When we prepare notes of ClearIAS – we always keep one important thing in mind. Our study materials should help our readers learn faster!
(See Major Ocean Currents: How to learn faster?)
Now, after a break, we have come up with another easy-to-understand article from Geography – about Clouds.
In this article, we are going to discuss Clouds – different types, their shape, and their altitude.
What is a cloud?
- A cloud is an accumulation or grouping of tiny water droplets and ice crystals that are suspended in the earth’s atmosphere.
- They are masses that consist of huge density and volume and hence it is visible to the naked eye.
- There are different types of it and they differ from each other in size, shape, or color.
- They play different roles in the climate system like being the bright objects in the visible part of the solar spectrum, they efficiently reflect light to space and thereby help in the cooling of the planet.
- They are formed when the air becomes saturated or filled, with water vapor. The warm air holds more water vapor than cold air.
- Being made of moist air it becomes misty when the moist air is slightly cooled, with further cooling the water vapor and ice crystals of these clouds grow bigger and fall to earth as precipitation such as rain, drizzle, snowfall, sleet, or hail.
What are the different types of clouds?
They are classified primarily based on – their shape and their altitude.
Classification based on their shape:
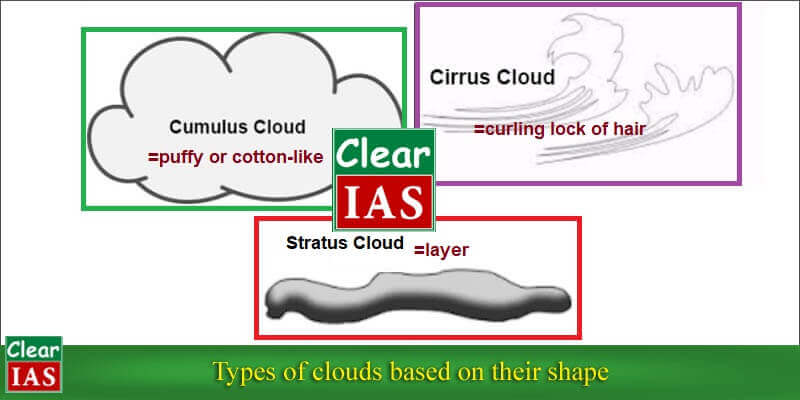
Based on shape, they are classified into three types:
- Cirrus
- Cumulus
- Stratus
Classification based on their altitude (height):
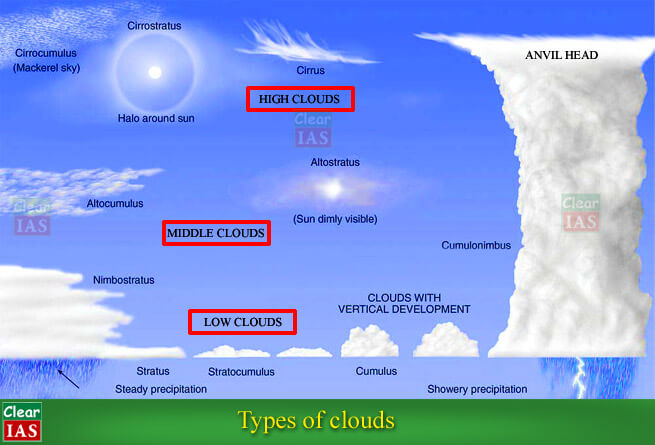
Based on their height or altitude they are classified into three types:
- High
- Middle
- Low
1) High Clouds
- They can reach above 6000 meters or 20,000 feet.
- They are also known as Cirrus Clouds.
- They are usually thin and are made up of ice.
- They often indicate fair weather and hence do not produce rain.

