
Satellite communication is a technology that uses artificial satellites to transmit signals for telecommunications. Read here to learn in detail about them.
By providing voice and data communication services in locations where terrestrial cellular and broadband connectivity is unavailable or network coverage is spotty, satellite communications have increased the resilience of terrestrial communications.
Examples of these locations include across oceans, at altitudes of up to 35,000 feet, and in remote areas of the earth.
This mode of communication enables data transfer and connectivity between distant points on Earth, providing vital links for television, radio, internet, and military applications.
How does Satellite Communication Work?
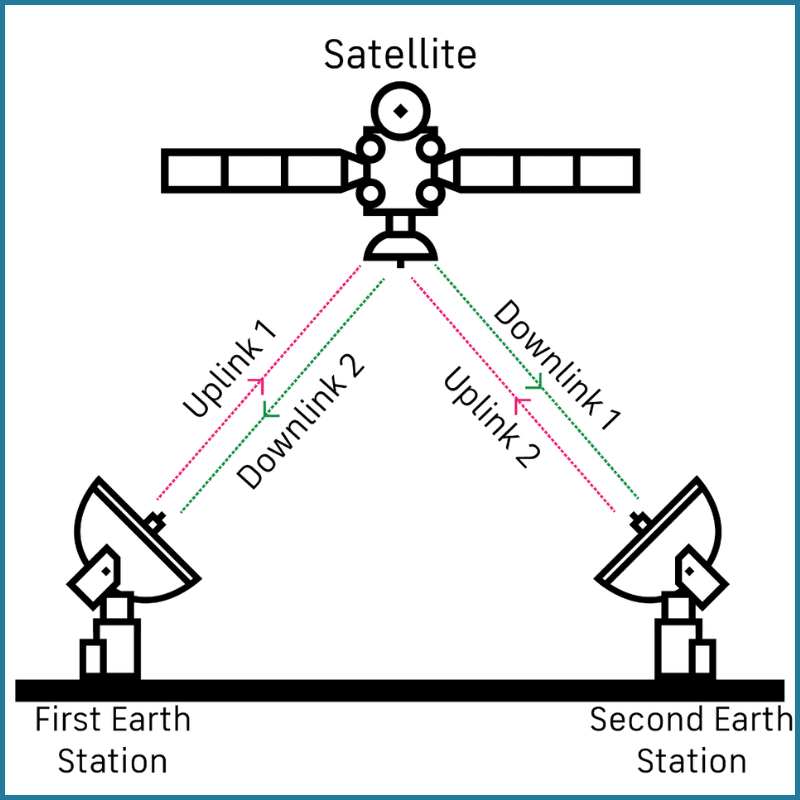
- Uplink Transmission: Information (voice, video, data) is transmitted from a ground station to the satellite using a high-frequency signal.
- Satellite Transponder: The satellite receives this signal via its transponder, which converts the received signal into a different frequency (to avoid interference with the uplink signal) and amplifies it.
- Downlink Transmission: The satellite sends the signal to Earth, where another ground station or a satellite receiver receives it.
Types of Satellites
- Geostationary Orbit (GEO): These satellites are positioned approximately 35,786 kilometres (about 22,236 miles) above the Earth’s equator and rotate with the Earth. They are stationary relative to a point on Earth, making them ideal for television broadcasts, weather forecasting, and telecommunications.
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO): Located between 2,000 and 35,786 kilometres above the Earth, these satellites are typically used for navigation systems like the Global Positioning System (GPS).
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO): Orbiting between 160 and 2,000 kilometres above the Earth, LEO satellites are primarily used for data communication such as email, video conferencing, and quickly updating scientific data.
Advantages of Satellite Communication
- Wide Coverage: Satellites can cover a large portion of the Earth, making them effective for broadcasting across vast areas where laying cables is impractical.
- Mobility: Satellite communication enables mobile data and voice services in remote or mobile environments, such as ships at sea, vehicles in remote areas, and handheld GPS devices.
- Disaster Recovery: Satellites play a critical role in emergency communications when terrestrial networks are unavailable due to natural or human-made disasters.
- Broadcast and Multicast Capabilities: Satellites are particularly effective for TV and radio broadcasting, enabling one-to-many communications efficiently.
Disadvantages of Satellite Communication
- Cost: Launching satellites and building and maintaining ground stations is very costly. The technology and infrastructure required are also complex.
- Propagation Delay: Because of the long distance between satellites and the Earth, there is a noticeable delay (approximately 240 milliseconds for a round trip to a GEO satellite), which can affect communication efficiency, particularly for voice and real-time data.
- Interference and Physical Obstructions: Satellite signals can be interfered with by buildings, trees, and other obstacles, particularly for lower orbit satellites.
- Vulnerability to Space Weather and Debris: Satellites can be damaged by space weather like solar flares or collisions with space debris.
Indian Communication satellites
INSAT Series
The Indian National Satellite System (INSAT) is one of the largest domestic communication satellite systems in the Asia-Pacific region.
- Established in 1983 with the commissioning of INSAT-1B, it initiated a major revolution in India’s communications sector and sustained the same later.
- The INSAT system with more than 200 transponders in the C, Extended C and Ku-bands provides services to telecommunications, television broadcasting, satellite newsgathering, societal applications, weather forecasting, disaster warning and Search and Rescue operations.
- Broadcasting: Television and radio broadcasting, are especially important for reaching India’s rural and remote areas.
- Telecommunications: Facilitating telecommunication networks, including teleconferences and tele-education networks.
- Meteorological Services: Providing vital weather forecasting and surveillance services.
- Disaster Management: Offering critical communication capabilities during disasters and emergencies.
