 End of the cold war and the rise of globalization has changed the concept of national security among the nations. As a consequence ‘Non-Traditional Security Issues’ are gaining the limelight against the traditional security issues. In this article, we discuss in detail about 16 non-traditional security issues faced by India, its challenges and possible remedies.
End of the cold war and the rise of globalization has changed the concept of national security among the nations. As a consequence ‘Non-Traditional Security Issues’ are gaining the limelight against the traditional security issues. In this article, we discuss in detail about 16 non-traditional security issues faced by India, its challenges and possible remedies.
What are non-traditional security issues?
“They are defined as challenges to the survival and well-being of peoples and states that arise primarily out of nonmilitary sources.”
– Professor Mely Caballero-Anthony (Secretary General, Consortium on Non-Traditional Security Studies in Asia).
Non-Traditional Security Issues and Non-State Actors

In general, non-traditional security threats as those threats which are emanated by the non-state actors.
These are challenges to the survival of the state and well-being of people that arise primarily out of nonmilitary sources, such as climate change, cross-border environmental degradation and resource depletion, infectious diseases.
How are non-traditional security issues different from traditional security issues?
The difference between traditional and non-traditional security threats is not so water-tight now as it appeared in the last century.
The traditional concept of security envisages the use of military means to deal with the threats to the unity, territorial integrity and sovereignty of a state.
Now, a level of ‘permeability‘ has evolved.
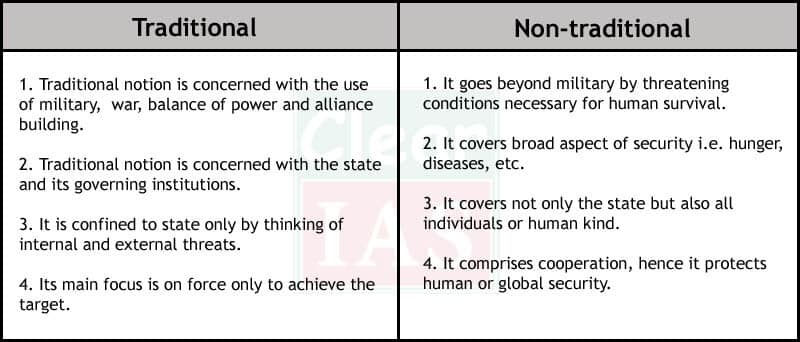
Features/characteristics of non-traditional security
- Non-military in nature.
- Transnational in scope-neither totally domestic nor purely interstate.
- Transmitted rapidly due to the globalization and communication revolution.
Non-Traditional Security Issues India Should Worry About
India faces unique challenges related to non-traditional security. We shall see each of them with the remedies.
1. Food security
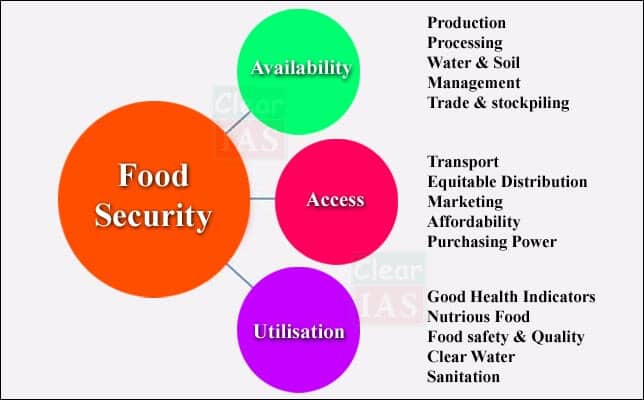
Challenges
- India’s population is still growing and will not stabilize until 2050/2060.
- Ranked among least developed nation when it comes to the problems of malnutrition and stunning.
Remedies
- We can learn from countries in Latin America, who have adopted short and long-term policy choices, categorized as consumer, producer and trade orientated policy approaches to national food security.
- The holistic approach includes political dialogue not only at national levels but intergovernmental levels encompassing the various government departments to effectively implement PDS.
- Community-based Management of Acute Malnutrition (CMAM) programme based on the micro-planning basis at the district level of Rajasthan can be replicated.