Types |
Description |
1. Cirrus |
They are thin and often wispy. Typically found at heights greater than 20,000 feet (6,000 meters), they are composed of ice crystals that originate from the freezing of supercooled water droplets. |
2. Cirrostratus |
They are high, very thin, comprise a uniform layer, and are composed of ice crystals. It isn’t easy to detect and is capable of forming halos when the cloud takes the form of thin cirrostratus nebulosus. |
3. Cirrocumulus |
They are small rounded puffs shaped, that usually appear in long rows high in the sky and are white, but sometimes appear grey. |
2) Middle Clouds
- They form between 6,500 feet and cirrus level or from 2000 to 6000 meters.
- They are also known as “Alto” clouds.
- They frequently indicate an approaching storm.
- They may sometimes produce Virga, which is rain or snow that does not reach the ground.
Types |
Description |
1. Altostratus |
These are in the form of continuous sheets or veils, grey or blue-gray. They are composed of ice crystals and water droplets. In its thinner areas, the sun can still be visible as a round, dim disk. These clouds may often form ahead of storms with continuous rain or snow. |
2. Altocumulus |
They are greyish sheet-like, characterized by globular masses or rolls in layers or patches, the individual elements being larger and darker than those of cirrocumulus and smaller than those of stratocumulus. |
3) Low Clouds
- They lie below 6,500 feet, which means from the surface to 2,000 meters.
- They are also known as Stratus Clouds.
- They may appear dense, dark, and rainy (or snowy) and can also be cottony white clumps interspersed with blue sky.

Types |
Description |
1. Strato Cumulus |
Usually arranged in large dark, rounded, or globular masses, usually in groups, lines, or waves. |
2. Stratus |
It usually looks like a huge grey blanket that hangs low in the sky resembles fog, comprises a uniform layer, and appears dull, if these clouds are warm it means rain and if it is cold it snows. |
3. Nimbostratus |
They are known as ‘Rain Clouds’ and they are dark, thick, and accompanied by light to moderately falling precipitation. |
4) Great Vertical Extent Clouds
- They are the most dramatic type.
- They are also known as Storm Clouds.
- They rise to dramatic heights, and sometimes well above the level of transcontinental jetliner flights.

Types |
Description |
1. Cumulus |
They are convection-type, puffy, and sometimes look like pieces of floating cotton. The base of each one is often flat and maybe only 1000 meters (3300 feet) above the ground. The top of the cloud has rounded towers. |
2. Cumulonimbus |
They are dense towering and vertical and their top acquires an ‘Anvil Shape’, associated with thunderstorms and atmospheric instability, forming from water vapor carried by powerful upward air currents. |
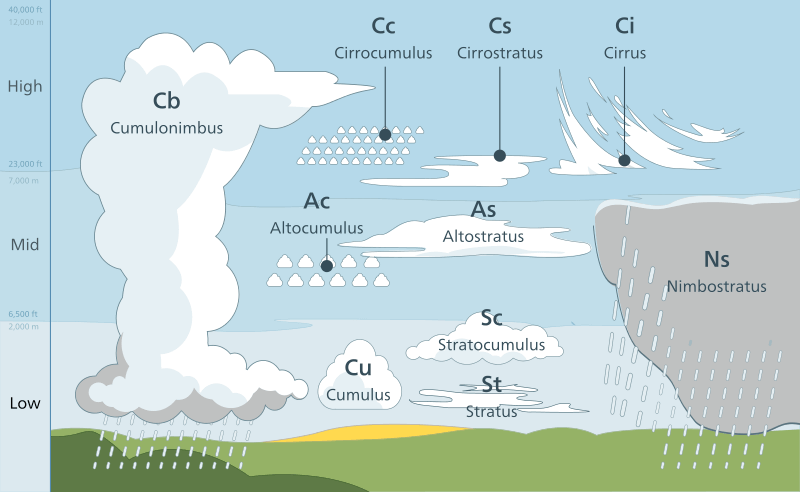
Learn all cloud types in a single diagram
What is International Cloud Atlas?

- The International Cloud Atlas describes the classification system for clouds and meteorological phenomena used by all World Meteorological Organization Members.