GSAT Series
The GSAT (Geo-Stationary Satellite) series is an extension of the INSAT series that focuses specifically on communication capabilities.
These satellites are placed in geostationary orbit and are used to support telecommunication, television broadcasting, satellite newsgathering, societal applications, weather forecasting, disaster warning, and search and rescue operations.
- GSAT-15: Launched in November 2015, GSAT-15 is designed to provide telecommunications services, DTH television services, digital satellite news gathering, and tiny aperture terminal (VSAT) communications across India.
- GSAT-29: Launched in November 2018, this high-throughput communication satellite aims to meet the communication requirements of users in remote areas of India.
- GSAT-30: Launched in January 2020 as a replacement for INSAT-4A, this satellite is intended to provide high-quality television, telecommunications, and broadcasting services.
NAVIC
While primarily a navigation system, the Navigation with Indian Constellation (NAVIC) also has implications for communications, particularly in enhancing the capabilities of mobile devices and communications in rural areas.
Future Projects
ISRO continues to expand its capabilities with new projects such as:
- GSAT-20: Planned as a high-throughput satellite, it is expected to provide significant improvements to internet services across India, particularly benefiting rural and remote areas with limited connectivity.
Legal provisions in India
- Under Telecommunications Act, 2023 satellite communication companies can get spectrum without auction for point-to-point communications.
- The Department of Telecommunication (DoT) issues Global Mobile Personal Communications by Satellite (GMPCS) Licenses for satellite telephony.
- Earlier, Bharati Group and Reliance Group were issued GMPCS licenses.
Why in the news?
Chinese scientists have developed the world’s first satellite capable of enabling smartphone calls directly, without the need for ground-based infrastructure like cellular towers.
- The satellite is named ‘Tiantong,’ which means “connecting with heaven”.
- The initiative draws inspiration from the biblical story of the Tower of Babel, aiming to bridge communication gaps rather than create them.
- The Tiantong-1 satellite series, which began with its first launch on August 6, 2016, now includes three satellites in a geosynchronous orbit at 36,000km, covering the entire Asia-Pacific region.
- In September 2023, Huawei Technologies launched the world’s first smartphone that supported satellite calls by directly connecting to the Tiantong satellites.
Tiantong-1 Satellite series
The Tiantong-1 (TT-1) satellite series is an initiative by China to develop and deploy a system of communication satellites, aimed at establishing a mobile satellite communication network.
This series is part of China’s broader effort to enhance its capabilities in satellite communications, expanding its reach both domestically and internationally.
- Development and Purpose: The Tiantong-1 satellites are developed by the China Academy of Space Technology (CAST), a subsidiary of the state-owned China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC).
- The system is designed to provide stable, reliable mobile communication services such as voice, short messages, and data transmission across China and neighbouring regions.
- Operational Use: The TT-1 satellite system primarily serves commercial purposes, focusing on providing communication services to mobile users in remote and rural areas, as well as supporting communication requirements during emergency or rescue missions.
- It is an integral component of China’s strategy to boost its technological infrastructure in areas that are traditionally underserved by terrestrial communication networks.
Launches and Configuration:
- The first satellite in the series, TT-1 01, was launched on August 6, 2016, aboard a Long March 3B rocket from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center.
- It operates in a geostationary orbit, providing stable coverage over China and surrounding areas.
- Subsequent Satellites: Following the initial launch, additional satellites, including Tiantong-1 02 and Tiantong-1 03, have been launched to expand and enhance the network’s coverage and capacity.
- These launches help ensure redundancy, improved network reliability, and expanded coverage potentially including other parts of Asia, the Middle East, and Africa.
Satellite Features:
- The TT-1 satellites are equipped with transponders that operate in the S-band spectrum.
- The use of the S-band allows for efficient mobile communication, which is less prone to interference and signal attenuation caused by atmospheric conditions, thus ensuring more reliable communication services.
- Alongside the satellite network, the Tiantong-1 system relies on a series of ground stations spread across China.
- These stations manage the satellite operations, handle the communication traffic, and ensure the integration of the satellite network with terrestrial communication networks.
Strategic Importance:
The Tiantong-1 satellite series is a significant part of China’s ambitions in space and communication technology sectors.
- It complements other satellite communication systems and navigation systems like BeiDou (China’s alternative to the Global Positioning System) by providing strategic communication capabilities.
- It also plays a role in China’s “One Belt, One Road” initiative by potentially offering communication services along the Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st-century Maritime Silk Road.
Current Trends
- The satellite communication field is evolving with advancements in satellite technology, such as the deployment of large constellations of small satellites in LEO to improve internet connectivity globally (projects like SpaceX’s Starlink).
- There’s also growing interest in using more advanced materials and propulsion technologies to reduce costs and extend the operational life of satellites.
Conclusion
Satellite communication remains a crucial technology for global connectivity, especially in underserved or difficult-to-reach areas, despite the emergence of alternative technologies like fibre optics.
As technology advances, the effectiveness, affordability, and applications of satellite communication are expected to expand significantly.
China plans to continue expanding its satellite communication capabilities, potentially adding more satellites to the Tiantong-1 series.
This expansion aims to enhance global coverage, increase capacity, and improve the quality of communication services, making China a significant player in the global satellite communication market.
The Tiantong-1 satellite series represents a critical step in China’s broader space strategy, which includes enhancing national security, technological prowess, and international cooperation and competition in the increasingly strategic space and satellite sectors.
Related articles:
- Indian space program
- Space economy
- Privatisation of the Indian Space sector
- Zero orbital debris
- Satellite-Based Tolling System
- Direct-to-Device (D2D) Satellite Connectivity in India
-Article by Swathi Satish






Leave a Reply