2. Climate Change and Environment Pollution
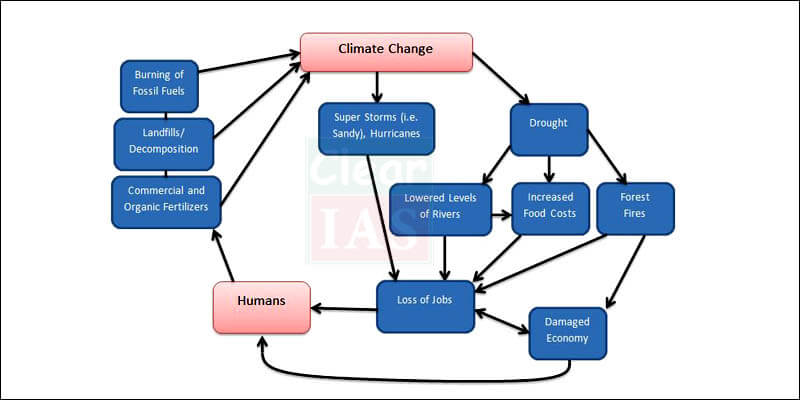
Challenges
- India’s development trajectory has had to contend with increasing environmental challenge. Ex- Indian cities are ranked among the most polluted cities in the world.
Remedies
- A successful example of Netherlands and France based on raising taxes on polluting inputs which are then invested in sustainable infrastructural development rather than to merely raise revenue can be implemented.
- India’s National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) problem of lack of transparency can tackle through Brazilian model involving a ranging number of stakeholders under the umbrella group Inter-Ministerial Committee on Climate Change (CIM).
3. Water Scarcity and Contamination
Challenges
- With a huge population, there is pressure on scarce water resources despite having abundant rain.
- Unsustainable water harvesting structure.
Remedies
- Denmark model which a focuses on collaborating research institutions adjoin to national universities in which the government awarded grants to follow up on clean water technologies.
- Collaboration with Israel in water technology can open new water conservation technique.
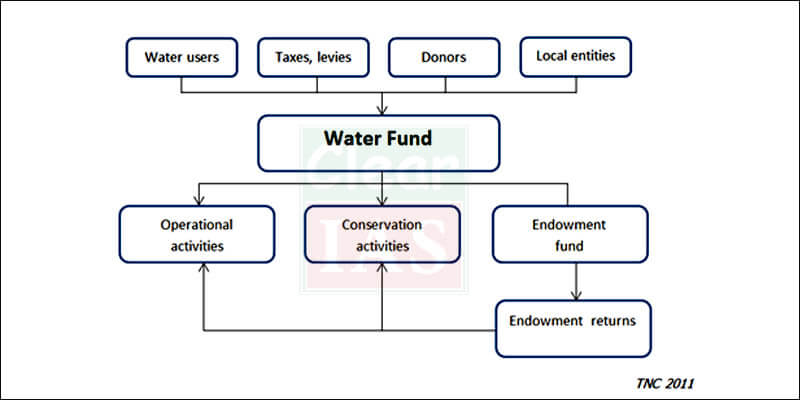
4. Energy Security Issues
Challenges
- An energy-hungry nation with high GDP growth rate and high dependency on the imported petroleum from the unstable Middle East.
Remedies
- Laws like Tunisia’s “energy conservation system” law should be passed which relies on the National Fund for Energy Management to encourage renewable energy investment and enhance skills capacity in the sector.
- Learning from China can be a great help based on looking beyond its neighbourhood and imports fuel from far and wide using a combination of economic diplomatic tools, and various other financial incentives.
5. Public health issues – infectious diseases, epidemics etc
Challenges
- Poor health infrastructure, high out of pocket expenditure. Ex- Gorakhpur BRB Hospital case, which led to the death of many children.
Remedies
- ‘Chilean Model’ based on Explicit Guarantees and Universal Access (AUGE) programme, which commits to providing universal health care for all citizens made through its two-tier system of Public Health care should be adopted.
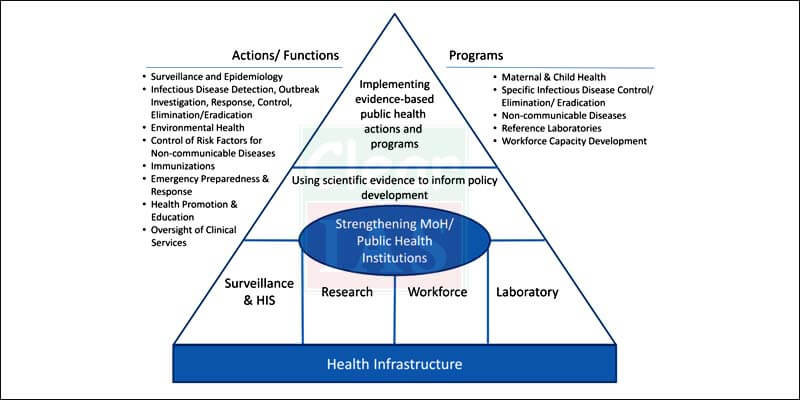
6. Disasters
Challenges
- Regular floods, droughts, landslides, cyclones need a 360-degree preparation. Ex- Bihar, Assam floods.
