Digital health is rapidly evolving and playing a significant role in transforming the healthcare landscape. It is also known as eHealth or healthcare technology, refers to the use of digital tools, technologies, and platforms to improve healthcare delivery, enhance patient outcomes, and streamline healthcare processes. Read here to learn the latest updates in the sector.
Healthcare technology encompasses a wide range of applications that leverage information technology to enhance medical services, patient care, and health management.
The World Health Organization (WHO) and the G20 India presidency announced a new Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH) at the Health Minister’s Meeting of the G20 Summit hosted by the Government of India.
The integration of technology into healthcare services has the potential to address various challenges, improve access to medical care, and enhance patient outcomes.
Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH)
The Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH) is a WHO-managed network of stakeholders organized to facilitate the implementation of the Global Strategy on Digital Health 2020-2025 and other WHO norms and standards for Digital Health System Transformation.
The Initiative will serve as a platform to enable a wide global ecosystem to work collectively to promote country capacity and strengthen international cooperation in digital health.
GIDH will prioritize the following core areas of work:
- Assessing and prioritizing Member States’ needs
- Evaluating the availability and reporting of country-level digital health resources and identifying under-funded priorities
- Supporting technically and financially the accelerated achievement of the strategic objectives defined in the Global Strategy on Digital Health 2020-2025
- Building capacity and converging efforts to encourage developing, maintaining, and adapting healthcare technologies to continuously changing needs.
- The Initiative will work to address variability in the quality of digital solutions and emerging technologies related to standards, data privacy, security, interoperability, etc., by amplifying identified best practices, open standards, and quality-assured building blocks.
The Initiative will strive to help Member States to advance their national e-health transformation by strengthening collaboration among partners and existing networks and amplifying current multi-national and regional activities.
The key components of the GIDH will leverage existing evidence, tools, and learnings and will be co-created through a transparent and inclusive process.
Through this evidence-based and comprehensive co-creation process, GIDH will ultimately aim to:
- ALIGN efforts to support the Global Strategy on Digital Health 2020–2025;
- SUPPORT quality-assured technical assistance to develop and strengthen standards-based and interoperable systems aligned to global best practices, norms, and standards;
- FACILITATE the deliberate use of quality-assured digital transformation tools that enable governments to manage their digital health transformation journey.
GIDH: a network of networks
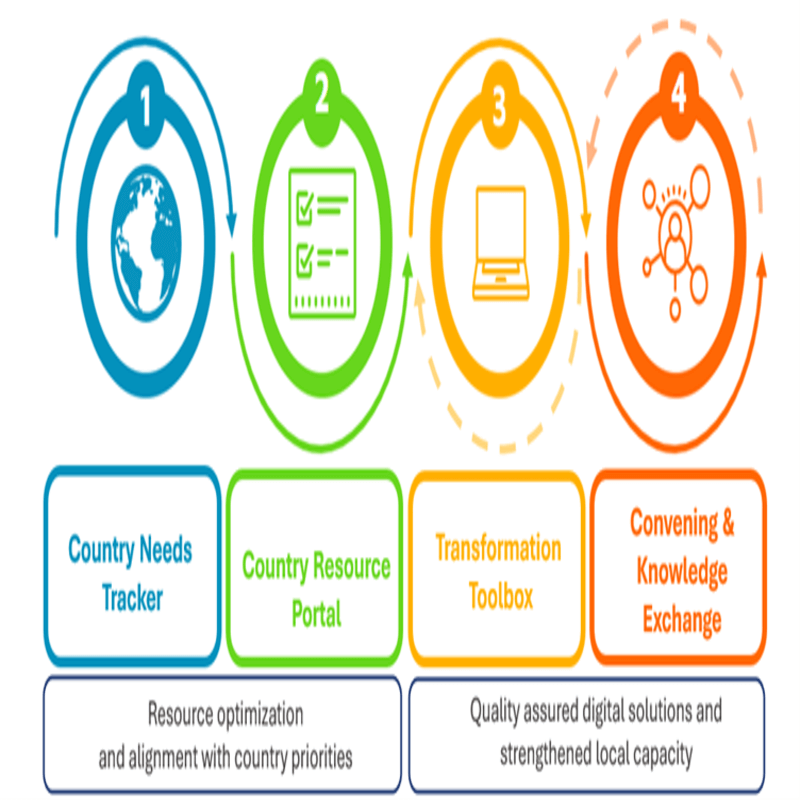
As a WHO Managed Network (“Network of Networks”), GIDH will address challenges such as duplication of efforts and “products-focused” digital health transformation through a focus on four foundational pillars:
- Country Needs Tracker: facilitating digital health investments to be informed by country priorities;
- Country Resource Portal: identifying traditional as well as innovative resource opportunities, and promoting transparency, while reducing the risk of duplication for enabling a standards-based prospective and retrospective analysis of resourcing gaps in healthcare technology.
