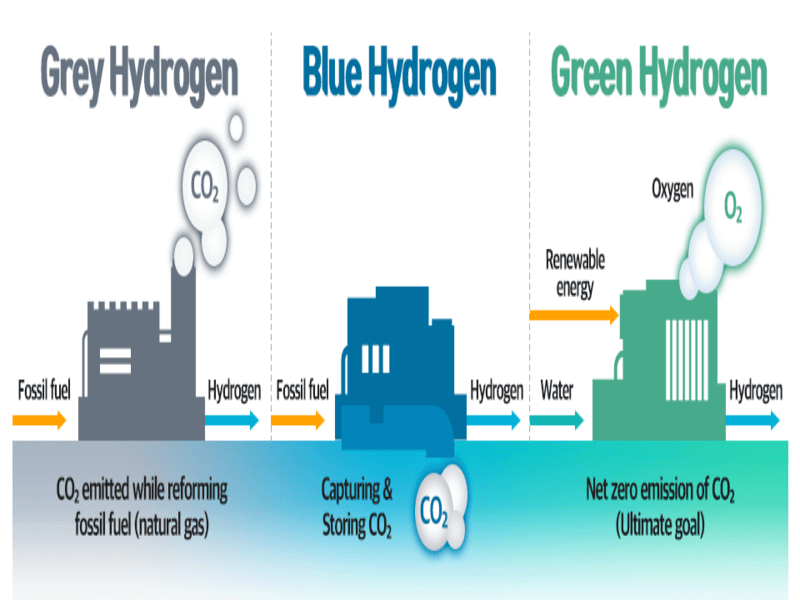
Green hydrogen is a clean, emission-free energy source produced through the electrolysis of water, using renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and hydropower.
- Unlike traditional, carbon-intensive “grey” hydrogen, green hydrogen is a virtually zero-emission fuel, making it an important component in the fight against climate change.
- The production of green hydrogen involves splitting water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen using an electrolyzer powered by renewable electricity.
- This process not only generates a clean fuel but also produces oxygen as a byproduct, further enhancing the environmental benefits of this technology.
- The global hydrogen market is set to reach $24-36 billion by 2030.
- As per a report by Alvarez & Marsal, India is planning to tap into the green hydrogen market, potentially leading to $3–5 billion in exports and $7–15 billion in import substitution within the next decade.
Applications of Green Hydrogen
It has the potential to revolutionize several critical sectors, offering a clean and sustainable alternative to traditional energy sources.
Transportation Sector
- It can be a game-changer in the transportation industry. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCEVs) utilize green hydrogen to generate electricity, which powers the vehicle’s electric motor.
- Unlike conventional gasoline or diesel-powered vehicles, FCEVs emit only water, making them a zero-emission mode of transportation.
- It can be especially beneficial for heavy-duty vehicles, such as buses, trucks, and even trains, where the weight and range limitations of battery-electric vehicles may pose challenges.
Industrial Sector
- By transitioning to this cleaner energy, industries can reduce their carbon footprint and become more environmentally sustainable.
- It can also be used as a feedstock for the production of various chemicals and materials, further expanding its industrial applications.
Residential and Commercial Sectors
- It can be used for heating and cooking in residential and commercial buildings.
- By blending green hydrogen with natural gas or using it in dedicated hydrogen-powered appliances, buildings can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels.
Agriculture Sector
- It can be used to produce green ammonia, a crucial component in the manufacturing of fertilizers.
- This process can significantly reduce the carbon emissions associated with traditional fertilizer production, making agriculture more environmentally friendly.
- Additionally, it can power farm machinery, reducing the sector’s dependence on fossil fuels.
Water Management
- It can be leveraged in water desalination and purification processes.
- Powering desalination plants with renewable energy can help address the pressing global issue of water scarcity, especially in water-stressed regions.
India’s Initiatives
Note: Subscribe to the ClearIAS YouTube Channel to learn more.
India has taken several initiatives to leap into Green Hydrogen production, such initiatives are:
National Green Hydrogen Mission
Recognizing the immense potential, the Government of India has launched the National Green Hydrogen Mission.
- The mission aims to position India as a global hub for the production, utilization, and export of green hydrogen and its derivatives.
The expected outcomes of this mission by 2030 are as follows:
- With a budgetary outlay of ₹19,744 crore (approximately $2.5 billion), India’s production capacity is expected to reach 5 million metric tons (MMT) per annum.
- This is anticipated to contribute to a reduction in India’s dependence on the import of fossil fuels.
- The achievement of the mission’s targets is expected to result in a cumulative reduction of ₹1 lakh crore ($12.5 billion) worth of fossil fuel imports by 2030.
