
The World Energy Outlook is an annual report published by the International Energy Agency (IEA), an autonomous agency within the framework of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Read here to learn more about the report.
The World Energy Outlook 2023 was released by the International Energy Agency (IEA) recently.
It provides in-depth analysis and strategic insights into every aspect of the global energy system. Against a backdrop of geopolitical tensions and fragile energy markets, this year’s report explores how structural shifts in economies and energy use are shifting the way that the world meets rising demand for energy.
World Energy Outlook
Published each year since 1998, its objective data and dispassionate analysis provide critical insights into global energy supply and demand in different scenarios and the implications for energy security, climate change goals, and economic development.
The report provides a comprehensive and in-depth analysis of global energy markets, including insights into current trends, future projections, and potential scenarios for the world’s energy systems.
- Energy Market Analysis: The report assesses the current state of the global energy market, including the production, consumption, and trade of various energy sources such as oil, natural gas, coal, renewables, and nuclear energy.
- Energy Projections: The World Energy Outlook presents projections and scenarios for future energy demand, production, and consumption. It considers various factors such as population growth, economic development, policy changes, and technological advancements.
- Energy Transition: The report focuses on the ongoing transition to a more sustainable and clean energy system. It examines the role of renewable energy sources, energy efficiency, and the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions in the global energy mix.
- Energy Access and Affordability: The report addresses issues related to energy access for underserved populations and the affordability of energy, particularly in developing countries. It explores ways to improve access to modern and sustainable energy sources.
- Environmental Impact: The environmental impact of energy production and consumption is a significant aspect of the report. It assesses the consequences of different energy scenarios on air quality, climate change, and other environmental factors.
- Energy Security: The World Energy Outlook examines the security of energy supplies and the resilience of energy systems in the face of geopolitical and natural disruptions.
- Policy and Regulation: The report provides insights into energy policies and regulations worldwide, including their impact on energy markets and the environment. It offers recommendations for policymakers to enhance energy security and sustainability.
- Technology Innovation: Technological advancements and innovations in the energy sector are a key focus. The report assesses the role of new technologies in transforming the energy landscape.
- Scenarios and Pathways: The World Energy Outlook typically presents different scenarios that explore potential future energy pathways, including a “New Policies Scenario” based on current policy trends, and a “Sustainable Development Scenario” that outlines a more environmentally friendly and sustainable future.
- Investment and Financing: The report examines the investment needs and financing mechanisms required to meet future energy demand and environmental goals.
- Regional Analyses: It provides detailed regional and country-level analyses, offering insights into regional variations in energy trends and challenges.
World Energy Outlook 2023
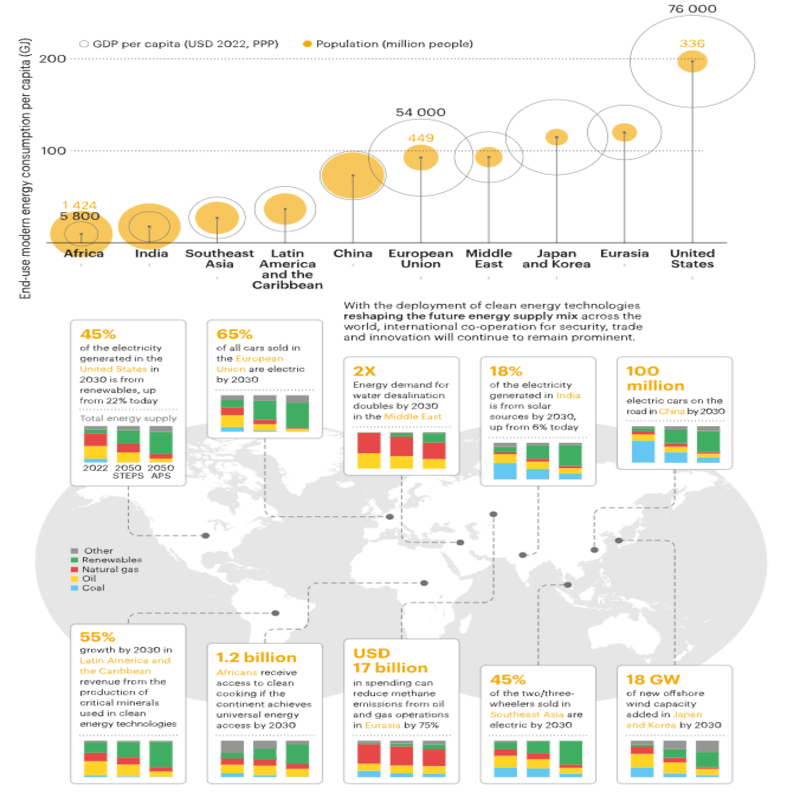
This Outlook assesses the evolving nature of energy security fifty years after the foundation of the IEA.