- Urban floods Ex- Chennai, Mumbai.
Remedies
- Can be learnt from Japan.
7. International Terrorism
“Deliberate creation and exploitation of fear through violence or threat of violence in pursuit of political change.”
Challenges
- State-funded terrorism by Pakistan through separatist movement in Kashmir valley,
- The insurgency in Nagaland, Manipur.
Remedies
- As per UNESCO, “Violence begins from the mind”, therefore re-engineering of minds of individuals by taking them away from the culture of violence and bringing them closer to the culture of peace is required.
- India should use the international platform to make the voice of consensus on the definition of the terrorism.
- Collaboration with Israel would be of great help in surveillance and spying.
8. Illegal Migration
Challenges
- Bangladeshi illegal immigrants, recent issue related to Rohingya Muslims, etc.
Remedies
- Encourage legal immigration through redefining citizenship act, reforming laws to inspire from the US immigration laws.
- Bilateral cooperation among neighbouring nations to have documentation of illegal immigrants and to have a decent solution.
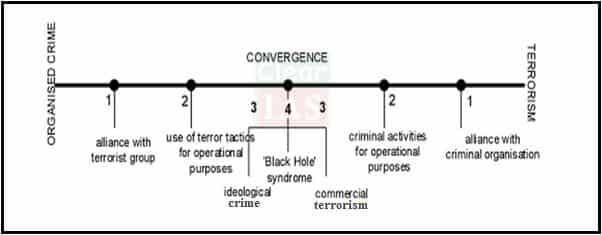
9. Organized crimes – national and transnational
Challenges
- Use of counterfeit currency, the finding of linkages between terrorists and underworld. Ex- Mumbai terror attack. (Terrorist groups such as the Shining Path (Peru) also tap into the organized crime network in order to set up a highly successful drugs smuggling network to fund their terrorist campaigns.)
- National and transnational crimes like piracy, smuggling and drugs.
Remedies
- Basic changes have to be made in substantive laws, investigative processes, and police organization.
- Localize programs- the comprehensive programme like Brazil’s Pronasci to tie up a lot of elements that were drivers of violence in the country, building local frameworks, gun-free zones and fostering the civic culture to reduce violence.
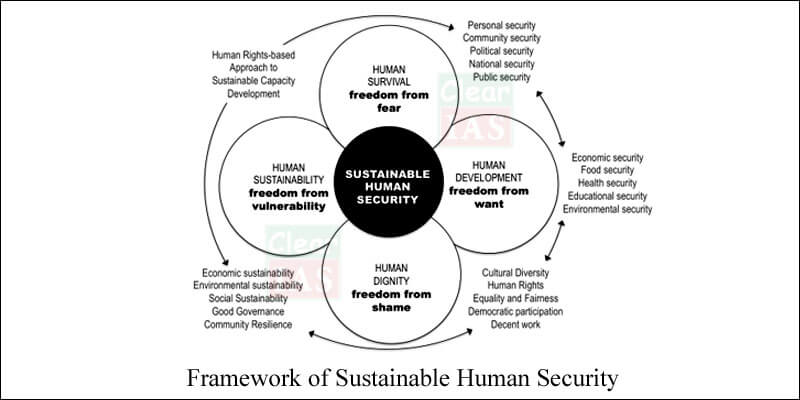
10. Human Security Issues
Challenges
- It is the combination of threats associated with war, genocide, and the displacement of populations. At a minimum, human security means freedom from violence and from the fear of violence.
Remedies
- The focus should be on early prevention to minimize the impacts of insecurity, to engender long-term solutions.
11. Poverty
Causes of poverty (Challenges)
- Poor agriculture.
- Growing population.
- The gap between the rich and the poor.
- Corruption and black-money.
Remedies
- Farmers must get all facilities for irrigation.
- They should be trained and educated.
- Agriculture must be made profitable.