- The mission is likely to leverage over ₹8 lakh crore ($100 billion) in total investments and create more than 6 lakh (600,000) new jobs.
Green Hydrogen Consumption Obligations
- To drive the adoption of green hydrogen, the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has proposed the introduction of green hydrogen consumption obligations for specific industries, such as fertilizers and petroleum refineries.
- These obligations will require these sectors to blend a certain percentage of green hydrogen into their overall hydrogen consumption, similar to the renewable purchase obligations (RPOs) for electricity distribution companies.
Green Hydrogen Hubs
- The MNRE has identified regions across India that have the potential to support large-scale production and/or utilization of green hydrogen.
- These regions will be developed as “green hydrogen hubs,” providing the necessary infrastructure, resources, and ecosystem to facilitate the growth of the industry.
Pilot Projects for Green Hydrogen in Transport
- The MNRE has announced a scheme to implement pilot projects for the use of green hydrogen in the transportation sector.
- The objectives of this scheme include validating the technical feasibility and economic viability of it as a transportation fuel, as well as demonstrating the safe operation of hydrogen-powered vehicles and refuelling stations.
Read: Green Energy Partnerships of India
Advantages
It has several advantages, a few prominent among them are:
Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
- The primary advantage is its potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- By replacing fossil fuels in various sectors, such as transportation, industry, and power generation, the carbon footprint of these industries can be drastically reduced, contributing to the global effort to mitigate climate change.
Creation of New Industries and Jobs
- The development of the clean energy ecosystem can potentially create new industries and job opportunities.
- From the manufacturing of electrolyzers and fuel cells to the construction of production and distribution infrastructure, the industry has the potential to become a significant driver of economic growth and employment.
Decarbonization of Hard-to-Abate Sectors
- It presents a viable solution for decarbonizing sectors that have traditionally been challenging to decarbonize, such as heavy industry, aviation, and maritime transportation.
- In these sectors, where the direct electrification of operations may not be feasible, it can serve as a clean alternative fuel, enabling a path to a low-carbon future.
Technological Advancements
- The pursuit of this cleaner fuel can catalyze technological advancements in various fields, including materials science, energy storage, and process engineering.
- As the industry matures, innovations in areas like more efficient electrolyzers, advanced hydrogen storage solutions, and optimized distribution networks can further enhance the viability and scalability of the fuel.
Challenges in Implementation
There are several challenges in the implementation, a few prominent among them are:
Cost of Production and Utilization
- One of the primary challenges facing the widespread adoption of new energy systems is the high cost of production compared to traditional, carbon-intensive hydrogen.
- The capital-intensive nature of the electrolysis process and the need for specialized infrastructure contribute to the elevated costs.
Infrastructure Development
- The large-scale deployment of it necessitates the development of a robust infrastructure for production, storage, transportation, and distribution.
- This includes the construction of electrolysis plants, hydrogen storage facilities, and dedicated distribution networks.
Energy Storage and Grid Integration
- The intermittent nature of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, can pose challenges in maintaining a consistent supply of the energy source.
Safety and Regulatory Frameworks
- Hydrogen is a highly flammable gas, and its safe handling and storage require specialized protocols and regulations.
The Way Forward
To make it more affordable, the focus should be on developing more efficient and cost-effective electrolysis technologies, leveraging economies of scale, and implementing policy incentives such as tax credits and subsidies.
Substantial investments are needed to build a comprehensive infrastructure for its production, storage, transportation, and distribution.
Governments, private companies, and public-private partnerships should collaborate to develop the necessary infrastructure, including hydrogen production plants, storage facilities, and dedicated distribution networks.
Integrating production with renewable energy sources and developing advanced energy storage solutions, such as hydrogen storage technologies, will be essential to ensure a reliable and continuous supply of green hydrogen.
As hydrogen is a highly flammable gas, developing comprehensive safety standards, training programs for personnel and robust regulatory frameworks will be important to build trust in the green hydrogen ecosystem.
Conclusion
Green hydrogen holds immense promise in the global search for clean and sustainable energy solutions.
India’s proactive initiatives, such as the National Green Hydrogen Mission and the development of green hydrogen hubs, demonstrate the country’s commitment to positioning itself as a global leader in this emerging field.
However, to realize the full potential of green hydrogen, India must address the challenges of high production costs, infrastructure development, energy storage, safety regulations, and stakeholder coordination.
By overcoming these obstacles and capitalizing on the numerous advantages of green hydrogen, India can unlock a future where clean energy fuels economic growth, enhances energy security and contributes significantly to the global fight against climate change.
Article Written By: Priti Raj






Leave a Reply