- Transformation Toolbox: advocating for quality-assured tools and resources that strengthen the country’s capacity and autonomy to manage the national digital health transformation.
- Convening and Knowledge Exchange: promoting strengthened collaboration and knowledge exchange across global, regional, and national networks in healthcare technology.
Digital Health in India
Digital health in India is rapidly evolving and playing a significant role in transforming the healthcare landscape.
- Telemedicine and Teleconsultation: Telemedicine has gained momentum in India, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. Teleconsultation platforms allow patients to consult healthcare providers remotely, improving access to medical advice and reducing the need for in-person visits, particularly in rural areas.
- mHealth Applications: Mobile health apps offer a range of services, including symptom tracking, medication reminders, fitness monitoring, mental health support, and health education. These apps are becoming popular tools for managing health and wellness.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): The adoption of EHRs is growing in India, enabling healthcare providers to access patient records digitally, leading to improved care coordination and patient safety.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Digital tools such as wearable devices and remote monitoring platforms help healthcare providers track patients’ health conditions, especially for chronic diseases like diabetes and hypertension.
- Health Information Exchange (HIE): HIE systems facilitate the secure sharing of patient information among healthcare providers, enabling better care coordination and reducing duplication of tests.
- E-Pharmacies: Digital platforms for ordering and delivering medicines (e-pharmacies) are gaining popularity, providing convenient access to medications and reducing the need for physical visits to pharmacies.
- AI and Data Analytics: Artificial intelligence is being used for medical imaging analysis, predictive analytics, and personalized treatment recommendations, aiding in early diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Remote Training and Education: Digital health platforms offer training and education to healthcare professionals, especially those in remote areas, helping them stay updated with the latest medical practices.
- Healthcare Awareness and Outreach: Digital platforms are being used to raise awareness about health issues and provide information on preventive measures and treatment options.
- Startups and Innovations: The digital health sector in India has witnessed the emergence of numerous startups working on innovative solutions, ranging from diagnostic tools to patient engagement platforms.
Government Initiatives
The Government of India has launched various healthcare technology initiatives, including the National Digital Health Mission (NDHM), which aims to create a digital health ecosystem with unique health IDs for citizens, electronic health records, and telemedicine services.
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission
- E-governance and Telemedicine
- In January 2022, the National Health Authority launched the Unified Health Interface (UHI) a digital healthcare service platform under the ABDM. Policy guidelines on the governance of the system are yet to follow
There is no specific legislation that governs Digital Health in India. The laws that broadly cover the services are listed here:
- Drugs and Cosmetics Act 1940 read with Drugs and Cosmetics Rules 1945 and Draft E-Pharmacy Rules, 2018
- The National Medical Commission Act, 2019, and The Indian Medical Council (Professional Conduct, Etiquette and Ethics) Regulations, 2002
- Telemedicine Practice Guidelines, 2020
- The Drugs and Magic Remedies (Objectionable Advertisements) Act, 195,4 and Drugs and Magic Remedies (Objectionable Advertisements) Rules, 1955 (“DMRA”)
- The Clinical Establishments (Registration and Regulation) Act, 2010
- Telecom Commercial Communication Customer Preference Regulations, 2018
- Consumer Protection (E-commerce) Rules, 2020
News
Under India’s G20 presidency, G20 nations deliberated on three health priorities:
- Health emergencies, prevention, preparedness, and response (with a focus on One Health and Antimicrobial Resistance [AMR]).
- Strengthening cooperation in the pharma sector.
- Digital health innovation and solutions to aid universal health coverage and improve healthcare service delivery.
WHO launched the GIDH initiative in February 2024 with its secretariat in WHO headquarters in Geneva.
Way forward
Digital technologies are now integral to daily life, and the world’s population has never been more interconnected. Innovation, particularly in the digital sphere, is happening at an unprecedented scale. Even so, its application to improve the health of populations remains largely untapped, and there is immense scope for the use of digital health solutions.
Digital health in India holds the potential to bridge the healthcare gap, particularly in rural and underserved areas. However, a balanced approach is needed to ensure that the benefits of digital health are accessible to all segments of society while addressing the associated challenges.
As technology continues to advance, digital health is likely to play an increasingly vital role in improving healthcare delivery and outcomes in India.
Also read: Indian Health Sector Problems – Can the National Health Policy 2017 Make a change?
-Article by Swathi Satish






Leave a Reply