- It includes a manual of standards and photographs of clouds and weather phenomena.
- It was first published in the 19th century and was last updated 30 years ago.
- The new 2017 version of International Cloud Atlas was a digitalized one and has many additions.
The new cloud classifications
1) The Species
Volutus
- They are long, typically low, horizontal, detached, tube-shaped cloud masses.
- They often appear to roll slowly about a horizontal axis.
- The species volutus is a soliton and hence not attached to other clouds.
- This species applies mostly to Stratocumulus and rarely Altocumulus.
2) The Supplementary Features
(a) Asperitas
- There are well-defined, wave-like structures on the underside of the cloud.
- Asperitas is characterized by localized waves in the cloud base, either smooth or dappled with smaller features, sometimes descending into sharp points, as if viewing a roughened sea surface from below.
- The varying levels of illumination and thickness of the cloud can lead to dramatic visual effects.
- They occur mostly with Stratocumulus and Altocumulus.
(b) Fluctus
- They are relatively short-lived wave formations, usually seen on the top surface of the cloud, in the form of curls or breaking waves (Kelvin-Helmholtz waves).
- They occur mostly with Cirrus, Altocumulus, Stratocumulus, Stratus, and occasionally Cumulus.
(c) Cavum
- These are well-defined generally circular holes in a thin layer of supercooled water droplet cloud.
- The Cavum is typically a circular feature when viewed from directly beneath, but may appear oval-shaped when viewed from a distance. When resulting directly from the interaction of an aircraft with the cloud, it is generally linear.
- They occur in Altocumulus and Cirrocumulus and rarely Stratocumulus.
(d) Murus
- It is a localized, persistent, and often abrupt lowering of cloud from the base of a Cumulonimbus from which tuba (spouts) sometimes form.
- Usually associated with a supercell or severe multi-cell storm.
- Murus showing significant rotation and vertical motion may result in the formation of tuba (spouts), Commonly known as a ‘wall cloud’.
(e) Cauda
- A horizontal, tail-shaped cloud (not a funnel) at low levels extends from the main precipitation region of a supercell Cumulonimbus to the murus (wall cloud).
- It is typically attached to the wall cloud, and the bases of both are typically at the same height.
- Cloud motion is away from the precipitation area and towards the murus, with rapid upward motion often observed near the junction of the tail and wall clouds and is commonly known as a ‘tail cloud’.
3) Accessory Cloud
Flumen
- They are bands of low clouds associated with a supercell severe convective storm (Cumulonimbus), arranged parallel to the low-level winds and moving into or towards the supercell.
- These accessory clouds form on an inflow band into a supercell storm along the pseudo-warm front.
- One particular type of inflow band cloud is the ‘Beaver’s tail’. This is distinguished by a relatively broad, flat appearance suggestive of a beaver’s tail.
4) Special Clouds
(a) Flammagenitus
- These are observed to have originated as a consequence of localized natural heat sources (forest fires, wildfires, or volcanic activity) and consist of water drops.
(b) Homogenitus
- These originated specifically as a consequence of human activity.
- They include aircraft condensation trails (contrails), or clouds resulting from industrial processes, such as cumuliform clouds generated by rising thermals above power station cooling towers.
(c) Homomutatus
- These are formed as a result of persistent contrails (Cirrus homogenitus) that may be observed, over some time and under the influence of strong upper winds, to grow and spread out over a larger portion of the sky, and undergo internal transformation such that the cloud eventually takes on the appearance of a more natural cirriform cloud.
(d) Cataractagenitus
- They may develop locally in the vicinity of large waterfalls due to water broken up into spray by the falls.
- Cataractagenitus is formed when the downdraft caused by the falling water is compensated for by the locally ascending motion of air.
(e) Silvagenitus
- These may develop locally over the forests as a result of increased humidity due to evaporation and evapotranspiration from the tree canopy.
What is Asperitas Cloud?