- It also examines what needs to happen at the COP28 climate conference in Dubai to keep the door open for the 1.5 °C goal.
This Outlook explores three scenarios that provide a framework for exploring the implications of various policy choices, investment, and technology trends.
- The Stated Policies Scenario is based on current policy settings and also considers the implications of industrial policies that support clean energy supply chains as well as measures related to energy and climate.
- The Announced Pledges Scenario gives governments the benefit of the doubt and explores what the full and timely implementation of national energy and climate goals, including net zero emissions targets, would mean for the energy sector.
- The Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario maps out a transition pathway that would limit global warming to 1.5 °C.
And, as it does every year, the Outlook examines the implications of today’s energy trends in key areas including investment, trade flows, electrification, and energy access.
- Following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, instability in the Middle East could lead to further disruption to energy markets and prices.
- In the Stated Policies Scenario, the average annual growth rate of 0.7% in total energy demand to 2030 is around half the rate of energy demand growth of the last decade. Demand continues to increase through 2050.
- In the Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario, electrification and efficiency gains proceed even faster, leading to a decline in primary energy of 1.2% per year to 2030.
- Solar manufacturing growth is outpacing the rise of solar PV deployment, creating some risks of imbalances but huge opportunities for the world to accelerate energy transitions.
- Numerous new LNG export projects (60% of which are accounted to the US and Qatar) are set to overturn gas markets.
- Fossil fuel share in the global energy supply is projected to reduce from around 80% to 73% by 2030.
- Global energy-related carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions peaking by 2025. Renewables are set to contribute 80% of new power capacity by 2030 in the stated policies scenario (STEPS), with solar PV alone accounting for more than half of this.
- Extreme volatility in energy markets highlighted the importance of affordable, reliable, and resilient supply.
Several countries have adopted policies that encourage the diversification of supply chains for clean energy technologies.
- This includes policies to promote clean energy technology manufacturing, for instance, the Inflation Reduction Act in the United States, the Net Zero Industry Act in the European Union, and the Production Linked Incentives scheme in India.
The global economy is assumed to increase at an average of 2.6% per year to 2050 in the three scenarios, while the global population expands from 8 billion today to 9.7 billion in 2050. Energy, carbon, and mineral prices find different equilibrium levels across the scenarios, but the potential for volatility remains high.
India
India has now become an importer of modern clean energy technologies as it scales up solar and wind power generation capacity.
- India is expected to meet its 2030 target to have half of its electricity capacity be non-fossil well before the end of the decade.
- Over the past five years, solar PV has accounted for nearly 60% of new generation capacity.
- India’s demand for electricity for running household air-conditioners is estimated to expand nine-fold by 2050.
Way forward
Despite moves by countries to reduce dependence on imported fuels and geographically concentrated clean energy technology supply chains, the need for international trade and cooperation remains strong.
No country can expect to be wholly self-sufficient, and most will continue to depend on imports and exports. International collaboration on innovation in particular will remain vital in the development of clean energy technologies.
Today, several countries rely heavily on revenue from oil and gas production, and they face the prospect that these revenues will decline as clean energy transitions advance. This underlines the need for broader economic diversification to compensate for falling fossil fuel export revenue.
The World Energy Outlook is considered a valuable resource for governments, industries, and organizations involved in energy and environmental policy, as well as for investors and researchers.
It plays a crucial role in shaping discussions and decisions related to global energy systems, sustainability, and climate change mitigation.
-Article by Swathi Satish






Leave a Reply