- Family planning schemes should be introduced.
- More and more industries should be set up to meet the needs of our country.
- Corruption must end. Our offices should work efficiently.
12. Nuclear Security Issues
Challenges
- The legal architecture for radioactive materials is weak.
- Lack of universal coverage and implementation of the Code of Conduct.
- Unsecured and open facilities pose a security challenge.
- Cradle-to-grave controls on radioactive materials remain weak.
- Tracking radioactive sources is a major challenge. Ex- Goiânia accident, Brazil: In the late 1980s, a widely publicized incident in Brazil highlighted the importance of properly securing dangerous radiological sources.
- Problems related to a rogue nation like North Korea having a nuclear arsenal.
- The possibility of non-state actors possessing a nuclear weapon in future because of instability in the international scenario.
Remedies
- Strengthen the role of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
- Adopting India’s stand of complete nuclear disarmament.
- Broaden universal coverage for the Code of Conduct.
- Increase voluntary actions.
13. Proliferation of weapons chemical and biological weapons
Challenges
- Use of these weapons in Syrian Civil War.
- The USA used Agent Orange in Vietnam War.
Remedies
- Strengthening Chemical Weapons Convention (1992) and the Biological Weapons Convention (1975).
- Strengthening export control regime.
14. Economic security Issues
It is the condition of having a stable income or other resources to support a standard of living now and in the foreseeable future.
Challenges
- Black money.
- High cash to GDP ratio.
- Counterfeit currency.
- Trade imbalance.
Remedies
- Facilitating the rapid deployment of civilian technologies.
- The increasing tax base.
- Reducing import through indignation.
15. Religious extremism
Religious extremism “describes faith-based actions that are deliberate attempts to cause harm to other people.”
Causes of extremism
- Personal causes.
- Religious beliefs and fundamentalism.
- An abhorrence of sexuality and a reaction to gender equality.
- Broken families.
- Social causes.
- Reactions to multiculturalism.
- Secularization.
- Disordered civic life, poor governance.
- A negative reaction to a dominant culture and modernism.
- Sectarianism and faith schools.
Challenges
- Day to day riots. Ex- Shamali riots, Saharanpur riots.
Remedies
- Religious Cure– Instead of giving severe punishments to extremists, they must be debated intellectually and counselled to reach a solution.
- Social Cure-youths engagement in constructive work.
- Media– A platform where all scholars can gather to debate and discuss religious issues can be arranged so that individual differences can be avoided.
- Legal Cure: In the efforts to curb extremism, a legal cure is necessary. This means making laws concerning extremist activities, amending the Religious Unity Act and terrorism laws.
16. Information Security Issues
It is the state of being protected against the unauthorized use of information, especially electronic data.
Challenges
- Confidentiality.
- Privacy.
- Data theft/cyber-attack: Stuxnet like attack can cripple the vital infrastructure is part of cyber terrorism.
- WannaCry, a crypto-ransomware can stop public life dependent on digital infrastructure.
- A weak IT Act which has become redundant due to non-exploitation and age-old cyber laws.
- Lack of awareness and the culture of cybersecurity at the individual as well as institutional level.
- Lack of trained and qualified manpower to implement the countermeasures.
Remedies
- Protection of Critical Information Infrastructure through Public-Private Partnership.
- Harmonizing the National Legal Regime with the International Legal Regime. Ex- the U.S.-India Cyber Relationship Framework.
- Setting up national cyber-security architecture will be of great help.
- Creation of a National Cyber Security Agency (NCSA) to assess the nature of cyber threats and respond to them effectively can be the answer.
- Acts like Singapore’s proposed Cyber Security Bill will offer a great safety measure to critical infrastructure.
India’s response towards these issues and the way forward
India has a long history of being sensitive to concerns relating to poverty, environment, population growth, socio-economic irregularities, etc. Over the last few decades, the Indian government has launched numerous schemes aiming towards these issues.
However, these issues were regarded as developmental issues and not security issues. Even today, the government is reluctant to regard climate change as a security issue.
It is felt, with some justification, that securitization of developmental issues will be counterproductive. While the government has focused on climate change, energy security, etc. as developmental issues, the security implications of non-traditional challenges cannot be ignored. What is needed is a holistic approach in addressing these non-traditional security issues.
Article by: Skand Kumar





Site is perfect for IAS…..
best
Very Useful
Best site for upsc topics