- Asperitas was formerly known as Undulatus asperitus.
- It is a cloud formation proposed by Gavin Pretor-Pinney of the Cloud Appreciation Society (2009).
- It was recently been accepted and added to the International Cloud Atlas on March 23, 2017, on the occasion of World Meteorological Day.
- The ‘Asperitas’ is a Latin word and its meaning is ‘Rough‘.
- The Asperitas clouds tend to be low-lying and are caused by weather fronts that create undulating waves in the atmosphere.
Pyrocumulonimbus clouds
2024: Wildfires raging in the United States and Canada are so intense that they have created pyrocumulonimbus clouds, which have the potential to spit out thunder and spark more fires.
Pyrocumulonimbus clouds (or pyroCb clouds) are a type of cumulonimbus cloud that forms specifically due to intense heat sources, such as wildfires, volcanic eruptions, or even nuclear explosions. These clouds are often associated with extreme weather phenomena and can have significant impacts on the environment.
- Formation: Pyrocumulonimbus clouds form when intense heat from a fire or eruption causes air to rise rapidly, creating an updraft. As the air ascends, it cools and condenses, forming a cloud. If the updraft is strong enough, it can create a cumulonimbus cloud, which is a thunderstorm cloud, but in this case, the “pyro” prefix indicates that it is fire-induced.
- Structure: These clouds can reach the stratosphere, much higher than typical thunderstorms, and are capable of producing lightning, hail, and even fire-induced tornadoes. They also generate strong downdrafts that can exacerbate the spread of fires on the ground.
- Environmental Impact: Pyrocumulonimbus clouds can inject large amounts of smoke, ash, and other aerosols into the upper atmosphere, affecting air quality and potentially influencing weather patterns. They are also known for their role in creating “dirty” thunderstorms, where lightning occurs in the absence of significant rainfall.
- Global Significance: Due to their ability to transport smoke and particles into the stratosphere, pyroCbs can have global implications, including contributing to climate change by affecting the Earth’s radiation balance.
- Examples: These clouds have been observed during significant wildfire events, such as the Australian bushfires in 2019-2020, and the massive wildfires in Canada and the western United States. They have also been associated with volcanic eruptions like the 1991 Mount Pinatubo eruption in the Philippines.
Conclusion
Why do clouds appear white?
- The clouds usually appear white because the tiny water droplets and ice crystals inside them are tightly packed, and they reflect most of the sunlight that falls on these masses (scattering).
- The tiny cloud particles equally scatter all colors of light, which makes the viewer perceive all wavelengths of sunlight mixed as white light.
Why do clouds darken at the time of rain?
- The clouds appear dark or grey at the time of rain due to their particulate density.
- The water vapor will bind together into raindrops, leaving larger spaces between these drops of water, and hence less amount of light is reflected, lending a darker appearance to the rain clouds.
Related article: Cloud seeding
Article by: Priyanka Sunil






Appreciate your efforts !!
Please upload notes on atmospheric circulation and weather systems soon 😊
thanks for providing creamy notes…
Excellent article with easy to understand diagrams. Thanks.
Thank you very much
Always ask mcq at end of lesson
PLZZ always ask some questions regarding the topic.
Plz ask mcq..
Thanks for the valuable note
Altocumulus clouds are warning signs that thunderstorms may happen in 6 hours. Good valuable information. Thanks.
Thanks for the detailed information with clear pictures. Please always ask mcqs from the point of examination at the end of the explanation.
Sir is this new addition of clouds added to international cloud atlas is important for upcoming exam..
It is so confusing.
Sir please tell that reading your notes are sufficient for pre
thankx for giving creamy notes
Thanks for all the notes clear ias team
Excellent notes
sir , are these topics of geography enough as per the syllabus of geography
Very Nice, effective and sufficient notes 📝
Very Nice, effective and sufficient notes 📝
Plz sir provide note in Marathi